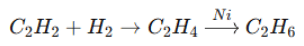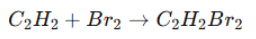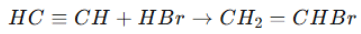|
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms. They form the basis of fuels like LPG, CNG, petrol, diesel, and coal gas and are also used in manufacturing polymers, dyes, and drugs. |
Card: 2 / 30 |
|
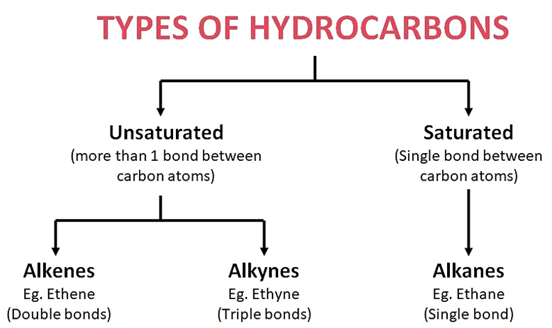
Hydrocarbons are classified based on carbon-carbon bonding:
|
Card: 4 / 30 |
|
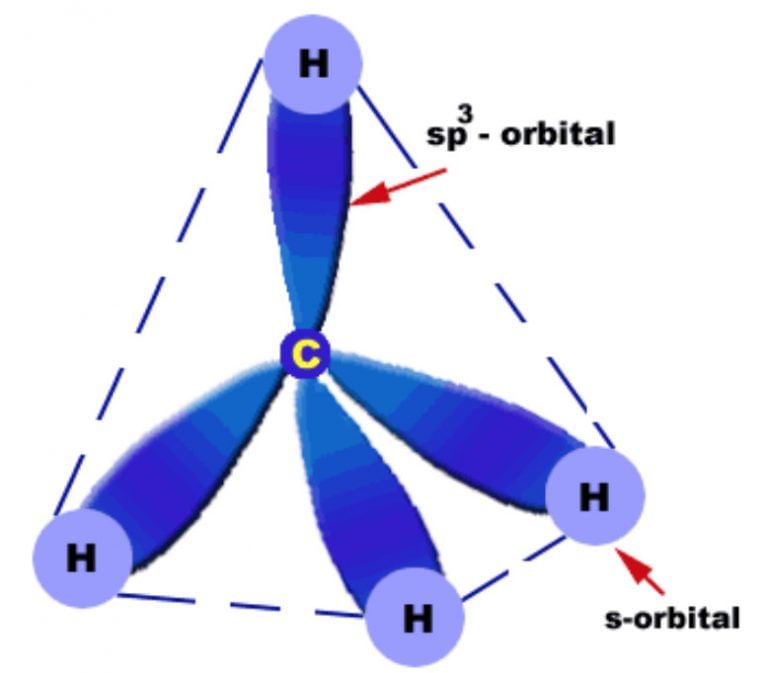
Alkanes have a tetrahedral geometry with a bond angle of 109.5°. The C-C and C-H bonds are σ (sigma) bonds formed by sp3 hybridization. |
Card: 8 / 30 |
|
Card: 10 / 30 |
|
Halogenation (Substitution reaction):
Combustion:
Pyrolysis (Cracking):
|
Card: 12 / 30 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Trigonal planar geometry, bond angle 120°. Double bond consists of:
|
Card: 16 / 30 |
|
Non-polar molecules with low boiling points. Slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents. |
Card: 18 / 30 |
|
Addition Reactions (Electrophilic Addition):
Oxidation Reactions:
Ozonolysis:
|
Card: 20 / 30 |
|
Linear geometry, bond angle 180°. Triple bond consists of:
|
Card: 24 / 30 |
|
1. Hydrogenation (Formation of alkenes and alkanes): 2. Electrophilic Addition:
3. Tautomerization (Formation of aldehydes and ketones from alkynes). |
Card: 26 / 30 |
|
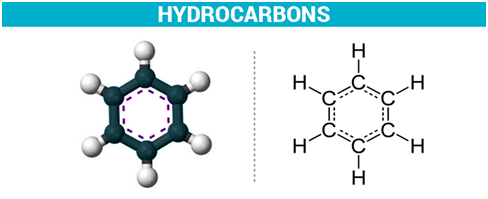
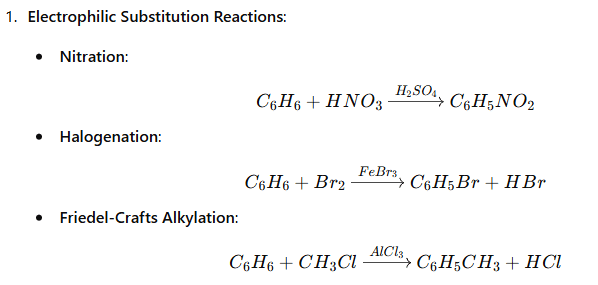
A compound is aromatic if it satisfies Hückel’s Rule: (4n+2)π-electrons where n is a whole number (n = 0, 1, 2, …). Example: Benzene (C6H6) has 6 π-electrons and is aromatic. |
Card: 28 / 30 |