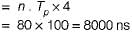Test: Pipelining- 1 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pipelining- 1
Given a 5 stage pipeline with stages taking 1,2, 3, 1, 1 units of time, the clock period of the pipeline is
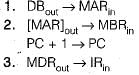
Which of following registers processor used for fetch and execute operations?
1. Program counter
2. Instruction register
3. Address register
A ________ is required to translate such microprogram into executable programs that can be stored in the control memory in microprogramming.
Which of the following statements is false about CISC architectures?
The register which holds the address of the location to or from which data are to be transferred is known as
Consider a case where 4-segment pipeline with a clock cycle time 20 ns in each sub operation to execute 100 tasks. Assume that a non pipeline unit that can perform the same operation. Pipelined system will take how much time to complete the task?
Find out the speed-up ratio between pipelined and non-pipelined system?
Assume that the time required for the eight functional units, which operate in each of the eight cycles, are as follows 5 ns, 8 ns, 6 ns, 10 ns, 15 ns, 12 ns, 6 ns, 8 ns. Assume that pipe lining adds 1 ns of overhead. Find the speedup versus the single cycle data path.