|
Fill in the blanks: The thermal expansion of solids can be classified into ___, ___, and ___. |
Card: 1 / 24 |
|
False. The coefficient of linear expansion is positive for most solids except for some materials like plastic, which have a negative coefficient. |
Card: 4 / 24 |
|
What is the relationship between the coefficient of linear expansion (α) and the coefficient of superficial expansion (β)? |
Card: 5 / 24 |
|
The relationship is given by β = 2α, meaning that the coefficient of superficial expansion is twice that of linear expansion. |
Card: 6 / 24 |
|
When a solid is heated, its density typically decreases because its volume increases due to thermal expansion while its mass remains constant. |
Card: 8 / 24 |
|
The formula is Q = m × s ×Δθ, where Q is the heat supplied, m is the mass, and Δθ is the change in temperature. |
Card: 10 / 24 |
|
Stefan's Law states that the amount of energy radiated per unit area per second is directly proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature (E ∝ T⁴). |
Card: 12 / 24 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Fill in the blank: The amount of radiant energy emitted per second from a unit area of a radiating surface is called ___ power. |
Card: 13 / 24 |
|
What happens to the energy distribution of black body radiation as the temperature increases? |
Card: 15 / 24 |
|
As the temperature increases, the total energy emitted by a black body increases and shifts towards shorter wavelengths. |
Card: 16 / 24 |
|
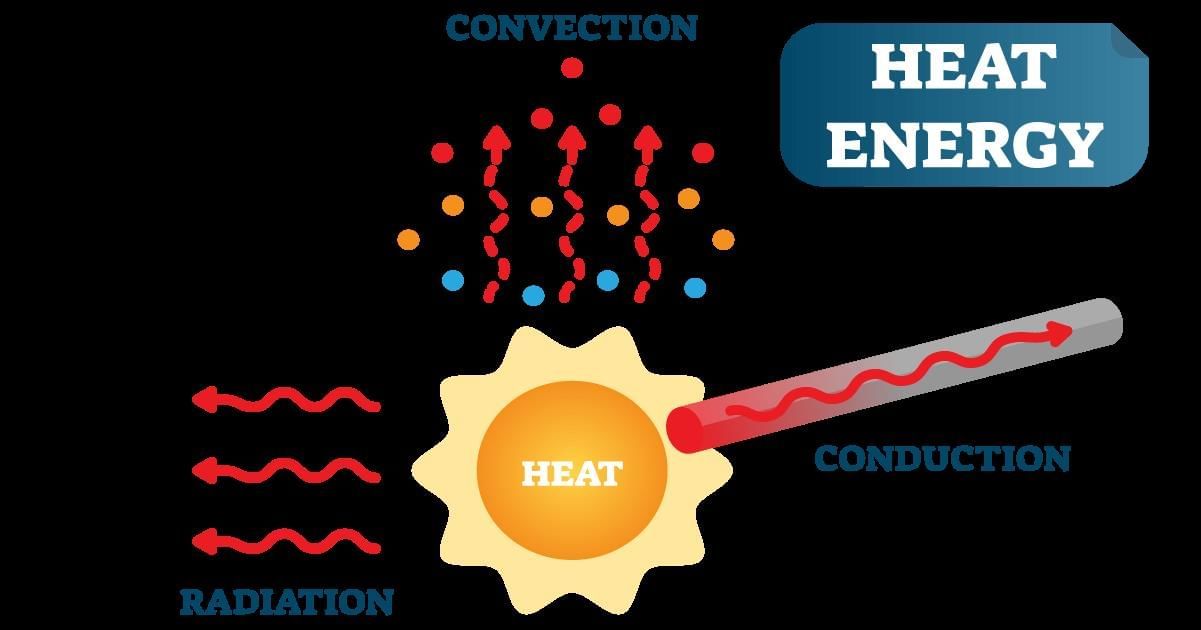
Fill in the blank: The process in which heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves is called ___. |
Card: 17 / 24 |
|
If the length of a rod at 0°C is ℓ₀, what is its length at T°C given the coefficient of linear expansion α? |
Card: 19 / 24 |
|
Water above 4 °C sinks; below 4 °C becomes less dense, stays on top and freezes. |
Card: 22 / 24 |