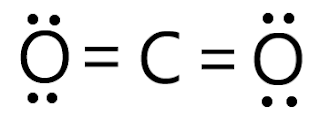|
A chemical bond is the force that holds atoms together in a molecule or compound. |
Card: 2 / 38 |
|
Chemical bonding is explained using different models, including the Kössel-Lewis theory, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory, Valence Bond (VB) theory, and Molecular Orbital (MO) theory. |
Card: 4 / 38 |
|
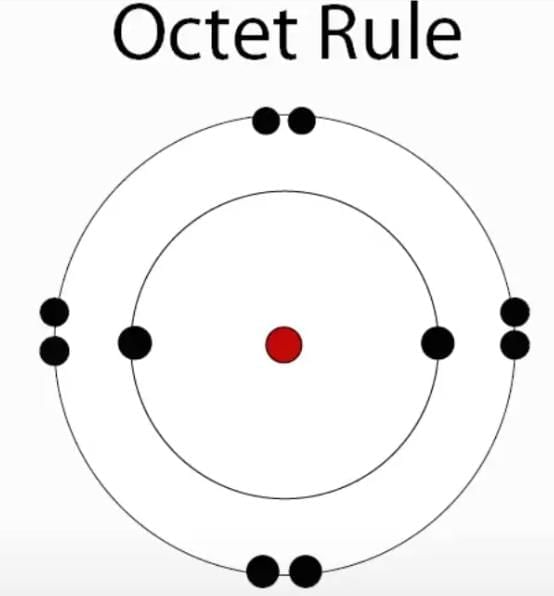
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve eight valence electrons, similar to noble gases. |
Card: 6 / 38 |
|
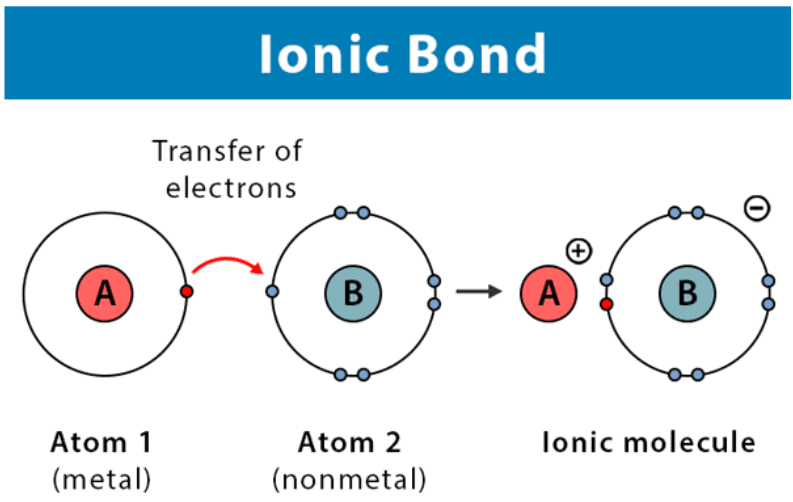
An ionic bond is formed when one atom transfers electrons to another, resulting in positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. |
Card: 8 / 38 |
|
A covalent bond occurs when two atoms share electrons instead of transferring them, as seen in molecules like H2 or O2. |
Card: 10 / 38 |
|
In a coordinate bond, both shared electrons originate from the same atom, whereas in a covalent bond, each atom donates an electron to the bond. |
Card: 12 / 38 |
|
Lewis symbols are a way to represent valence electrons around an atom using dots. |
Card: 14 / 38 |
|
CO2 is represented as O=C=O, where carbon forms two double bonds with oxygen atoms.
|
Card: 16 / 38 |
|
Bond length is the fixed distance between the nuclei of two atoms connected by a bond. |
Card: 18 / 38 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
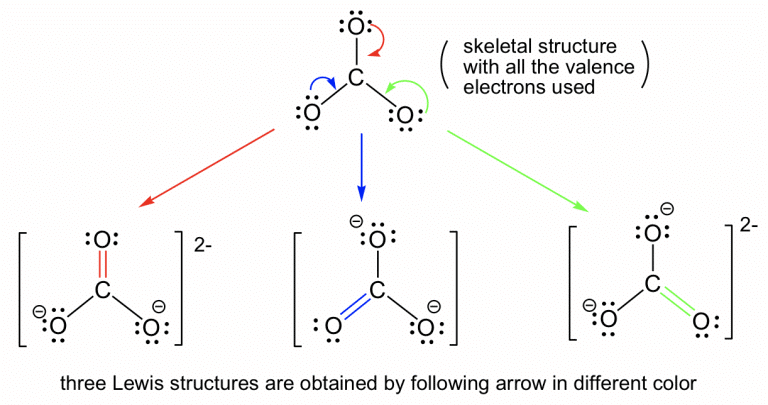
Resonance occurs when multiple Lewis structures are required to describe a molecule accurately. |
Card: 20 / 38 |
|
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new, equivalent orbitals for bonding. |
Card: 22 / 38 |
|
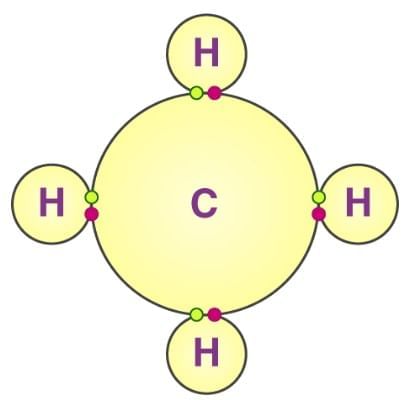
In methane (CH4), carbon undergoes sp3 hybridization to form four equivalent bonds. |
Card: 24 / 38 |
|
The two lone pairs on oxygen repel the bonding pairs, pushing them closer together. |
Card: 28 / 38 |
|
It suggests that atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals, which can be bonding or antibonding. |
Card: 30 / 38 |
|
Hydrogen bonding is an attractive force between hydrogen and highly electronegative elements like O, N, or F (e.g., in water, H2O). |
Card: 34 / 38 |
|
In NH3, the lone pair dipole aligns with the bond dipoles, reinforcing the dipole moment. In NF3, the lone pair dipole opposes the bond dipoles, reducing the overall dipole moment. |
Card: 38 / 38 |