|
Card: 1 / 40 |
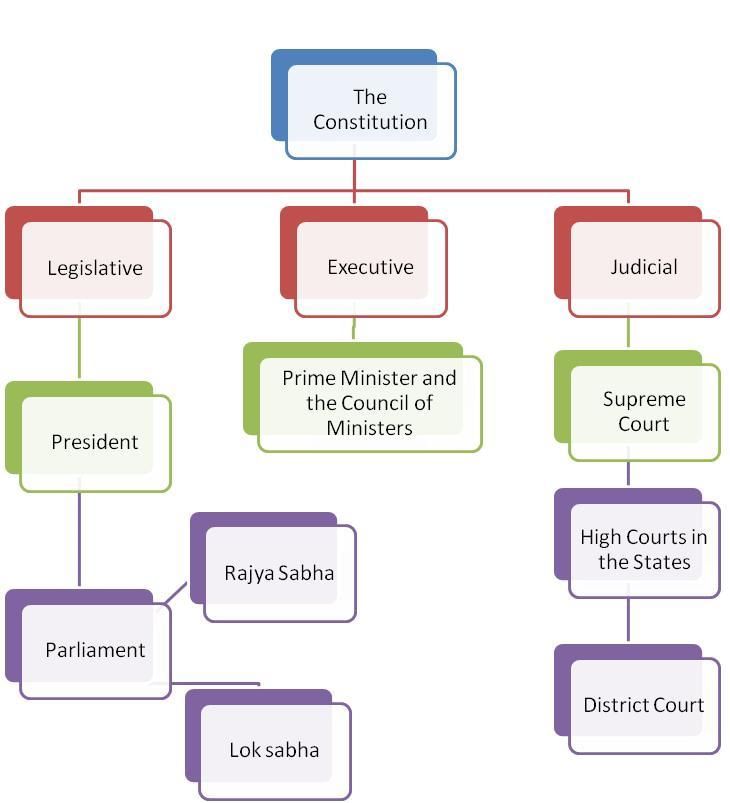
The Indian Constitution was adopted on ___ and was originally the lengthiest written constitution in the world with ___ Articles. |
|
Card: 3 / 40 |
True or False: The Constitution (105th Amendment) Act, 2021 reduced the number of Articles in the Indian Constitution. |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
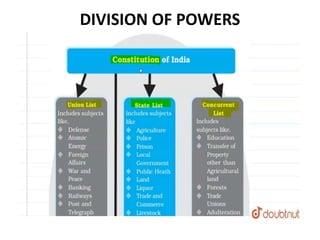
The Constitution of India is characterized primarily as a ___ constitution, which includes a division of powers between the federal and state governments. |
|
Card: 7 / 40 |
True or False: The Preamble of the Indian Constitution was first introduced in the 42nd Amendment of 1976, which added the words 'socialist', 'secular', and 'integrity'. |
|
Card: 8 / 40 |
False. The Preamble existed before the 42nd Amendment; the amendment only added those specific words.  |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
The Preamble to the Constitution of India declares the country to be a ___, ___, democratic, and republican nation. |
|
Card: 11 / 40 |
True or False: The Preamble is considered a part of the Constitution of India. |
|
Card: 12 / 40 |
False. The Preamble is not legally enforceable but reflects the guiding principles of the Constitution.  |
|
Card: 13 / 40 |
What was the significance of the Keshavananda Bharati Case (1973) regarding the Preamble of the Constitution? |
|
Card: 14 / 40 |
The Keshavananda Bharati Case established that the Preamble is part of the Constitution and can be amended, provided that such amendments do not violate the Basic Features of the Constitution.  |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
The Preamble was amended in 1976 to include the words ‘socialist, secular, and integrity’. True or False? |
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
True; the amendment was clarificatory and did not significantly change the underlying principles of the Constitution.  |
|
Card: 19 / 40 |
True or False: The Indian Constitution now consists of 448 Articles, 25 Parts, and 10 Schedules. |
|
Card: 20 / 40 |
False. The Indian Constitution consists of 448 Articles, 25 Parts, and 12 Schedules. 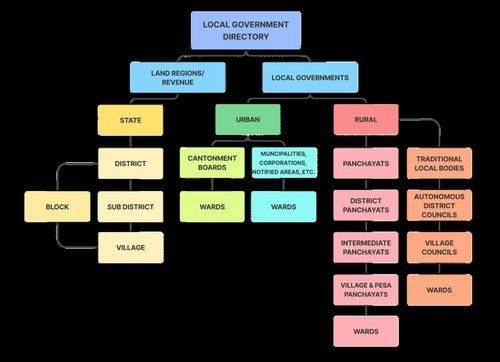 |
|
Card: 23 / 40 |
True or False: The Fourth Schedule of the Indian Constitution relates to the provisions for the allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha. |
|
Card: 24 / 40 |
False. The Fourth Schedule relates to the allocation of seats for States and Union Territories in the Rajya Sabha.  |
|
Card: 26 / 40 |
It deals with the 22 official languages recognized by the Constitution of India.  |
|
Card: 27 / 40 |
The Ninth Schedule was added to protect certain laws from judicial scrutiny. True or False? |
|
Card: 28 / 40 |
True. The Ninth Schedule was added by the 1st Amendment Act 1951 to protect laws related to land reforms and the zamindari system from judicial review.  |
|
Card: 29 / 40 |
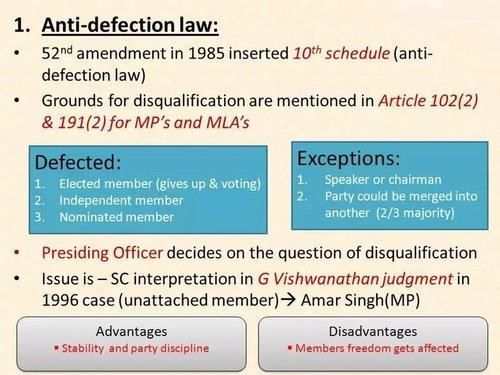
Fill in the blank: The Tenth Schedule contains provisions relating to the disqualification of members of Parliament and State Legislatures on the ground of ___. |
|
Card: 31 / 40 |
How many matters does the Eleventh Schedule specify for the powers and responsibilities of Panchayats? |
|
Card: 33 / 40 |
Riddle: I am a schedule that specifies the powers of Municipalities, and I contain 18 matters. What am I? |
|
Card: 37 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The ___ Schedule deals with state acts and regulations related to land reforms and the abolishment of the zamindari system. |
|
Card: 39 / 40 |
True or False: Laws included in the Ninth Schedule after April 24, 1973, are immune to judicial review. |
|
Card: 40 / 40 |
False. The Supreme Court ruled in 2007 that such laws are now open to judicial review.  |