Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Explain classification of organic compounds?
Start Learning for Free
Explain classification of organic compounds?
Verified Answer
Explain classification of organic compounds?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain classification of organic compounds?
Classification of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other atoms, typically hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or halogens. These compounds are diverse and can be classified based on various factors such as functional groups, structure, and properties.
Functional Group Classification
One common way to classify organic compounds is by their functional groups. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that determine the compound's chemical behavior and reactivity. Some common functional groups include:
1. Alkanes: Alkanes are hydrocarbons that consist of only carbon-carbon single bonds. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 and are often referred to as saturated hydrocarbons.
2. Alkenes: Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n.
3. Alkynes: Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. The general formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2.
4. Alcohols: Alcohols are compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group bonded to a carbon atom. The general formula for alcohols is R-OH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
5. Aldehydes: Aldehydes are compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The general formula for aldehydes is R-CHO, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
6. Ketones: Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula for ketones is R-CO-R', where R and R' represent alkyl or aryl groups.
7. Carboxylic Acids: Carboxylic acids are compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). The general formula for carboxylic acids is R-COOH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
8. Esters: Esters are compounds that contain an ester functional group (-COO-) where one oxygen is bonded to a carbon atom and the other oxygen is bonded to an alkyl or aryl group. The general formula for esters is R-COO-R', where R and R' represent alkyl or aryl groups.
Structural Classification
Organic compounds can also be classified based on their structural characteristics, such as the arrangement and connectivity of atoms. Some common structural classifications include:
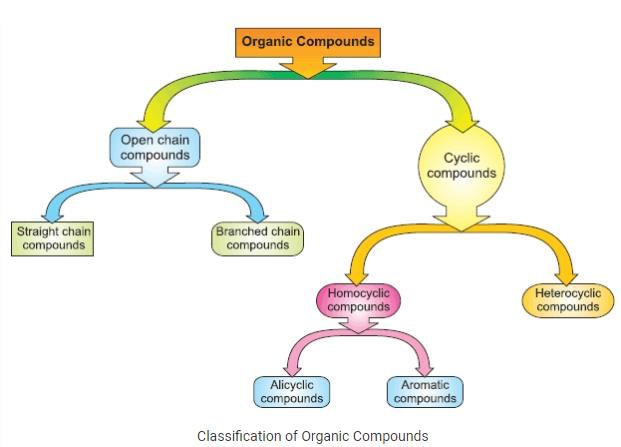
1. Acyclic compounds: Acyclic compounds are open-chain compounds that do not form a ring structure.
2. Cyclic compounds: Cyclic compounds are compounds that contain a ring structure.
3. Homocyclic compounds: Homocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds in which all the atoms in the ring are of the same element, typically carbon.
4. Heterocyclic compounds: Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds in which the ring contains atoms of different elements
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other atoms, typically hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or halogens. These compounds are diverse and can be classified based on various factors such as functional groups, structure, and properties.
Functional Group Classification
One common way to classify organic compounds is by their functional groups. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that determine the compound's chemical behavior and reactivity. Some common functional groups include:
1. Alkanes: Alkanes are hydrocarbons that consist of only carbon-carbon single bonds. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 and are often referred to as saturated hydrocarbons.
2. Alkenes: Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n.
3. Alkynes: Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. The general formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2.
4. Alcohols: Alcohols are compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group bonded to a carbon atom. The general formula for alcohols is R-OH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
5. Aldehydes: Aldehydes are compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The general formula for aldehydes is R-CHO, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
6. Ketones: Ketones are compounds that contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula for ketones is R-CO-R', where R and R' represent alkyl or aryl groups.
7. Carboxylic Acids: Carboxylic acids are compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). The general formula for carboxylic acids is R-COOH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
8. Esters: Esters are compounds that contain an ester functional group (-COO-) where one oxygen is bonded to a carbon atom and the other oxygen is bonded to an alkyl or aryl group. The general formula for esters is R-COO-R', where R and R' represent alkyl or aryl groups.
Structural Classification
Organic compounds can also be classified based on their structural characteristics, such as the arrangement and connectivity of atoms. Some common structural classifications include:
1. Acyclic compounds: Acyclic compounds are open-chain compounds that do not form a ring structure.
2. Cyclic compounds: Cyclic compounds are compounds that contain a ring structure.
3. Homocyclic compounds: Homocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds in which all the atoms in the ring are of the same element, typically carbon.
4. Heterocyclic compounds: Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds in which the ring contains atoms of different elements
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Explain classification of organic compounds?
Question Description
Explain classification of organic compounds? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain classification of organic compounds? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain classification of organic compounds?.
Explain classification of organic compounds? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain classification of organic compounds? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain classification of organic compounds?.
Solutions for Explain classification of organic compounds? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain classification of organic compounds? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain classification of organic compounds?, a detailed solution for Explain classification of organic compounds? has been provided alongside types of Explain classification of organic compounds? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain classification of organic compounds? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























