Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > What is the difference between cooperative so...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu bus...
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu bus...
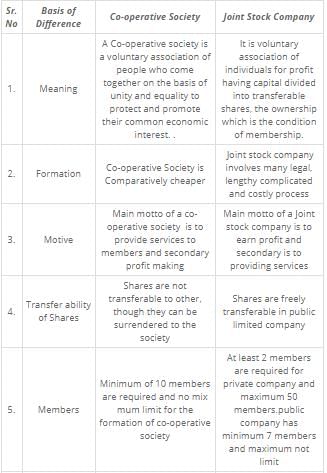
Difference between Cooperative Society and Joint Hindu Business
Introduction:
Both cooperative societies and joint Hindu businesses are forms of business organizations that serve specific purposes and have distinct features. While cooperative societies are formed by individuals voluntarily coming together to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs, joint Hindu businesses are based on the principles of Hindu law and are formed by members of the Hindu community for carrying on joint business activities.
1. Formation:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are formed by a group of individuals who voluntarily associate themselves for a common objective, such as production, distribution, or consumption of goods or services. They are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act and function on the principle of mutual assistance and cooperation.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses, on the other hand, are formed by members of the Hindu community who come together to carry on a joint business venture. These businesses are governed by Hindu law and do not require any formal registration.
2. Members:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies can have members from any community or religion. Membership is open to all individuals who are willing to contribute to and benefit from the cooperative's activities.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are specifically formed by members of the Hindu community. Membership is restricted to Hindus only, and non-Hindus cannot become members of such businesses.
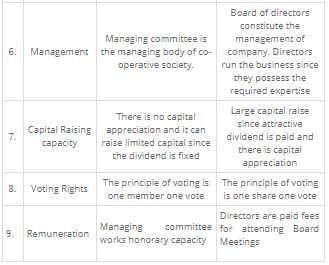
3. Liability:
- Cooperative Society: The liability of members in a cooperative society is usually limited to the extent of their share capital or the guarantee provided by them during the formation of the society.
- Joint Hindu Business: In a joint Hindu business, the liability of the members is unlimited. Each member is personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business.
4. Management and Control:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are democratically managed and controlled by their members. The members elect a board of directors or committee to oversee the operations and decision-making of the society.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are generally managed by the eldest member or a designated manager from the family. The control and decision-making power lie with the managing members of the business.
5. Purpose and Objectives:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are formed to promote the economic and social interests of their members. They aim to provide benefits, services, and support to their members while ensuring equitable distribution of resources.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are primarily formed for carrying on business activities and generating profits. The purpose is usually to support the livelihood and financial well-being of the Hindu joint family.
Conclusion:
In summary, cooperative societies and joint Hindu businesses differ in terms of their formation, membership, liability, management, and objectives. Cooperative societies are open to individuals from all communities and are formed for mutual assistance, while joint Hindu businesses are limited to Hindu members and are based on Hindu law. Understanding these differences can help individuals choose the most suitable form of business organization based on their specific needs and objectives.
Introduction:
Both cooperative societies and joint Hindu businesses are forms of business organizations that serve specific purposes and have distinct features. While cooperative societies are formed by individuals voluntarily coming together to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs, joint Hindu businesses are based on the principles of Hindu law and are formed by members of the Hindu community for carrying on joint business activities.
1. Formation:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are formed by a group of individuals who voluntarily associate themselves for a common objective, such as production, distribution, or consumption of goods or services. They are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act and function on the principle of mutual assistance and cooperation.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses, on the other hand, are formed by members of the Hindu community who come together to carry on a joint business venture. These businesses are governed by Hindu law and do not require any formal registration.
2. Members:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies can have members from any community or religion. Membership is open to all individuals who are willing to contribute to and benefit from the cooperative's activities.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are specifically formed by members of the Hindu community. Membership is restricted to Hindus only, and non-Hindus cannot become members of such businesses.
3. Liability:
- Cooperative Society: The liability of members in a cooperative society is usually limited to the extent of their share capital or the guarantee provided by them during the formation of the society.
- Joint Hindu Business: In a joint Hindu business, the liability of the members is unlimited. Each member is personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business.
4. Management and Control:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are democratically managed and controlled by their members. The members elect a board of directors or committee to oversee the operations and decision-making of the society.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are generally managed by the eldest member or a designated manager from the family. The control and decision-making power lie with the managing members of the business.
5. Purpose and Objectives:
- Cooperative Society: Cooperative societies are formed to promote the economic and social interests of their members. They aim to provide benefits, services, and support to their members while ensuring equitable distribution of resources.
- Joint Hindu Business: Joint Hindu businesses are primarily formed for carrying on business activities and generating profits. The purpose is usually to support the livelihood and financial well-being of the Hindu joint family.
Conclusion:
In summary, cooperative societies and joint Hindu businesses differ in terms of their formation, membership, liability, management, and objectives. Cooperative societies are open to individuals from all communities and are formed for mutual assistance, while joint Hindu businesses are limited to Hindu members and are based on Hindu law. Understanding these differences can help individuals choose the most suitable form of business organization based on their specific needs and objectives.
Attention Commerce Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Commerce study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Commerce.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Similar Commerce Doubts
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business?
Question Description
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business?.
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business?.
Solutions for What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between cooperative society and joint Hindu business? tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























