|
The Indian Independence Act came into effect on ___, marking the end of British rule. |
Card: 1 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The drafting committee of the Indian Constitution was formed on ___ and was chaired by ___ . |
Card: 5 / 48 |
|
The Preamble declares the fundamental principles and values of the Constitution, representing the will of the people of India and outlining the nation as a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic. |
Card: 8 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The original structure of the Constitution consisted of ___ articles, ___ parts, and ___ schedules. |
Card: 9 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Indian Constitution is the shortest written constitution in the world. |
Card: 11 / 48 |
|
False. The Indian Constitution is the most extensive and detailed constitution globally. |
Card: 12 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Constitution of India came into force on ___, which is celebrated as ___ . |
Card: 13 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Constitution allows Parliament to legislate on state matters only with the state legislature's consent. |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
False. Parliament can legislate on state matters under certain conditions, such as during a national emergency or if the Rajya Sabha passes a resolution. |
Card: 16 / 48 |
|
What is meant by the term 'quasi-federal' in the context of the Indian Constitution? |
Card: 17 / 48 |
|
It refers to a system that is primarily unitary but incorporates some federal features, reflecting a strong central government with subordinate provincial units. |
Card: 18 / 48 |
|
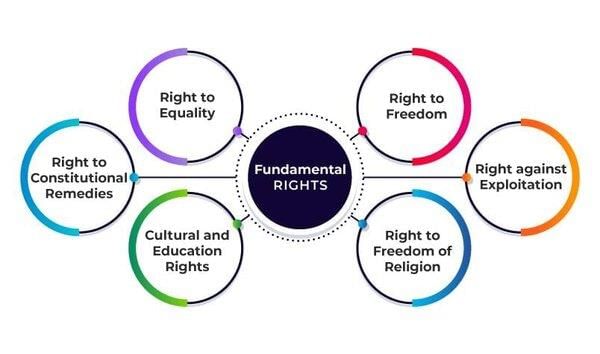
Fill in the blank: The fundamental rights are enshrined in Articles ___ to ___ of the Indian Constitution. |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
True or False: The fundamental rights can be suspended during a national emergency. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
They outline the socio-economic goals of the government and are meant to guide the state in making policies to promote the welfare of the people. |
Card: 24 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: The President of India has the authority to grant pardons for offenses against state laws. |
Card: 25 / 48 |
|
False. The President can grant pardons for offenses against Union laws, while Governors can grant pardons for state law offenses. |
Card: 26 / 48 |
|
It established the Basic Structure Doctrine, asserting that certain fundamental features of the Constitution cannot be amended by Parliament. |
Card: 28 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The procedure for amending the Constitution is laid out in Article ___ . |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
False. The Rajya Sabha is not subject to dissolution but one-third of its members retire every two years. |
Card: 32 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Supreme Court of India is the highest court of appeal and is established under Article ___. |
Card: 33 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Governor of a state has the same pardoning powers as the President of India. |
Card: 35 / 48 |
|
False. The Governor's powers are limited to state law offenses and do not include pardoning death sentences. |
Card: 36 / 48 |
|
The drafting committee was responsible for formulating the Constitution's text and structure, ensuring it reflected the principles and values necessary for governing India. |
Card: 38 / 48 |
|
What are the three types of emergencies provided for in the Indian Constitution? |
Card: 39 / 48 |
|
National Emergency, State Emergency (Failure of Constitutional Machinery), and Financial Emergency. |
Card: 40 / 48 |
|
True or False: The Indian Constitution allows for the creation of new states by Parliament without the need for a constitutional amendment. |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
What does the term 'judicial review' mean in the context of the Indian Constitution? |
Card: 43 / 48 |
|
Judicial review is the power of the Supreme Court to declare laws or executive actions unconstitutional if they violate fundamental rights or the Constitution. |
Card: 44 / 48 |