|
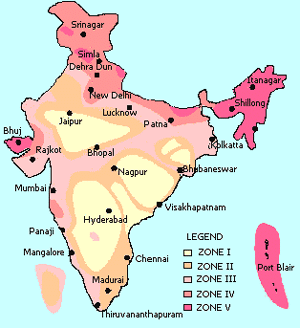
Disasters are events that occur due to forces largely beyond human control and lead to ___ and significant disruption of life. |
Card: 1 / 26 |
|
True or False: Historically, disasters were seen as primarily caused by human activities. |
Card: 3 / 26 |
|
Fill in the blank: Human activities can contribute to disasters, with one example being ___ resulting from deforestation. |
Card: 5 / 26 |
|
Fill in the blank: Disasters require efforts exceeding those typically provided by ___ services. |
Card: 9 / 26 |
|
True. Ocean currents are inherent characteristics of the environment that can pose risks. 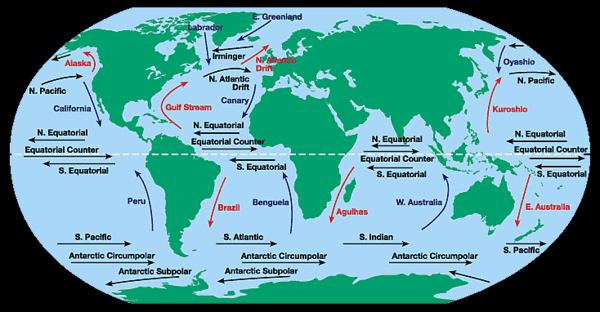 |
Card: 12 / 26 |
|
True or False: The advancement of technology has decreased human manipulation of natural environments. |
Card: 13 / 26 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False. The advancement of technology has empowered humans to manipulate nature to a significant extent.  |
Card: 14 / 26 |
|
The shift in understanding of natural hazards has led to a greater susceptibility to disasters in ___ zones. |
Card: 17 / 26 |
|
True or False: The Yokohama Strategy primarily focuses on developed nations and overlooks the needs of developing countries. |
Card: 19 / 26 |
|
False. The strategy emphasizes special focus on developing nations, particularly the least developed and land-locked countries. 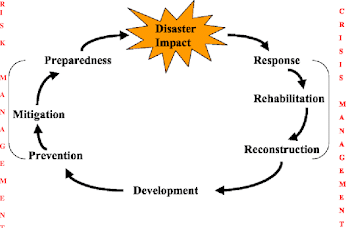 |
Card: 20 / 26 |
|
Fill in the blank: The decade 1990-2000 was designated as the ___ for Natural Disaster Reduction. |
Card: 21 / 26 |
|
They are involved in enhancing national capacities and legislation for disaster prevention, mitigation, and preparedness. |
Card: 24 / 26 |
|
What is one of the main objectives of the Yokohama Strategy regarding disaster management? |
Card: 25 / 26 |
|
To enhance national capacities and legislation for disaster prevention, mitigation, and preparedness. |
Card: 26 / 26 |