|
Fill in the blanks: The timeline of the Harappan civilization spans from ___ BCE to ___ BCE. |
Card: 3 / 44 |
|
True or False: The Harappan civilization is known for its undeciphered script found on seals. |
Card: 5 / 44 |
|
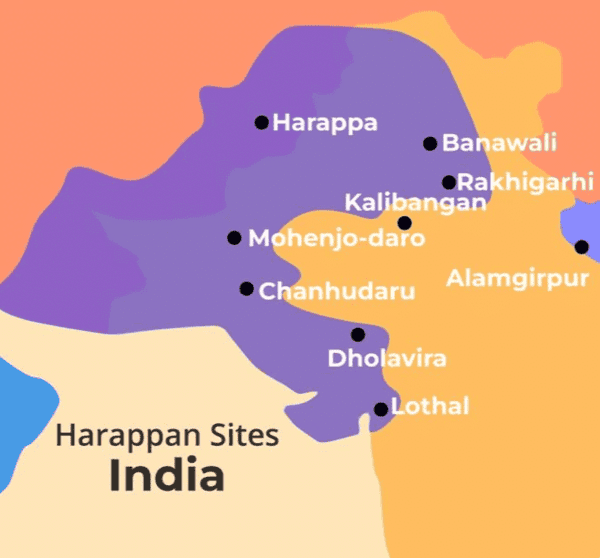
What does the term 'Harappa' refer to in the context of the Harappan civilization? |
Card: 13 / 44 |
|
What significant information do we gain from the archaeological evidence of the Harappan civilization? |
Card: 17 / 44 |
|
We gain insights into the lives of the people, including their houses, tools, and daily activities. |
Card: 18 / 44 |
|
What significant change indicates a break between the Early Harappan and Harappan civilization? |
Card: 19 / 44 |
|
The discovery of large-scale burning at some archaeological sites and the abandonment of certain settlements indicates a significant break.  |
Card: 20 / 44 |
|
The Harappans may have used ___ for ploughing, as suggested by seals and terracotta sculptures. |
Card: 21 / 44 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What types of domesticated animals were indicated by animal bones found at Harappan sites? |
Card: 25 / 44 |
|
Cattle, sheep, goat, buffalo, and pig are some of the domesticated animals indicated by the bones found. |
Card: 26 / 44 |
|
What evidence suggests that irrigation may have been necessary for Harappan agriculture? |
Card: 27 / 44 |
|
The presence of traces of canals and water reservoirs indicates that irrigation was likely necessary in semi-arid areas.  |
Card: 28 / 44 |
|
Wheat, barley, lentil, chickpea, sesame, and millets were commonly found at Harappan sites. |
Card: 30 / 44 |
|
True or False: The Harappans relied solely on hunting for their animal protein sources. |
Card: 31 / 44 |
|
False; they had domesticated animals and also possibly obtained meat from other hunting communities. |
Card: 32 / 44 |
|
Mohenjodaro is known for its advanced urban planning, which includes the construction of the Citadel and the Lower Town. What are the main features of each section? |
Card: 33 / 44 |
|
The Citadel is smaller, elevated, and surrounded by walls with buildings on mud brick platforms, while the Lower Town is walled and features a grid layout of streets and buildings also on platforms. |
Card: 34 / 44 |
|
The drainage system of Harappan cities was notable for its design. Describe the layout and purpose of the drainage system in Mohenjodaro. |
Card: 35 / 44 |
|
The drainage system featured streets with drains that were constructed before houses, ensuring that each house had a wall along the street to facilitate wastewater flow into the drains, promoting sanitation.  |
Card: 36 / 44 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Great Bath in the Citadel of Mohenjodaro is believed to have been used for ___ purposes. |
Card: 37 / 44 |
|
True or False: All houses in the Lower Town of Mohenjodaro had windows on their ground-level walls for ventilation. |
Card: 39 / 44 |
|
How many wells were estimated to be present in Mohenjodaro, and what was their significance? |
Card: 41 / 44 |
|
An estimated total of 700 wells were present in Mohenjodaro, providing water for domestic use.  |
Card: 42 / 44 |
|
Standardized bricks were used in construction with a consistent ratio of length, breadth, and height across Harappan settlements, indicating advanced planning. |
Card: 44 / 44 |