JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H1...
Start Learning for Free
Passage I
An alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).
Q. The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?
- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in...
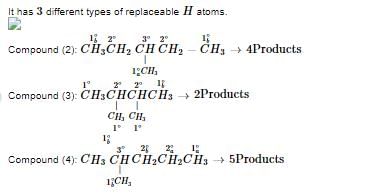
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in...
Explanation:
The passage describes a series of reactions involving an alkane (A) and the products derived from it. We are given that the alkane reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C), and (D).
Step 1: Formation of Monochloro Derivatives (B), (C), and (D)
- The alkane (A) reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C), and (D).
Step 2: Dehydrohalogenation of (C) and (D)
- Only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene.
- Moreover, (C) and (D) yield the same alkene (E) (C6H12).
Step 3: Hydrogenation of (E)
- Hydrogenation of the alkene (E) produces the original alkane (A).
Step 4: Treatment of (E) with HCI
- Treating the alkene (E) with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C), and (D).
Step 5: Treatment of (F) with Zn and acetic acid
- Treating the compound (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with the original alkane (A).
Number of Monochloro Derivatives of (G)
- The passage does not explicitly mention the number of monochloro derivatives obtained from (G) when it reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light. However, since (G) is isomeric with (A), it is reasonable to assume that (G) will also yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives, just like (A).
Therefore, the compound (G) reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three isomers as monochloro derivatives.
Hence, the correct answer is option (c) 3.
The passage describes a series of reactions involving an alkane (A) and the products derived from it. We are given that the alkane reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C), and (D).
Step 1: Formation of Monochloro Derivatives (B), (C), and (D)
- The alkane (A) reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C), and (D).
Step 2: Dehydrohalogenation of (C) and (D)
- Only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene.
- Moreover, (C) and (D) yield the same alkene (E) (C6H12).
Step 3: Hydrogenation of (E)
- Hydrogenation of the alkene (E) produces the original alkane (A).
Step 4: Treatment of (E) with HCI
- Treating the alkene (E) with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C), and (D).
Step 5: Treatment of (F) with Zn and acetic acid
- Treating the compound (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with the original alkane (A).
Number of Monochloro Derivatives of (G)
- The passage does not explicitly mention the number of monochloro derivatives obtained from (G) when it reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light. However, since (G) is isomeric with (A), it is reasonable to assume that (G) will also yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives, just like (A).
Therefore, the compound (G) reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three isomers as monochloro derivatives.
Hence, the correct answer is option (c) 3.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Passage IAn alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).Q.The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?a)1b)2c)3d)4Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























