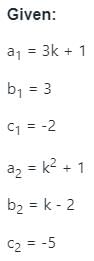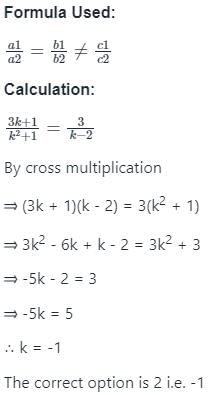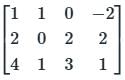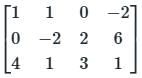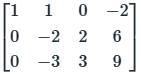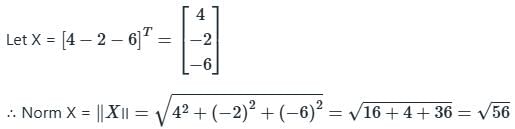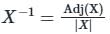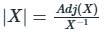Test: Systems of Linear Equations, Matrix Algebra & Transform Theory- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Systems of Linear Equations, Matrix Algebra & Transform Theory- 2
Consider the system of equations given below:
x + y = 2
2x + 2y = 5
This system has
x + y = 2
2x + 2y = 5
This system has
For what value of a, if any, will the following system of equations in x, y and z have a solution?
2x + 3y = 4
x+y+z = 4
x + 2y - z = a
2x + 3y = 4
x+y+z = 4
x + 2y - z = a
Solution for the system defined by the set of equations
4y + 3z = 8;
2x – z = 2
and 3x + 2y =5 is
4y + 3z = 8;
2x – z = 2
and 3x + 2y =5 is
For what values of α and β the following simultaneous equations have an infinite numberof solutions?
x + y + z = 5; x + 3y + 3z = 9; x + 2y + αz = β
Let A be a 3 × 3 matrix with rank 2. Then AX = 0 has
A is a 3 x 4 real matrix and A x = b is an inconsistent system of equations. The highest possible rank of A is
Consider the matrices X (4 × 3), Y (4 × 3) and P (2 × 3). The order of [P(XTY)−1PT] will be
Given matrix [A] = the rank of the matrix is
The Laplace transform of
For what value of k, the system linear equation has no solution
(3k + 1)x + 3y - 2 = 0
(k2 + 1)x + (k - 2)y - 5 = 0
If L defines the Laplace Transform of a function, L [sin (at)] will be equal to
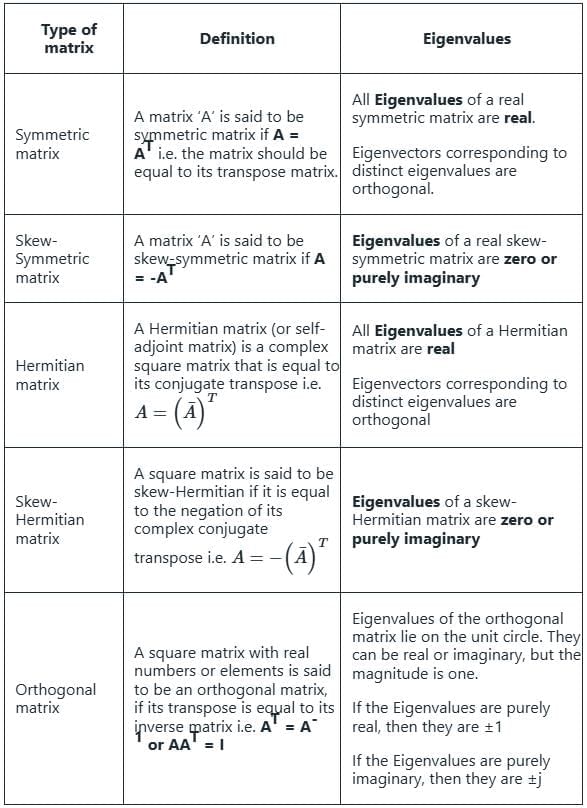
Which one of the following statements is true for all real symmetric matrices?
Two matrices A and B are given below:
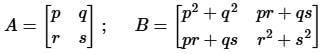
If the rank of matrix A is N, then the rank of matrix B is
A set of linear equations is given in the form Ax = b, where A is a 2 × 4 matrix with real number entries and b ≠ 0. Will it be possible to solve for x and obtain a unique solution by multiplying both left and right sides of the equation by AT (the super script T denotes the transpose) and inverting the matrix AT A? Answer is
The rank of the following matrix is
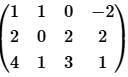
Laplace transform of (a + bt)2 where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constants is given by:
A delayed unit step function is defined as Its Laplace transform is
The Laplace transform of the function sin2 2t is
Find the rank of the matrix
Euclidean norm (length) of the vector [4 – 2 - 6]T is
The state transition matrix for the system X- = AX with initial state X(0) is
The Fourier transform of x(t) = e–at u(–t), where u(t) is the unit step function
Let X be a square matrix. Consider the following two statements on X.
I. X is invertible.
II. Determinant of X is non-zero.
Which one of the following is TRUE?
u(t) represents the unit step function. The Laplace transform of u(t – ζ) is
The fundamental period of x(t) = 2 sin πt + 3 sin 3πt, with t expressed in seconds, is
If the Fourier transform of x[n] is X(ejω), then the Fourier transform of (–1)n x[n] is
Given f(t) and g(t) as shown below:
g (t) can be expressed as
Given f(t) and g(t) as shown below:
The Laplace transform of g(t) is
The Laplace transform of g(t) is
Let Y(s) be the Laplace transformation of the function y (t), then final value of the function is