JEE Exam > JEE Questions > 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorime...
Start Learning for Free
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed?
Verified Answer
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 1...
Ans.
Method to Solve :
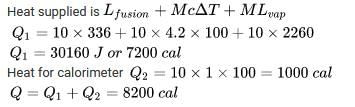
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 1...
Introduction:
To calculate the amount of heat required to evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius, we need to consider the heat transfer involved in the process. The heat transfer occurs in two steps: first, the ice is heated to its melting point, and secondly, the water is heated to its boiling point and then evaporated.
Step 1: Heating the ice to its melting point:
To heat the ice from 0 degrees Celsius to its melting point, we need to calculate the heat required using the formula:
Q = mcΔT
where Q is the heat required, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
In this case, the mass of the ice is 10 gm and the specific heat capacity of ice is approximately 2.09 J/g°C. The change in temperature is the difference between the melting point of ice (0 degrees Celsius) and the initial temperature (also 0 degrees Celsius), which is 0°C.
Using the formula, we can calculate the heat required to heat the ice to its melting point:
Q1 = (10 gm) * (2.09 J/g°C) * (0°C - 0°C) = 0 J
Therefore, no heat is required to heat the ice from 0 degrees Celsius to its melting point since the temperature remains constant during this phase change.
Step 2: Heating the water to its boiling point and evaporating:
To heat the water to its boiling point and evaporate it, we need to calculate the heat required using the formula:
Q = mcΔT
where Q is the heat required, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
In this case, the mass of the water formed is also 10 gm (since the ice and water have the same mass) and the specific heat capacity of water is approximately 4.18 J/g°C. The change in temperature is the difference between the boiling point of water (100 degrees Celsius) and the initial temperature (0 degrees Celsius), which is 100°C.
Using the formula, we can calculate the heat required to heat the water to its boiling point and evaporate it:
Q2 = (10 gm) * (4.18 J/g°C) * (100°C - 0°C) = 4180 J
Therefore, the amount of heat required to evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius is 4180 J.
Conclusion:
To evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius, a total of 4180 J of heat needs to be supplied to the apparatus. This heat is required to heat the water to its boiling point and then provide the energy necessary for the phase change from liquid to gas.
To calculate the amount of heat required to evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius, we need to consider the heat transfer involved in the process. The heat transfer occurs in two steps: first, the ice is heated to its melting point, and secondly, the water is heated to its boiling point and then evaporated.
Step 1: Heating the ice to its melting point:
To heat the ice from 0 degrees Celsius to its melting point, we need to calculate the heat required using the formula:
Q = mcΔT
where Q is the heat required, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
In this case, the mass of the ice is 10 gm and the specific heat capacity of ice is approximately 2.09 J/g°C. The change in temperature is the difference between the melting point of ice (0 degrees Celsius) and the initial temperature (also 0 degrees Celsius), which is 0°C.
Using the formula, we can calculate the heat required to heat the ice to its melting point:
Q1 = (10 gm) * (2.09 J/g°C) * (0°C - 0°C) = 0 J
Therefore, no heat is required to heat the ice from 0 degrees Celsius to its melting point since the temperature remains constant during this phase change.
Step 2: Heating the water to its boiling point and evaporating:
To heat the water to its boiling point and evaporate it, we need to calculate the heat required using the formula:
Q = mcΔT
where Q is the heat required, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
In this case, the mass of the water formed is also 10 gm (since the ice and water have the same mass) and the specific heat capacity of water is approximately 4.18 J/g°C. The change in temperature is the difference between the boiling point of water (100 degrees Celsius) and the initial temperature (0 degrees Celsius), which is 100°C.
Using the formula, we can calculate the heat required to heat the water to its boiling point and evaporate it:
Q2 = (10 gm) * (4.18 J/g°C) * (100°C - 0°C) = 4180 J
Therefore, the amount of heat required to evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius is 4180 J.
Conclusion:
To evaporate the water formed from 10 gm of ice at 0 degrees Celsius, a total of 4180 J of heat needs to be supplied to the apparatus. This heat is required to heat the water to its boiling point and then provide the energy necessary for the phase change from liquid to gas.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed?
Question Description
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed?.
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed?.
Solutions for 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed?, a detailed solution for 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? has been provided alongside types of 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice 10 gm ice at 0 degree C is kept in a calorimeter of water equivalent 10 gm . How much heat should be supplied to the apparatus to evaporate the water thus formed? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























