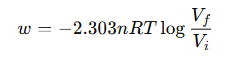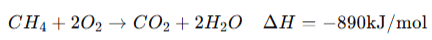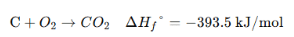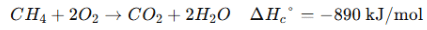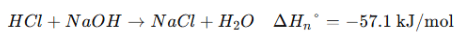|
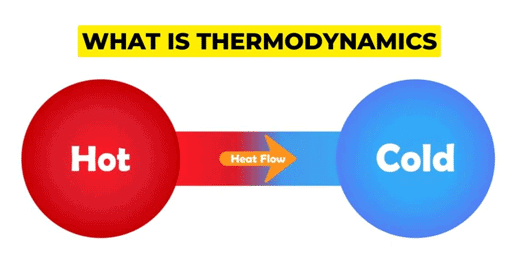
Thermodynamics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of energy changes during chemical and physical processes. It focuses on macroscopic properties like temperature, pressure, volume, and internal energy, and how they influence the energy transformations of a system. |
Card: 2 / 38 |
|
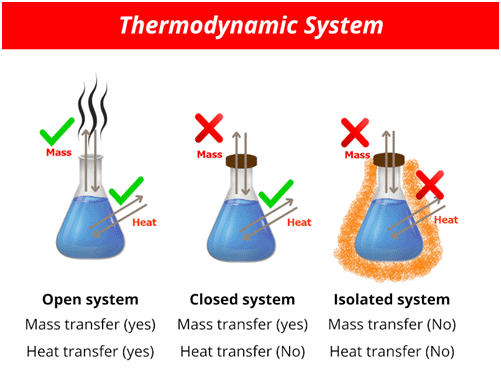
A thermodynamic system is the part of the universe under study, while the rest of the universe is called the surroundings. |
Card: 4 / 38 |
|
Card: 6 / 38 |
|
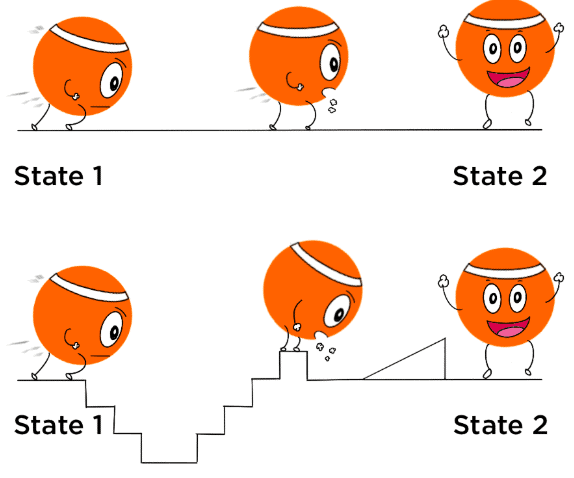
State functions depend only on the initial and final states of a system and not on the path taken. Examples: Internal energy (U), Enthalpy (H), Entropy (S), Gibbs Free Energy (G), Pressure (P), Volume (V), Temperature (T). |
Card: 8 / 38 |
|
Card: 10 / 38 |
|
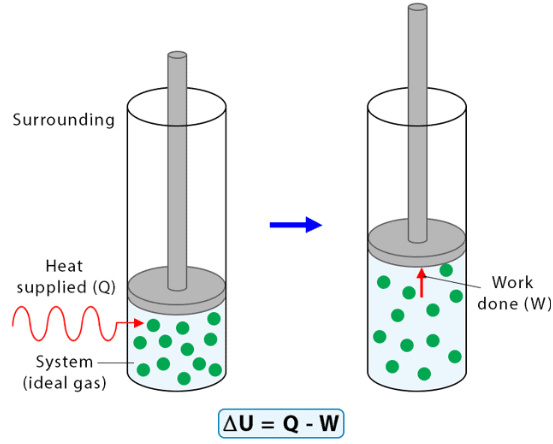
Work done in a pressure-volume process is given by: W = −PextΔV where:
For reversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas:
|
Card: 12 / 38 |
|
Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system. It is defined as: H=U+PV where:
|
Card: 14 / 38 |
|
At constant pressure, the change in enthalpy is: ΔH = ΔU+PΔV where ΔH is heat absorbed/released at constant pressure. |
Card: 16 / 38 |
|
Heat capacity (C) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1°C (or 1K).
|
Card: 18 / 38 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
A thermochemical equation is a balanced chemical equation that includes the enthalpy change (ΔH). |
Card: 22 / 38 |
|
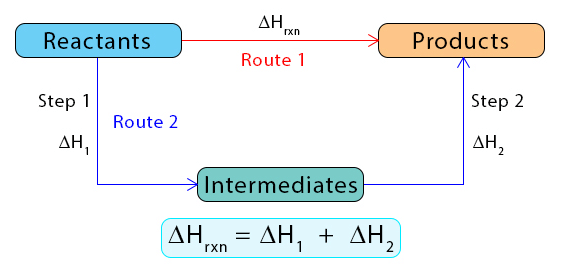
Hess’s Law states that the total enthalpy change in a reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or multiple steps. |
Card: 24 / 38 |
|
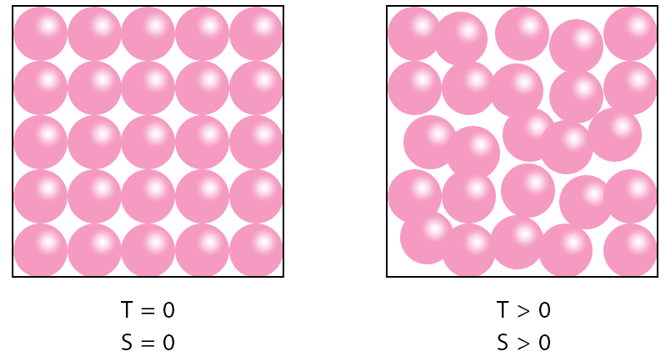
Entropy (S) is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system. Higher entropy means greater disorder. |
Card: 26 / 38 |
|
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of the universe always increases in a spontaneous process. |
Card: 28 / 38 |
|
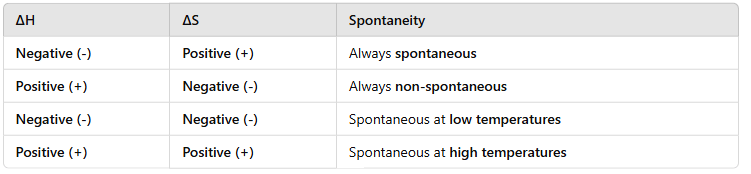
Gibbs Free Energy (G) predicts the spontaneity of a reaction.
|
Card: 30 / 38 |
|
1. Enthalpy of Formation (ΔH⁰_f) → Heat change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states. 2. Enthalpy of Combustion (ΔH⁰_c) → Heat released when 1 mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen. 3. Enthalpy of Neutralization (ΔH⁰_n) → Heat released when 1 mole of H⁺ reacts with 1 mole of OH⁻ to form water. |
Card: 32 / 38 |
|
Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and the equilibrium constant (K) are related by the equation: ΔG °= −RTlnK where:
|
Card: 34 / 38 |
|
The Third Law of Thermodynamics states that the entropy of a perfect crystalline substance at absolute zero (0 K) is zero. Mathematically,
This means that at absolute zero temperature, all molecular motion ceases, and the system is in a perfectly ordered state. |
Card: 36 / 38 |