|
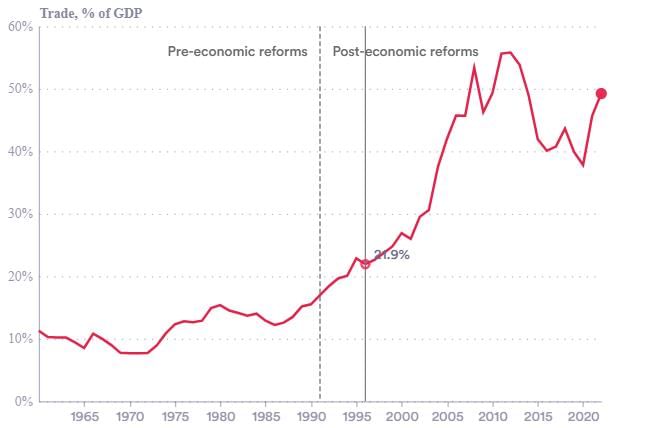
India's external trade grew from Rs. 1,214 crore in 1950-51 to Rs. 77,19,796 crore by 2020-21. True or False? |
Card: 1 / 50 |
|
True. This represents significant growth in India's international trade over the decades. |
Card: 2 / 50 |
|
India's trade expansion can be attributed to the acceleration of its ___ sectors, government liberalization policies, and diversification into new markets. |
Card: 3 / 50 |
|
What were the key drivers of India's international trade growth as outlined in the content? |
Card: 5 / 50 |
|
The key drivers included the acceleration of manufacturing sectors, government liberalization policies, and strategic diversification into new markets and product segments. |
Card: 6 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The historical growth of India's trade illustrates the country's integration into the ___ market. |
Card: 7 / 50 |
|
True or False: The chapter emphasizes that India's trade has become less significant in the context of global economic interdependencies. |
Card: 9 / 50 |
|
False. The chapter highlights India's trade as increasingly significant in global economic interdependencies. |
Card: 10 / 50 |
|
Short Answer: What is the significance of infrastructure development in the context of India's international trade? |
Card: 11 / 50 |
|
Infrastructure development facilitates smoother trade operations, enhances connectivity, and supports the growth of export and import activities.  |
Card: 12 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The percentage growth of India's external trade from 1950-51 to 2020-21 can be calculated to understand the extent of its ___ over time. |
Card: 13 / 50 |
|
Short Answer: How did liberalization policies impact India's international trade? |
Card: 15 / 50 |
|
Liberalization policies opened up the Indian economy, reduced trade barriers, and encouraged foreign investment, leading to increased trade activities. |
Card: 16 / 50 |
|
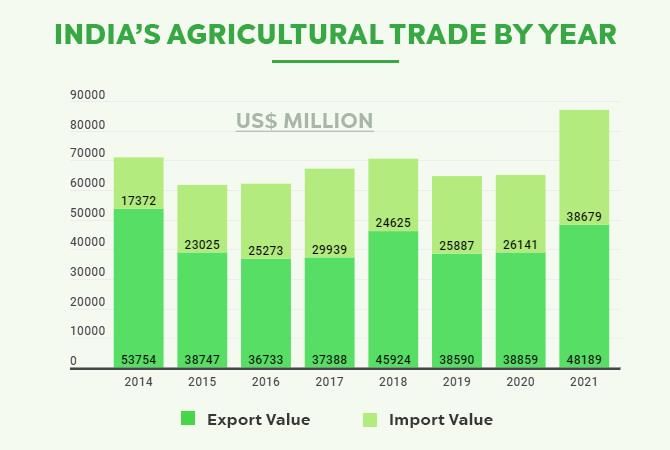
The share of agricultural and allied products in India's exports has seen a ___ in recent years. |
Card: 17 / 50 |
|
True or False: Manufactured goods and petroleum products have decreased in their contribution to India's exports. |
Card: 19 / 50 |
|
False. Manufactured goods and petroleum products have surged in their contribution. |
Card: 20 / 50 |
|
The shift in India's import structure after the 1973 oil crisis focused on the import of ___ and ___ due to increased domestic needs. |
Card: 21 / 50 |
|
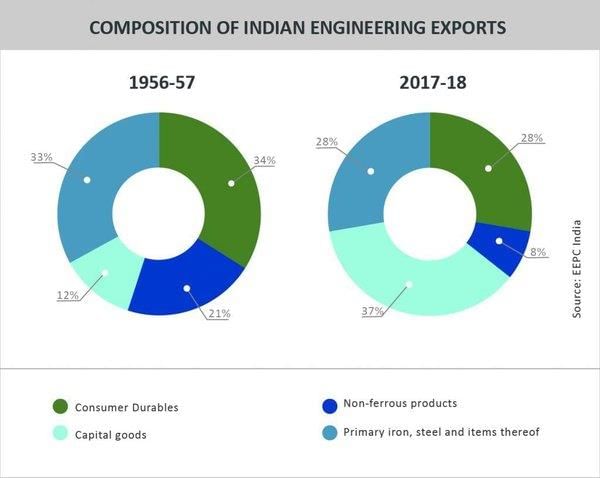
What has significantly contributed to the growth of India's engineering goods sector? |
Card: 23 / 50 |
|
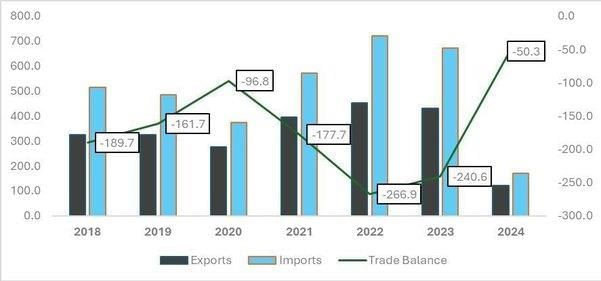
Fill in the blank: India's trade deficits over the years illustrate that imports have generally ___ exports. |
Card: 25 / 50 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: The success of the Green Revolution reduced India's reliance on food grain imports. |
Card: 27 / 50 |
|
Economic development and the need for high-value capital goods and electronic components. 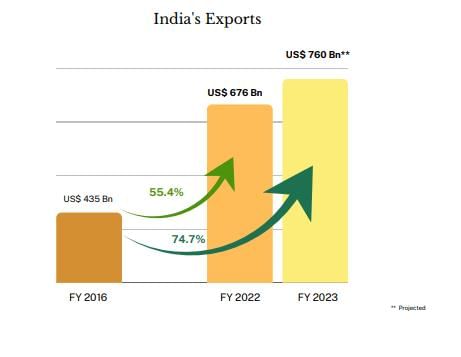 |
Card: 30 / 50 |
|
India's trade partnerships are influenced by changing geopolitical landscapes and policy reforms. True or False? |
Card: 31 / 50 |
|
True. India's trade partnerships reflect an integrated approach to global economics shaped by these factors. |
Card: 32 / 50 |
|
India's significant trade relationships include the United States, the European Union, and ___ regions. |
Card: 33 / 50 |
|
What are the main types of commodities traded by India with regions like Europe and North America? |
Card: 35 / 50 |
|
India trades a diverse range of commodities including technology products and consumer goods. 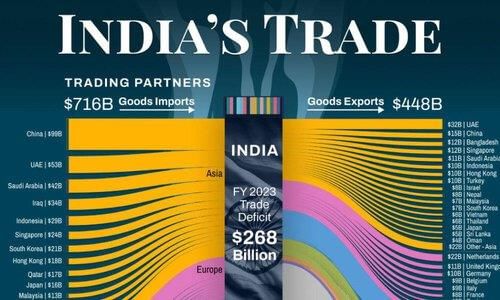 |
Card: 36 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: India's participation in agreements like SAFTA and the ASEAN Free Trade Area is crucial for understanding trade flows and ___ strategies. |
Card: 37 / 50 |
|
True or False: India aims to enhance its global trade share through policy liberalization and infrastructural upgrades. |
Card: 39 / 50 |
|
Trade agreements facilitate trade flows, reduce tariffs, and enhance economic cooperation with partner nations. |
Card: 42 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: Regional trade dynamics highlight the diversity of traded commodities, ranging from technology products to ___ goods. |
Card: 43 / 50 |
|
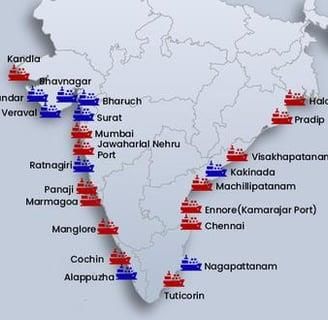
India has a total of ___ major ports and around ___ minor or intermediate ports. |
Card: 45 / 50 |
|
True or False: Mumbai Port is the largest port in India and serves as a crucial trade point with the Middle East. |
Card: 47 / 50 |
|
Fill in the blank: The partition in 1947 resulted in the loss of key ports like Karachi and Chittagong, leading to the development of ___ and ___ in India. |
Card: 49 / 50 |