|
True or False: Islamic law was relevant in India before the advent of the Mughal Empire. |
Card: 3 / 32 |
|
False. Islamic law became relevant during the medieval period with the Mughal Empire. |
Card: 4 / 32 |
|
The court systems under the Mauryas and Mughals were essential for ___ and ___ matters. |
Card: 5 / 32 |
|
What significant transition occurred in the court systems of India during British rule? |
Card: 7 / 32 |
|
British courts replaced the Mughal court systems that had been prevalent in India. |
Card: 8 / 32 |
|
Hindu law can be primarily divided into three categories: Classical Hindu Law, Anglo-Hindu Law, and ___ Hindu Law. |
Card: 9 / 32 |
|
True or False: The Anglo-Hindu Law was established during the British rule and replaced all existing Indian laws. |
Card: 11 / 32 |
|
False. While Anglo-Hindu Law was established during the British rule, it did not replace family or personal laws related to marriage, inheritance, and succession of property. |
Card: 12 / 32 |
|
Classical Hindu Law covers the legal practices connected with Vedic traditions from ancient Vedic times until 1772. |
Card: 14 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blank: The British adopted rules for administration of justice in Bengal in the year ___. |
Card: 15 / 32 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
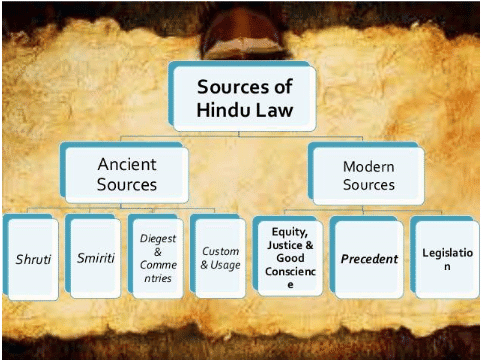
True or False: The Vedas are considered the second source of Dharma in Hindu law. |
Card: 19 / 32 |
|
The term 'Dharmashastra' refers to texts that provide rules for the life of an ideal ___. |
Card: 21 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blank: The third source of Dharma is referred to as ___, which means customary law. |
Card: 23 / 32 |
|
True or False: The British legal system in India began to replace the Mughal court systems in the late 18th century. |
Card: 27 / 32 |
|
Islamic law in India primarily addresses issues related to ___, inheritance, and personal law matters. |
Card: 29 / 32 |
|
The Mughal Empire introduced judicial systems in India during the ___ century AD. |
Card: 31 / 32 |