Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > what is the difference between mass and weigh...
Start Learning for Free
what is the difference between mass and weight
Verified Answer
what is the difference between mass and weight
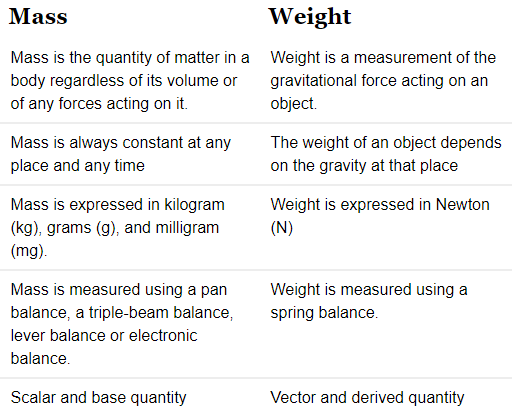
Mass is the amount of matter present in a body while weight is a measure of how strongly gravity pulls on that matter. Mass is an intrinsic property of the body and remains the same wherever the body might be. Weight is a force, and force is (Mass * Acceleration). The weight of an object is its mass times the acceleration due to gravity. The weight of the body differs by place. For example, objects weigh less on the moon where gravity is lower compared to the Earth.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is the difference between mass and weight
Mass and weight are two fundamental concepts in physics that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and properties. Understanding the difference between mass and weight is crucial in order to grasp various scientific principles and phenomena.
Mass:
- Mass is a fundamental property of matter that quantifies the amount of matter present in an object. It is an intrinsic property and is independent of external factors.
- Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g) and is a scalar quantity. It represents the inertia of an object, which is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion.
- The mass of an object remains constant regardless of its location in the universe. For instance, an object on Earth would have the same mass if it were on the Moon or any other celestial body.
- Mass can be determined by using a balance or a scale, comparing the object's mass to a known reference mass.
Weight:
- Weight, on the other hand, is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. It is a vector quantity and is measured in newtons (N).
- Weight depends on both the mass of an object and the gravitational acceleration of the planet or celestial body it is on. The weight of an object can vary depending on its location in the universe.
- The weight of an object can be calculated using the formula: weight = mass × gravitational acceleration. On Earth, the standard gravitational acceleration is approximately 9.8 m/s^2.
- Weight is directly proportional to the mass of an object. As the mass increases, the weight also increases.
- Weight can be measured using a spring scale or a weighing scale that takes into account the gravitational force acting on the object.
Difference between Mass and Weight:
1. Definition:
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity.
2. Units:
- Mass is measured in kilograms or grams, while weight is measured in newtons.
3. Independence:
- Mass is an intrinsic property and remains constant regardless of the location, while weight depends on the location and varies accordingly.
4. Measurement:
- Mass can be measured using a balance or a scale, whereas weight can be measured using a spring scale or a weighing scale that accounts for the gravitational force.
5. Variation:
- Mass does not vary with the location in the universe, while weight varies depending on the strength of gravity at that location.
In summary, mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity and varies depending on the gravitational acceleration and location.
Mass:
- Mass is a fundamental property of matter that quantifies the amount of matter present in an object. It is an intrinsic property and is independent of external factors.
- Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g) and is a scalar quantity. It represents the inertia of an object, which is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion.
- The mass of an object remains constant regardless of its location in the universe. For instance, an object on Earth would have the same mass if it were on the Moon or any other celestial body.
- Mass can be determined by using a balance or a scale, comparing the object's mass to a known reference mass.
Weight:
- Weight, on the other hand, is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. It is a vector quantity and is measured in newtons (N).
- Weight depends on both the mass of an object and the gravitational acceleration of the planet or celestial body it is on. The weight of an object can vary depending on its location in the universe.
- The weight of an object can be calculated using the formula: weight = mass × gravitational acceleration. On Earth, the standard gravitational acceleration is approximately 9.8 m/s^2.
- Weight is directly proportional to the mass of an object. As the mass increases, the weight also increases.
- Weight can be measured using a spring scale or a weighing scale that takes into account the gravitational force acting on the object.
Difference between Mass and Weight:
1. Definition:
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity.
2. Units:
- Mass is measured in kilograms or grams, while weight is measured in newtons.
3. Independence:
- Mass is an intrinsic property and remains constant regardless of the location, while weight depends on the location and varies accordingly.
4. Measurement:
- Mass can be measured using a balance or a scale, whereas weight can be measured using a spring scale or a weighing scale that accounts for the gravitational force.
5. Variation:
- Mass does not vary with the location in the universe, while weight varies depending on the strength of gravity at that location.
In summary, mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity and varies depending on the gravitational acceleration and location.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
what is the difference between mass and weight
Question Description
what is the difference between mass and weight for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between mass and weight covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between mass and weight.
what is the difference between mass and weight for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between mass and weight covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between mass and weight.
Solutions for what is the difference between mass and weight in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is the difference between mass and weight defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is the difference between mass and weight, a detailed solution for what is the difference between mass and weight has been provided alongside types of what is the difference between mass and weight theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is the difference between mass and weight tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























