|
Card: 1 / 40 |
The British Imperial history can be divided into two phases: the 'first empire' and the 'second empire'. True or False? |
|
Card: 2 / 40 |
True. The first empire focused on America and the West Indies, while the second empire began around 1783 and expanded into East Asia and Africa.  |
|
Card: 3 / 40 |
What year is often cited as the beginning of the British period in India due to the defeat of the Nawab of Bengal at Plassey? |
|
Card: 5 / 40 |
The Anglo-French struggle for supremacy in India began in the year ___, which some historians consider the start of the British period. |
|
Card: 8 / 40 |
It was a diplomatic strategy employed to extend British control over Indian territories by forming alliances that effectively made Indian rulers dependent on British forces for their protection.  |
|
Card: 9 / 40 |
The British success in India was largely attributed to their use of ___ arms and superior military strategy. |
|
Card: 11 / 40 |
True or False: The British military officers were selected based on hereditary ties rather than skills and reliability. |
|
Card: 12 / 40 |
False. The British military officers were selected based on their reliability and skill, not on hereditary ties. |
|
Card: 14 / 40 |
A regular system of payment of salaries and strict discipline ensured the loyalty of British troops.  |
|
Card: 15 / 40 |
What economic significance did Bengal hold in the Mughal Empire prior to British conquest? |
|
Card: 16 / 40 |
Bengal was the richest province of the Mughal Empire, exporting valuable raw products to Europe, including saltpetre, rice, indigo, pepper, sugar, silk, cotton textiles, and handicrafts.  |
|
Card: 17 / 40 |
True or False: The Battle of Plassey, fought on June 23, 1757, was a decisive victory for Siraj-ud-daula. |
|
Card: 18 / 40 |
False: The Battle of Plassey resulted in a decisive victory for the British, leading to the establishment of their control in Bengal.  |
|
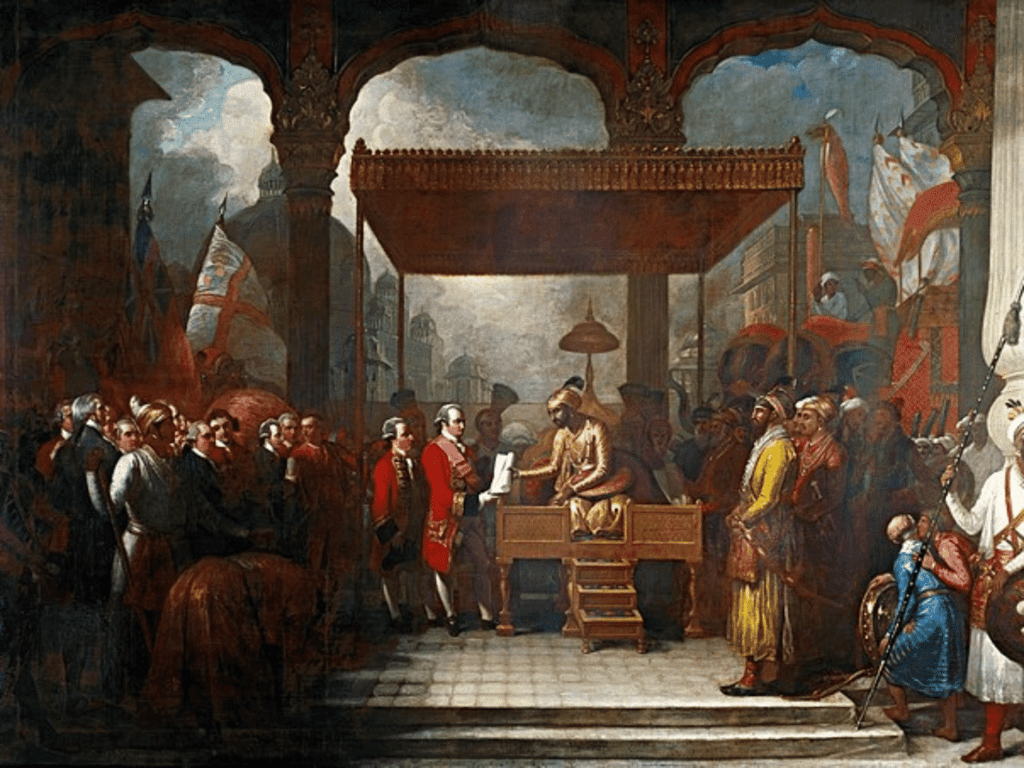
Card: 20 / 40 |
The Treaty of Allahabad resulted in the Nawab of Awadh surrendering Allahabad and Kara to Emperor Shah Alam II, payment of Rs. 50 lakh as war indemnity to the Company, and Shah Alam II granting the Diwani of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to the East India Company. |
|
Card: 21 / 40 |
Fill in the blank: The dual system of government introduced by Robert Clive in Bengal involved the rule of ___ and the ___ in which both revenue collection and judicial functions were controlled by the Company. |
|
Card: 23 / 40 |
The Battle of Buxar in 1764 established the English as a major power in northern India by defeating the combined forces of which three leaders? |