|
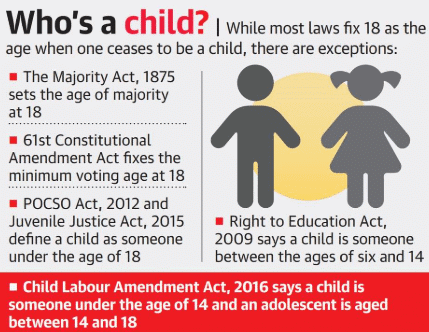
True or False: The legal age of adulthood in India, as per the Indian Majority Act, 1875, is 18 years. |
Card: 3 / 30 |
|
The rights-based perspective on child welfare emerged in the ___ century, moving away from a welfare-centric approach. |
Card: 5 / 30 |
|
Fill in the blank: The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child was ratified by India in ___, granting children basic human rights. |
Card: 7 / 30 |
|
The Constitution of India guarantees the right to education through which article? |
Card: 9 / 30 |
|
True or False: The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act mandates that all children aged six to fourteen must pay for their education. |
Card: 11 / 30 |
|
False. The Act mandates free and compulsory education for all children aged six to fourteen years. |
Card: 12 / 30 |
|
True or False: The state is not responsible for ensuring the health and well-being of its citizens. |
Card: 15 / 30 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
False. The state is constitutionally obligated to safeguard the health and well-being of its citizens. |
Card: 16 / 30 |
|
True or False: The right to shelter includes access to basic amenities such as water and sanitation. |
Card: 19 / 30 |
|
Child labour refers to children being made to work, involving factors such as ___, ___, ___, and ___. |
Card: 21 / 30 |
|
True or False: The Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act of 1986 allows children under 14 years to work in hazardous occupations. |
Card: 23 / 30 |
|
False. The Act prohibits child employment under 14 years in hazardous occupations. |
Card: 24 / 30 |
|
The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 (POCSO Act) addresses ___ and ___ related to child sexual abuse. |
Card: 25 / 30 |
|
False. A person under 18 years may also commit sexual abuse due to incapacity to give consent. |
Card: 28 / 30 |
|
The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 emphasizes a ___ approach towards children in conflict with the law. |
Card: 29 / 30 |