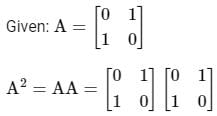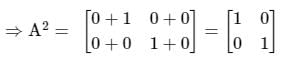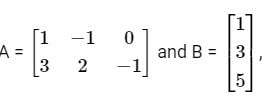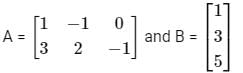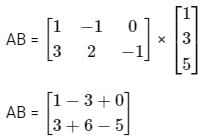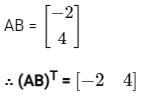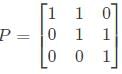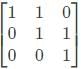Test: Matrices - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Engineering Mathematics - Test: Matrices
Comprehension:
Direction: Based on the following information, answer the questions:
Abhi, Badri, and Chintan were given the task of creating a square matrix of order 3.
Below are the matrices created by them. A, B, and C are the matrices created by Abhi, Badri, and Chintan respectively.
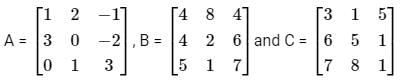
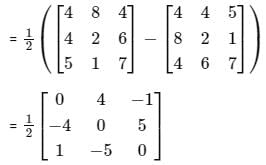
Let matrix B = P + Q, where P is a symmetric matrix and Q is a skew - symmetric matrix. What is Q?
Direction: Based on the following information, answer the questions:
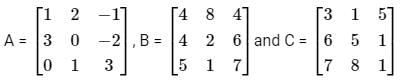
Direction: Based on the following information, answer the questions:
Abhi, Badri, and Chintan were given the task of creating a square matrix of order 3.
Below are the matrices created by them. A, B, and C are the matrices created by Abhi, Badri, and Chintan respectively.
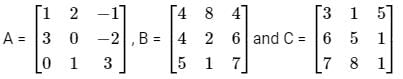
What is (AT)T
Below are the matrices created by them. A, B, and C are the matrices created by Abhi, Badri, and Chintan respectively.
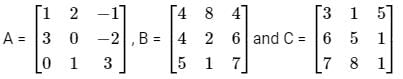
lf the order of A is 4 × 3, the order of B is 4 × 5 and the order of C is 7 × 3, then the order of (ATB)T CT is
Given that the determinant of the matrix

is -12, the determinant of the matrix
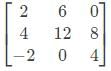
If A is an Involuntary matrix and I is a unit matrix of same order, then (I − A) (I + A) is
The matrix 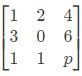 has one Eigenvalue equal to 3. The sum of the other two Eigenvalues is
has one Eigenvalue equal to 3. The sum of the other two Eigenvalues is
The transformation matrix for mirroring a point in x-y plane about the line y=x is given by
In matrix equation [A]{X} = {R},
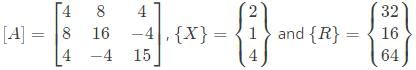
One of the eigenvalues of matrix [A] is
Consider the following two statements with respect to the matrices Am x n, Bn x m, Cn x n, Dn x n.
Statement 1 : tr(AB) = tr(BA)
Statement 2 : tr(CD) = tr(DC)
where tr( ) represents the trace of a matrix. Which one of the following holds?
|
65 videos|122 docs|94 tests
|


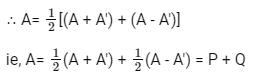
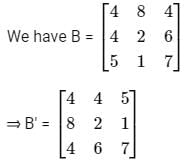
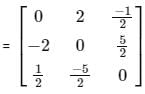
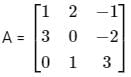
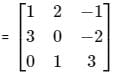

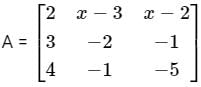 is a symmetric matrix then x
is a symmetric matrix then x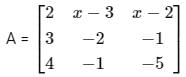
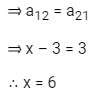
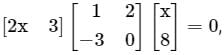 then the value of x is
then the value of x is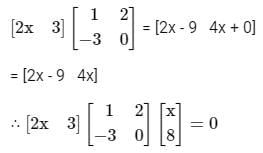
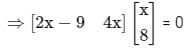
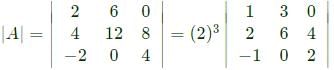
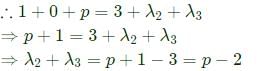
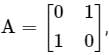 then the value of A4 is
then the value of A4 is