|
Regional aspirations in India are often related to the demands for ___ and ___ from various cultural and linguistic groups. |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
True or False: The Indian approach to nation-building views regional aspirations as inherently anti-national. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
False. The Indian approach allows for the political expression of regional aspirations without viewing them as anti-national. |
Card: 4 / 50 |
|
What major political issue arose from the integration of Jammu and Kashmir into India post-independence? |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
The Kashmir dispute, including the local aspirations of the Kashmiri people and the conflict with Pakistan.  |
Card: 6 / 50 |
|
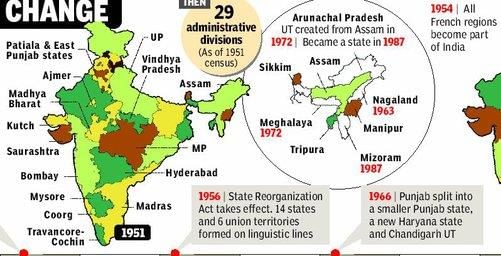
Fill in the blank: The reorganization of states in India was influenced by the demand for states based on ___ during the late 1950s. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I am a region with a mixed population, a historical princely state, and a major point of contention between India and Pakistan. What am I? |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
Article 370 granted special autonomy to Jammu and Kashmir, allowing it to have its own constitution and greater rights compared to other Indian states.  |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
True or False: The Akali Dal was formed in response to the demand for an independent Sikh state known as Khalistan. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
True. The Akali Dal, while initially a political wing for Sikhs, later supported the demand for Khalistan. |
Card: 14 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The ___ movement in Punjab emphasized the need for a Punjabi-speaking state. |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
What event in June 1984 significantly affected Sikh sentiments and escalated violence in India? |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
Operation Blue Star, which involved the military action against militants in the Golden Temple.  |
Card: 18 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following was a consequence of the 1984 anti-Sikh riots following the assassination of Indira Gandhi? A) Increased support for the Congress party B) Over two thousand Sikhs were killed C) Strengthening of the Akali Dal D) Formation of a new state |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The region of North-East India consists of ___ states, commonly referred to as the ___ sisters. |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
True or False: The Mizo National Front (MNF) was formed in response to the Assam Government's adequate response to the famine of 1959. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False; the MNF was formed due to the Assam Government's failure to respond adequately to the famine.  |
Card: 26 / 50 |
|
What was the outcome of the peace agreement signed in 1986 between Rajiv Gandhi and Laldenga? |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
Mizoram was granted full statehood with special powers, and the MNF agreed to give up its secessionist struggle.  |
Card: 28 / 50 |
|
Riddle: I am a movement that sought to identify and remove those who entered after 1951. What am I? |
Card: 29 / 50 |
|
How did the central government respond to the demands for statehood from various communities in Assam? |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
The government created separate states like Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh from Assam. 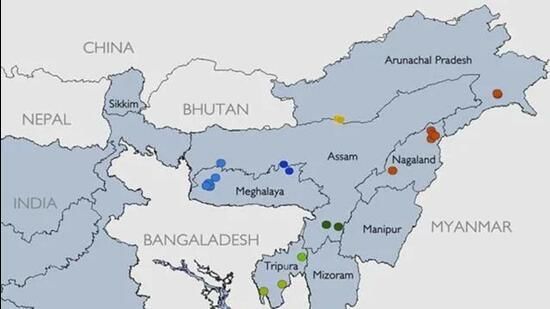 |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The All Assam Students' Union (AASU) led an anti-foreigner movement from ___ to ___. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
What was the primary demand of the leaders of the Eastern India Tribal Union formed in the 1960s? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
True or False: The Nagaland secessionist movement concluded successfully with a peace agreement acceptable to all factions. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following states was NOT created from Assam? A) Meghalaya B) Arunachal Pradesh C) Nagaland D) Tripura |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
What was the primary demand of the leaders of the large tribal community in Assam during the rise of political autonomy? |
Card: 41 / 50 |
|
In what year did the All Party Hills Conference evolve from the Eastern India Tribal Union? |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The central government created ___, ___, and ___ by dividing Assam. |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
True or False: The demand for autonomy ended completely after the creation of Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh. |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
False. The demand for autonomy continued, especially from communities like the Bodo, Karbis, and Dimsas. 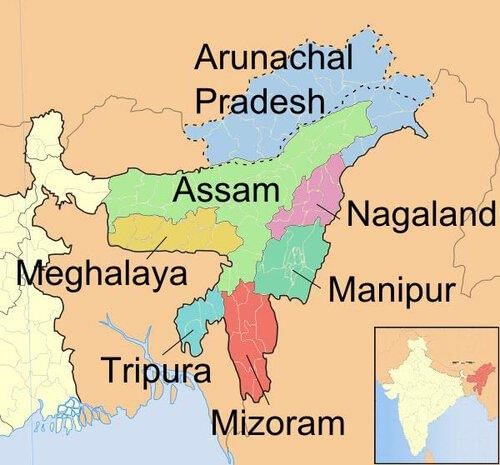 |
Card: 48 / 50 |
|
What strategy did the central government use to address the demands for separate states in Assam? |
Card: 49 / 50 |
|
The central government attempted to satisfy the demands through other provisions rather than dividing the state further.  |
Card: 50 / 50 |