|
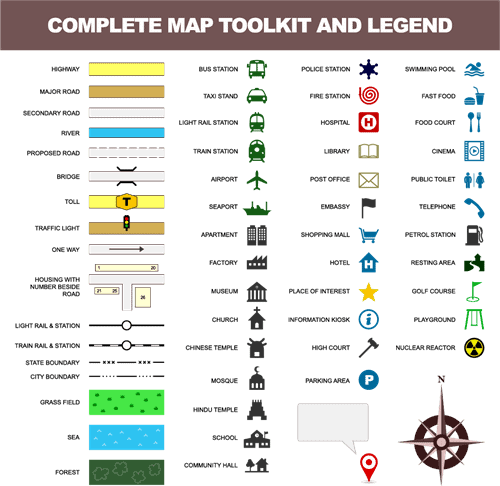
Fill in the blank: A map's ___ explains the symbols used to represent different features. |
Card: 1 / 32 |
|
False. Thematic maps focus on specific types of information, such as population density or climate zones. 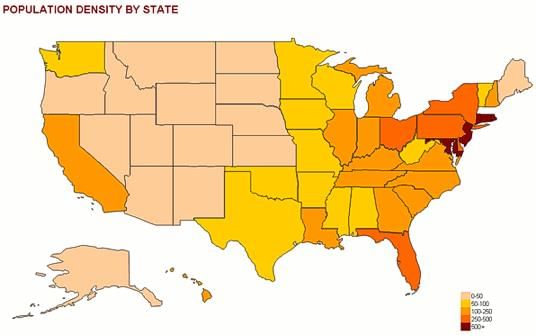 |
Card: 4 / 32 |
|
Cardinal directions (North, South, East, West) and intermediate directions help indicate orientation and navigation on a map. |
Card: 6 / 32 |
|
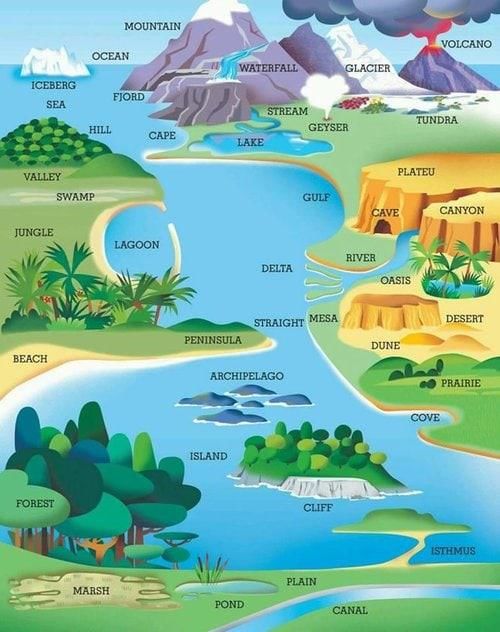
Fill in the blank: Physical maps primarily display ___ features like mountains and rivers. |
Card: 7 / 32 |
|
Symbols represent different features on a map, such as a tree for a forest or a dotted line for a road, and are explained in the map's legend. |
Card: 10 / 32 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which type of map would you use to find the boundaries of countries? |
Card: 11 / 32 |
|
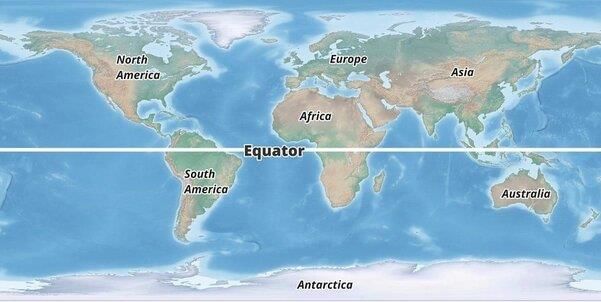
Which climate zone is characterized by hot temperatures and is located near the Equator? |
Card: 15 / 32 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Fill in the blank: The areas between the tropics and the polar circles are referred to as ___ zones. |
Card: 19 / 32 |
|
True or False: A globe is less accurate than a flat map in representing the Earth. |
Card: 23 / 32 |
|
The Prime Meridian, located at 0° longitude, serves as the reference line from which all other longitudes are measured, facilitating global navigation and timekeeping. |
Card: 26 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Earth is divided into ___ time zones, each representing one hour of time. |
Card: 27 / 32 |
|
True or False: When crossing the International Date Line from west to east, the date changes by subtracting a day. |
Card: 29 / 32 |
|
What standard time does India follow, and how does it relate to Greenwich Mean Time? |
Card: 31 / 32 |
|
India follows Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5.5 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). |
Card: 32 / 32 |