Test: Linear Algebra - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Engineering Mathematics - Test: Linear Algebra
If A is a non–singular matrix and the eigen values of A are 2 , 3 , -3 then the eigen values of A-1 are:
If -1, 2, 3 are the eigen values of a square matrix A then the eigen values of A2 are:
If 2, - 4 are the eigen values of a non–singular matrix A and |A| = 8, then the eigen values of adjA are:
If 2 and 4 are the eigen values of A then the eigenvalues of AT are
If 1 and 3 are the eigenvalues of a square matrix A then A3 is equal to:
If A is a square matrix of order 3 and |A| = 2 then A (adj A) is equal to:
If the product of matrices
is a null matrix, then θ and Ø differ by:
If A and B are two matrices such that A + B and AB are both defined, then A and B are:
Consider a 3 × 3 matrix A whose (i, j)-th element, ai,j = (i − j)3. Then the matrix A will be
For a skew symmetric even ordered matrix A of integers, which of the following will not hold true:
The condition for which the eigenvalues of the matrix
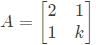
are positive, is
If A = 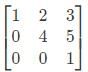 then det(A −1 ) is __________ (correct to two decimal places).
then det(A −1 ) is __________ (correct to two decimal places).
|
65 videos|122 docs|94 tests
|



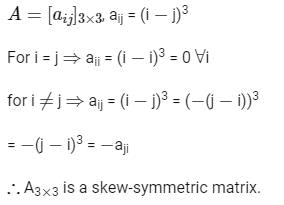
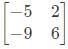 is
is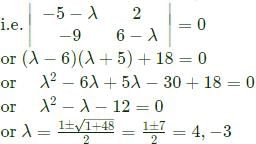
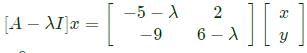
 = 0 which gives only one independent equation,
= 0 which gives only one independent equation,
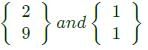
 are positive
are positive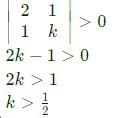
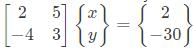
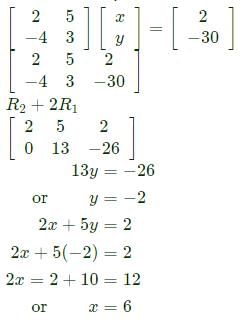
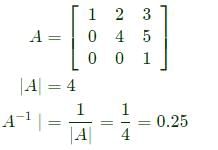
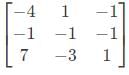 is
is 











