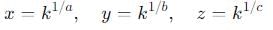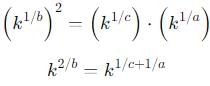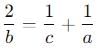GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 1 - GATE Architecture and Planning MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - GATE Architecture and Planning Mock Test - 1
The second-hand and minute-hand of a clock intersect _______ times between 09:15:00 AM and 09:45:00 AM on a given day.
Planting : Seed : : Raising : _____ (Based on word meaning)
If xa = yb = zc and y2 = z x, then what is the value of (1 / a + 1 / c)?
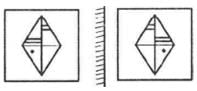
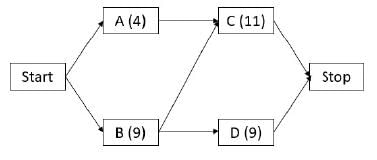
What will the reflection of the figure shown below appear as?
4. Problem figure
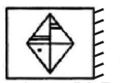
Answer Figures
Examine the following inequalities:
p2 - 4q < 4
3p + 2q < 6
where p and q are positive integers.
What is the value of (p + q)? ______
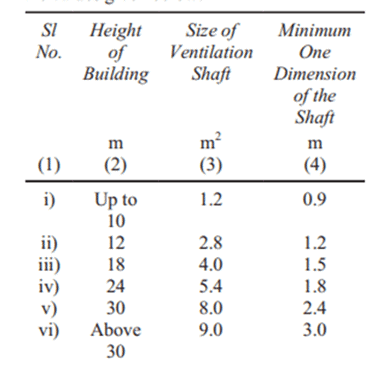
The minimum required area for a ventilation shaft in square meters for a structure with a height of 10 meters is
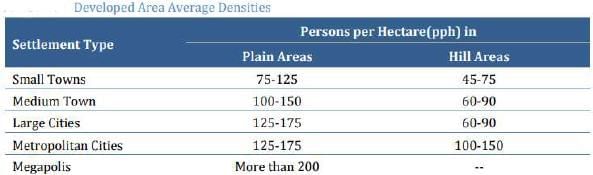
According to the URDPFI (2015), what is the recommended density range (in persons per Hectare) for an overall planning strategy for small towns located in hilly regions?
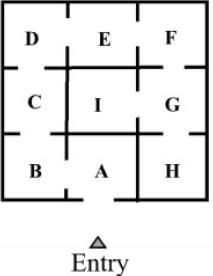
The diagram shown below illustrates the layout of rooms within a building, with external access denoted as 'entry'. Determine the correct diagram that represents the room access beginning from the entry point.
Identify the Act that specifies a restricted area of 100 m surrounding centrally protected monuments in India.
What is the hydraulic radius (in mm) of a circular pipe that is flowing full with a diameter of 450 mm?
A solar cell with an area of 3 m² and an efficiency of 18% is exposed to full sunlight at an angle of incidence of 60 degrees relative to the normal of the cell. What is the power output (in Watts) of the solar cell?
The standard duration and standard cost of an activity are 28 days and Rs. 55,000, respectively. The crash duration of the activity is 24 days, and the indirect cost amounts to Rs. 1,000 per day. Given that the cost slope is Rs. 1,500 per day, what will be the total cost of the activity (in rupees) after it has been crashed?
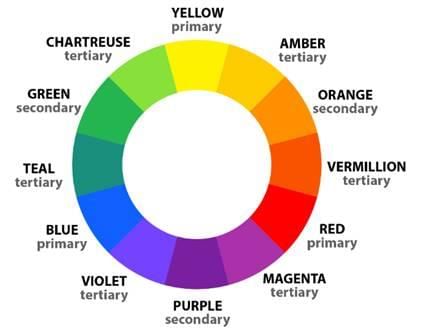
In a colour wheel, the hues Orange and Violet are
The Sustainable Development Goal 10, which is endorsed by the UN, aims to address:
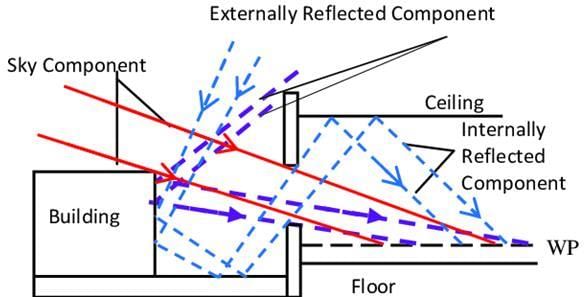
The term ‘Sky Component’ refers to which aspect of the environment?
Which of the following statements is accurate concerning PERT, the tool used for project management planning?
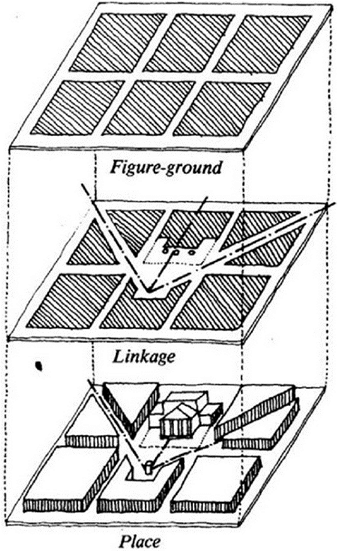
Which of the following represent the three primary theories of urban spatial design?
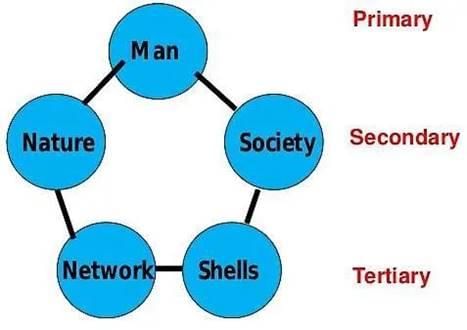
Which of the following are included in the four principles of Ekistics?
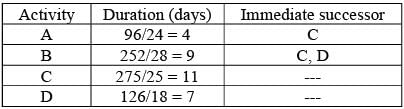
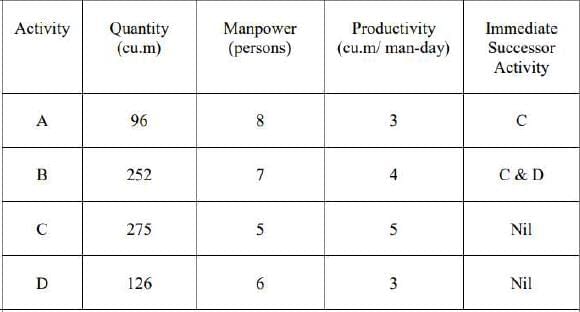
A construction endeavor comprises four tasks. The table below outlines the amount of work, manpower needs, and productivity for each task. Additionally, the interdependencies between the tasks are specified in the table. The construction project is scheduled to commence on January 29. Assume there are no holidays throughout the project duration. The project is expected to conclude on February _____ [indicate the date in numerical form].
A town has an annual precipitation of 400 mm. Rainwater is collected from the flat roof of a building, which is then treated to meet potable standards and stored. The total harvested volume experiences a water loss of 40 percent due to evaporation, transmission, and treatment. The area of the roof is 500 sq.m. There are 3 residents in the household, with an average daily water requirement of 200 liters per capita per day (lpcd). How many days will the stored rainwater sufficiently meet the daily needs of the household, expressed as an integer?
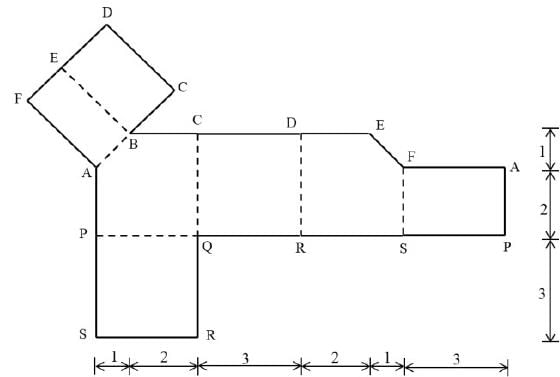
The development of the surface of a three-dimensional figure is illustrated in the image below. The dashed lines represent the folds. The measurements shown in the diagram are in centimeters. What is the volume of the three-dimensional figure (in cu.cm), rounded to one decimal place?
In a privately initiated residential housing project, the ratio of the total number of dwelling units designated as HIG, MIG, and LIG is 3:2:1. The intended average sizes of the HIG, MIG, and LIG units in square meters are 100, 60, and 30, respectively. What is the integer value of the ratio of the total built-up area of (MIG LIG) to that of HIG? The ratio is 1: ______.
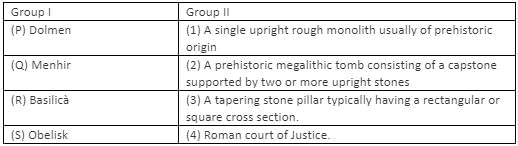
Pair the historical edifices in Group I with their corresponding descriptions in Group II.
The ratio of the dimensions of a traditional Japanese tatami mat is _______.
Which of the following sites from India were inscribed as World Heritage Sites in the year 2022?
Which of the following components in clay, when present in excess, may lead to the bricks shrinking, warping, or cracking during the drying and firing processes?
Which of the following methods serves to prevent the corrosion of iron?
The first listener is positioned 680 meters away from the sound source, while the second listener is located 1360 meters from the same source. Assume there are no obstructions and that the sound travels through the same medium. With the speed of sound given as 340 meters per second, calculate the time difference for the sound to travel from the first listener to the second listener in ______ sec.
Determine the thermal transmittance (U) value in (kcal /(m2 h deg C)) for a 12 cm thick external brick wall (with thermal resistivity = 0.0143 m2 h deg C/( kcal cm)) that is coated with 15 mm thick cement plaster on both surfaces. The thermal conductivity of the cement plaster is given as 81.8 kcal cm /(m2 h deg C). Additionally, for the walls, take 1/fi = 0.125 and 1/fo = 0.0515.
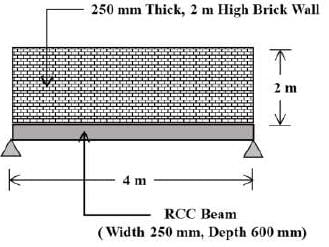
A simply supported RCC beam with a span of 4 m is subjected to the load of a brick wall that spans its entire length. The brick wall has a thickness of 250 mm and a height of 2 m. The RCC beam has dimensions of 600 mm in depth and 250 mm in width. The densities of brick masonry and RCC are given as 18 KN/m3 and 25 KN/m3, respectively. Taking into account the weight of the wall and the self-weight of the RCC beam, what is the maximum bending moment in the beam (in KN-m), rounded to two decimal places?