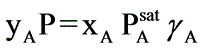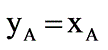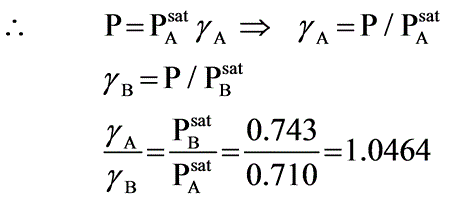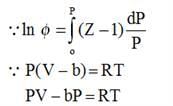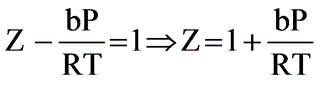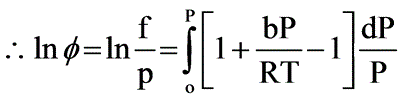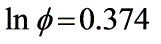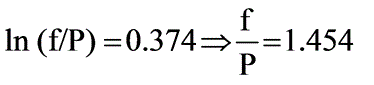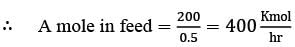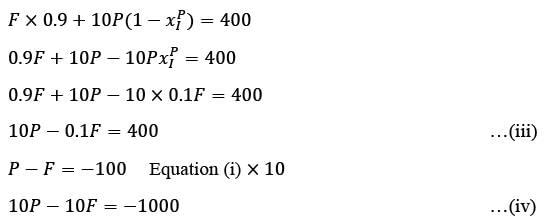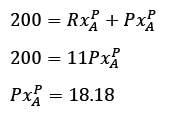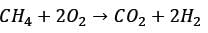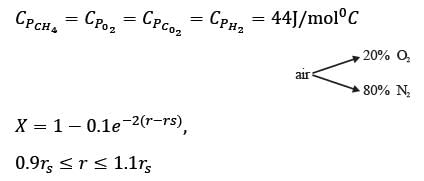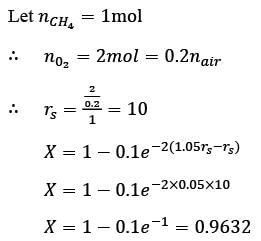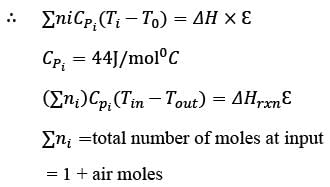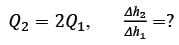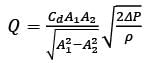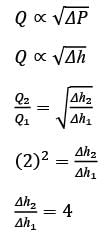GATE Chemical Engineering Mock Test - 3 - GATE Chemical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GATE Chemical Engineering Mock Test - 3
Identify the segment containing the mistake in the following sentence:
(i) No sooner had the hockey match begun (ii) than it started (iii) to rain (iv) no error.
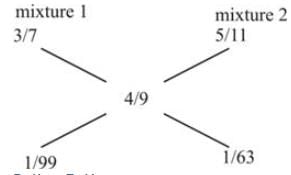
Somnath purchased two types of oil: soya oil and olive oil. He prepared two mixtures using these oils. The first mixture contains soya and olive oil in a ratio of 3:4, while the second mixture has a ratio of 5:6. When he combines these two mixtures to create a third mixture of 36 liters, the ratio of soya oil to olive oil in this new mixture is 4:5. What is the amount of the second mixture that is needed?
During a fixed period, a boy swims twice the distance downstream compared to the distance he swims upstream. Given that the speed of the current is 3 km/hr, what is the speed of the boy in still water?
The first non-zero term in the Taylor series expansion of (1 - x) - e-x around x = 0 is
Let [A] represent a square matrix that is neither symmetric nor skew-symmetric, with [A]T denoting its transpose. The matrices' sum is defined as [S] = [A] [A]T, and their difference is defined as [D] = [A] - [A]T. Which of the following statements is correct?
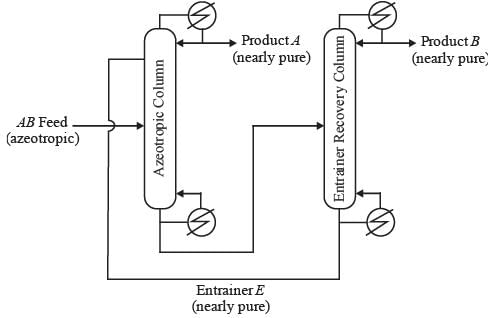
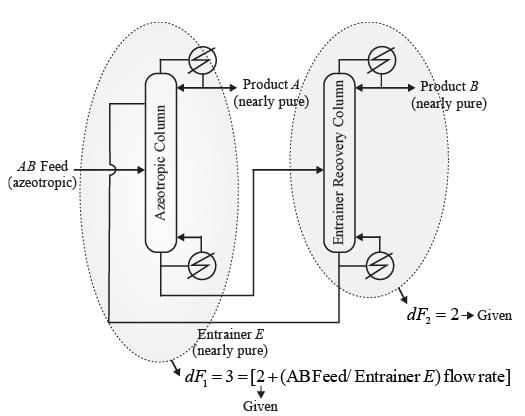
In a homogeneous azeotropic distillation setup, an azeotropic binary feed of components A and B is separated using a heavy entrainer, E, as illustrated in the figure. The amount of E lost in the two product streams is minimal, allowing E to circulate in a closed loop throughout the process. For a distillation column with fully specified feed(s) and defined operating pressure, where there is one distillate stream and one bottoms stream, the steady-state degrees of freedom is determined to be 2. In the process depicted in the figure, with a fully specified AB feed stream and given column operating pressures, the steady-state degrees of freedom is equal to
The velocity field in a flow that is incompressible is represented as 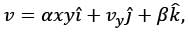 where
where 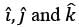 are unit vectors within the Cartesian coordinate system (x, y, z). Given that α and β are constants, determine the appropriate expression for vy when y = 0.
are unit vectors within the Cartesian coordinate system (x, y, z). Given that α and β are constants, determine the appropriate expression for vy when y = 0.
Ethyl Alcohol is generated through the fermentation of:
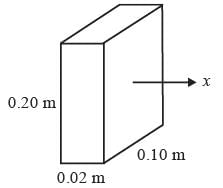
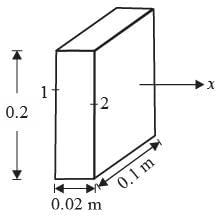
Consider the steady, one-dimensional diffusion of a binary mixture consisting of A and B across a vertical slab measuring 0.2 m x 0.1 m x 0.02 m as illustrated in the figure. The total molar concentration of A and B remains constant at 100 molm−3. The mole fractions of A at the left and right surfaces of the slab are held at 0.8 and 0.2, respectively. Given that the binary diffusion coefficient DAB is 1 x 10−5 m2s-1, determine the molar flow rate of A in mol s−1 along the horizontal x direction.
What is the most efficient technique for washing the filter cake?
Consider a linear homogeneous equation system given by Ax = 0, where A is an n x n matrix, x is an n x 1 vector, and 0 represents an n x 1 null vector. Let r denote the rank of A. Which of the following conditions must be satisfied for a non-trivial solution to exist?
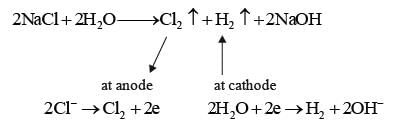
In the context of the electrolytic cell utilized in a chlor-alkali manufacturing facility, which of the following statements is/are accurate?
Consider a binary mixture consisting of components A and B at a given temperature T and pressure P. Let 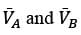 represent the partial molar volumes of A and B, respectively. At a specific mole fraction of A, denoted as xA, what is the value of xA, rounded to two decimal places? Where
represent the partial molar volumes of A and B, respectively. At a specific mole fraction of A, denoted as xA, what is the value of xA, rounded to two decimal places? Where
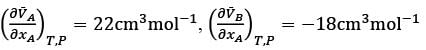
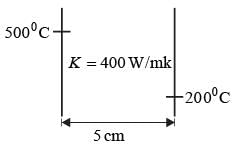
A metal slab with a thickness of 5 cm and a thermal conductivity of 400 Wm−1 °C−1 has its opposite faces kept at temperatures of 500°C and 200°C. Each face has an area of 0.02 m2. Assuming that heat transfer is steady and occurs solely in the direction perpendicular to the surfaces, what is the heat transfer rate, in kW, rounded to the nearest integer?
The inverse Laplace transform of the function 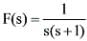 is represented by ________
is represented by ________
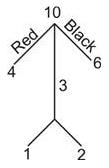
A container holds 4 red balls and 6 black balls. Three balls are drawn randomly from the container one at a time, without replacement. What is the probability that the chosen group includes one red ball and two black balls? _____
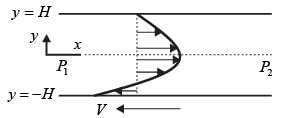
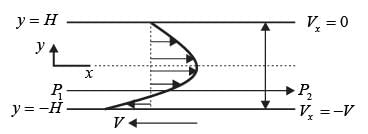
Consider a steady, fully-developed, uni-directional laminar flow of an incompressible Newtonian fluid (viscosity μ) occurring between two infinitely long horizontal plates that are separated by a distance of 2H as depicted in the figure. The flow is induced by the combined effects of a pressure gradient and the movement of the lower plate at y = −H in the negative x direction. Given that 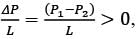 , where P1 and P2 denote the pressures at two x positions separated by a distance L. The lower plate has a velocity of magnitude V relative to the stationary upper plate at y = H. Which of the following expressions represents the x-component of the fluid velocity vector?
, where P1 and P2 denote the pressures at two x positions separated by a distance L. The lower plate has a velocity of magnitude V relative to the stationary upper plate at y = H. Which of the following expressions represents the x-component of the fluid velocity vector?
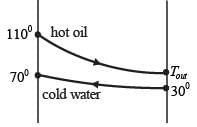
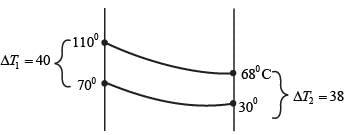
Hot oil at a temperature of 110°C is used to raise the temperature of water from 30°C to 70°C in a counter-current double-pipe heat exchanger. The flow rates for the water and oil are 50 kg min-1 and 100 kg min-1, respectively, with their specific heat capacities being 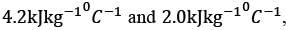 and
and 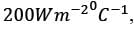 respectively. Assume that the heat exchanger operates under steady-state conditions. What is the heat transfer area in m2?
respectively. Assume that the heat exchanger operates under steady-state conditions. What is the heat transfer area in m2?
A scientist has identified a novel type of force that arises when a specific kind of particle settles in any fluid. The formula representing this new force is 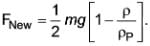
In this equation, m, ρP, and ρ denote the mass of the particle, the density of the particle, and the density of the fluid, respectively. This force acts in the upward direction.
Determine the terminal velocity given that CD represents the drag coefficient and AP is the projected area of the particle.
Consider the ordinary differential equation 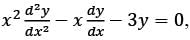 with the boundary conditions y(1) = 2 and y(2) = 17/2. Determine the value of the solution y(x) at x = 3/2, rounded to two decimal places, which is ______.
with the boundary conditions y(1) = 2 and y(2) = 17/2. Determine the value of the solution y(x) at x = 3/2, rounded to two decimal places, which is ______.
A solution with 10% solids is to be concentrated to 50% solids. Steam is available at a pressure of 0.20 MPa and a saturation temperature of 120oC. The feed rate to the evaporator is 30,000 kg/h at a temperature of 20oC. The evaporator operates at a reduced pressure where the boiling point is 50oC. The overall heat transfer coefficient is 2.9 kW / (M2 - K). What is the steam economy for this evaporation process?

Latent heat of condensation of steam at 0.20 MPa 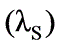 = 2202 kJ/kg
= 2202 kJ/kg
Latent heat of vaporization of water at 323 K 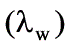 = 2383 kJ/kg
= 2383 kJ/kg
In a laboratory investigation regarding the absorption of ammonia by water in a wetted-wall column, the overall mass transfer coefficient, KG, was determined to be 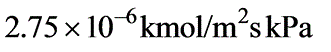 . At a specific location within the column, the gas and liquid phase compositions were recorded at 8.0 and 0.115 mole % NH3, respectively. The system was maintained at a temperature of 300 K and a total pressure of 1 atm. It was observed that 85% of the overall resistance to mass transfer occurred in the gas phase. At 300 K, ammonia-water solutions adhere to Henry’s law up to a concentration of 5 mole % ammonia in the liquid, with m = 1.64 at 1 atm pressure.
. At a specific location within the column, the gas and liquid phase compositions were recorded at 8.0 and 0.115 mole % NH3, respectively. The system was maintained at a temperature of 300 K and a total pressure of 1 atm. It was observed that 85% of the overall resistance to mass transfer occurred in the gas phase. At 300 K, ammonia-water solutions adhere to Henry’s law up to a concentration of 5 mole % ammonia in the liquid, with m = 1.64 at 1 atm pressure.
What is the molar flux of ammonia expressed in kmol/m2 sec? (rounded to two decimal places)
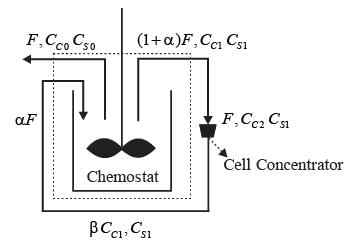
A chemostat with cell recycle is shown in the figure. The feed flow rate and culture volume are F = 75Lh-1 and V = 200L, respectively. The glucose concentration in the feed CS0 = 15gL-1. Assume Monod kinetics with specific cell growth rate 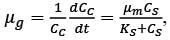 where μm= 0.25h−1 and Ks = 1gL-1 . Assume maintenance and death rates to be zero, input feed to sterile (CC0 = 0) and steady-state operation. The glucose concentration in the recycle stream, CS1, in gL−1, rounded off to 1 decimal place, is _________.
where μm= 0.25h−1 and Ks = 1gL-1 . Assume maintenance and death rates to be zero, input feed to sterile (CC0 = 0) and steady-state operation. The glucose concentration in the recycle stream, CS1, in gL−1, rounded off to 1 decimal place, is _________.
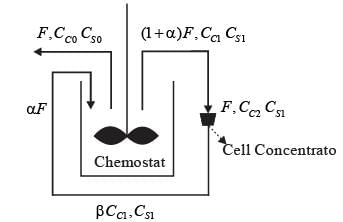
F: Volumetric flow rate
CC : Cell concentration
CS : Substrate (glucose) concentration
α ∶ Recycle ratio (α = 0.5)
β ∶ Concentration factor (β = 2.0)
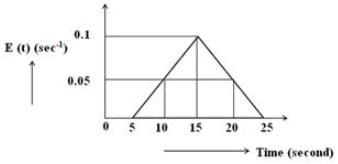
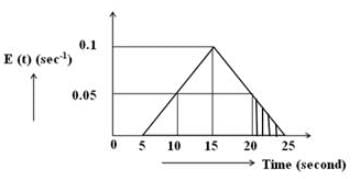
Based on the provided diagram, what is the percentage of the fraction of material that spends time between 20 and 25 seconds in the reactor?
A reversible isothermal reaction in an aqueous phase, represented as P 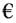 R, is to be conducted in a mixed flow reactor. The reaction rate, expressed in (kmol/m3 -h), is defined by -rP = 0.5CP - 0.125CR. A feed stream containing solely P is introduced into the reactor. What will be the residence time (in minutes) required for a 40% conversion of P?
R, is to be conducted in a mixed flow reactor. The reaction rate, expressed in (kmol/m3 -h), is defined by -rP = 0.5CP - 0.125CR. A feed stream containing solely P is introduced into the reactor. What will be the residence time (in minutes) required for a 40% conversion of P?
A binary mixture of components A and B creates an azeotrope with a boiling point of 71.8°C at a pressure of 1 bar, where the azeotropic composition consists of 55 mol percent of A. The saturated vapor pressures at 71.8°C are PA,sat = 0.710 bar and PB,sat = 0.743 bar. Assuming the vapor behaves ideally, what will be the ratio of the activity coefficients of A to B in the liquid phase?
Under conditions of high temperature and pressure, nitrogen (N2) follows the equation P(V - B) = RT. Determine the fugacity (in atm) of N2 at 1000°C and 1000 atm, given that b = 39.1 ml/mol.
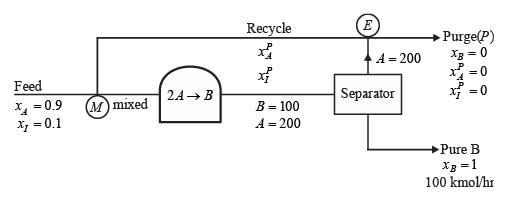
Analyze the process depicted in the figure for the production of B. The input to this process consists of 90 mol% A along with a closely boiling inert component I. Under steady-state conditions, the following information is provided:
- The rate of production of B is 100 kmol h−1
- The single-pass conversion of A within the reactor is 50%
- The flow ratio of recycle to purge stream is 10
The flow rate of A in the purge stream, expressed in kmol h−1, rounded to one decimal place, is _______.
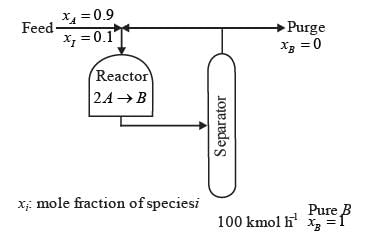
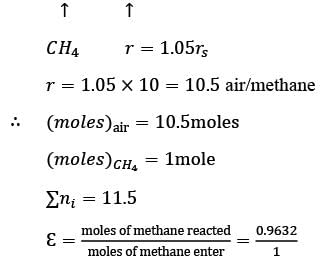
Methane reacts with air in a furnace according to the equation CH4 2O2 → CO2 2H2O, with a heat of reaction ΔHrxn = -880 kJ per mole of CH4, which is considered constant. The furnace is perfectly insulated, and there are no additional side reactions. All substances are treated as ideal gases, exhibiting a constant molar heat capacity of 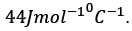 . The composition of air is approximated as 20 mol% O2 and 80 mol% N2. The air-fuel mixture enters the furnace at a temperature of 50°C. The conversion of methane, X, is influenced by the air-to-methane mole ratio, r, as described by
. The composition of air is approximated as 20 mol% O2 and 80 mol% N2. The air-fuel mixture enters the furnace at a temperature of 50°C. The conversion of methane, X, is influenced by the air-to-methane mole ratio, r, as described by
\n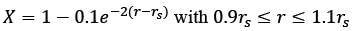
\nwhere rs represents the stoichiometric air-to-methane mole ratio. For r = 1.05rs, determine the exit flue gas temperature in °C, rounded to one decimal place, as ___________.
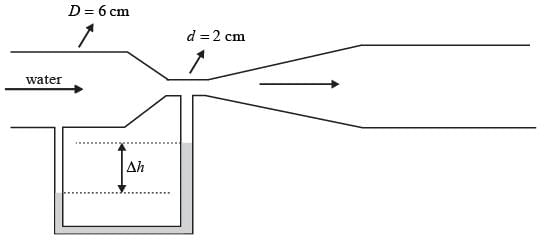
A Venturi meter, featuring a throat diameter of d = 2cm, is utilized to measure the flow rate in a pipe with a diameter of D = 6cm, as illustrated in the accompanying figure. A U-tube manometer is attached to gauge the pressure drop. Assume the discharge coefficient remains constant regardless of the Reynolds number and geometric ratios. If the volumetric flow rate in the pipe is increased to Q2 = 2Q1, what is the corresponding ratio of the manometer readings Δh2/Δh1, rounded to the nearest integer?


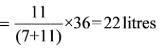

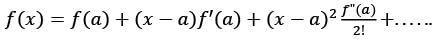
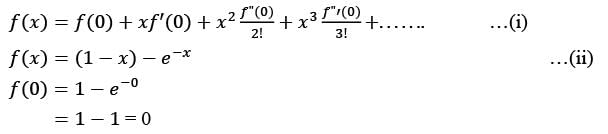
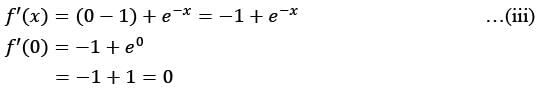


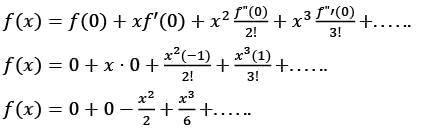
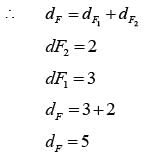
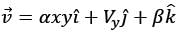
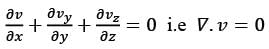
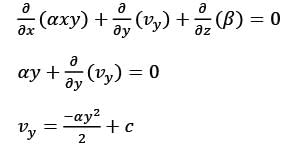
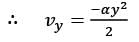
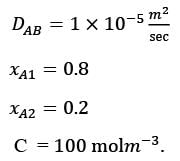
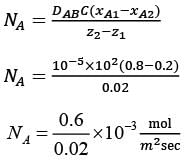


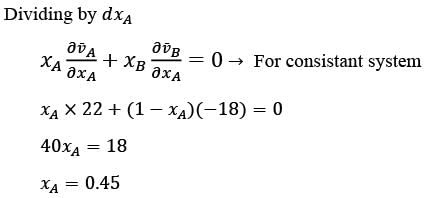

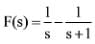
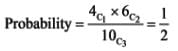
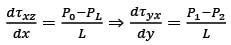
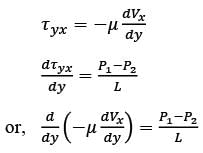
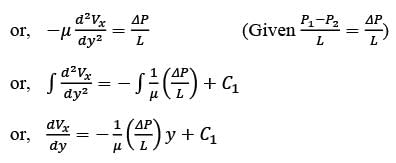

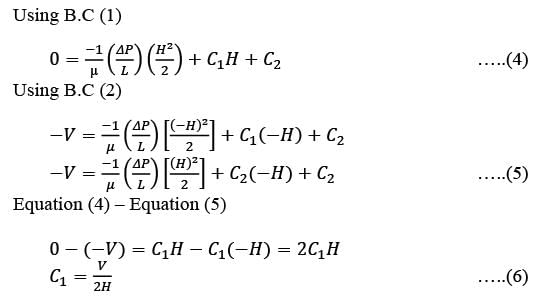
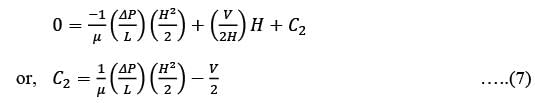
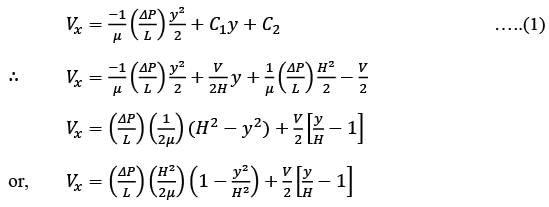

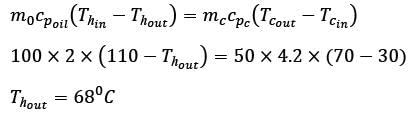
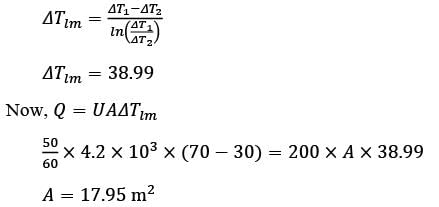
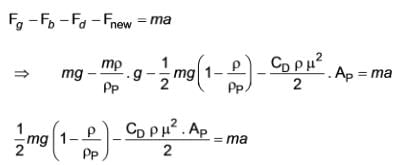
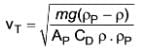
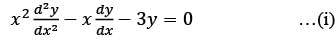
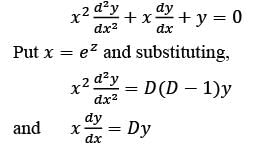
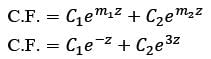
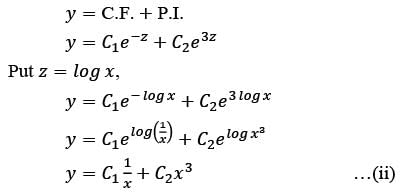
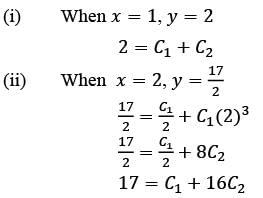
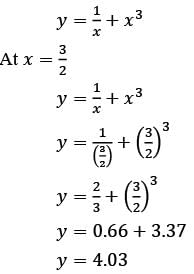
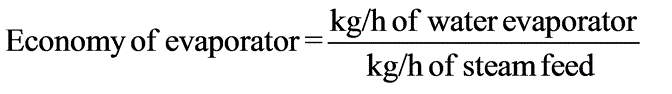
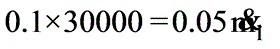
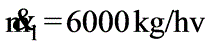

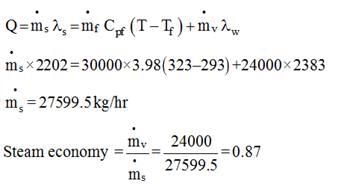
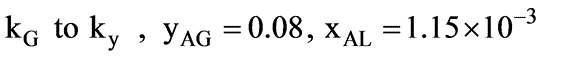
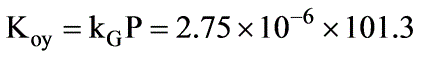
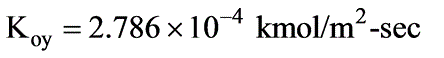
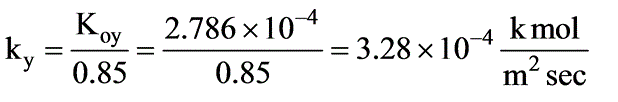
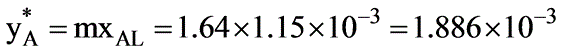
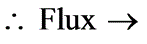
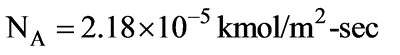

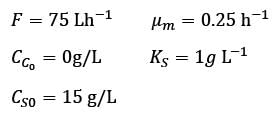
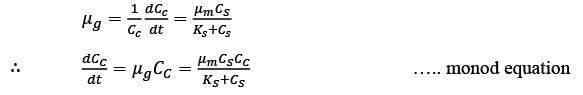
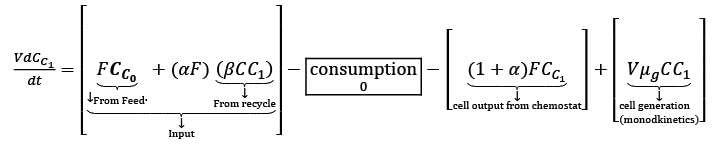 Step II :
Step II :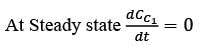
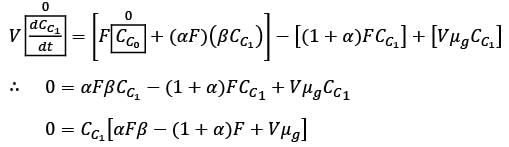
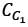 is steady state cell concentration in chemostate and recycle stream
is steady state cell concentration in chemostate and recycle stream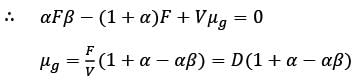
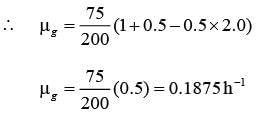
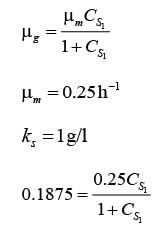
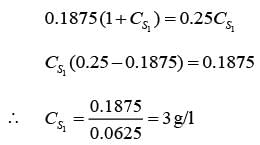
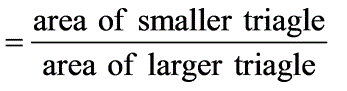
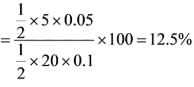
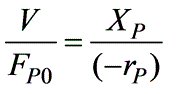
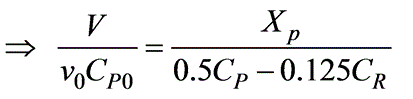
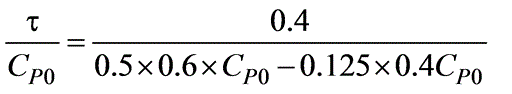
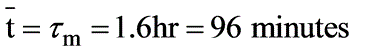
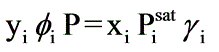
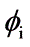 = 1
= 1