Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphe...
Start Learning for Free
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]
- a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxide
- b)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxide
- c)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4
- d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl...
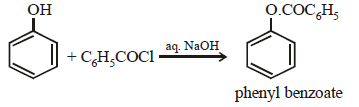
The function of NaOH is
(i) To convert phenol to more stronger
nucleophile PhO–
(ii) To neutralize the acid formed
(i) To convert phenol to more stronger
nucleophile PhO–
(ii) To neutralize the acid formed
Most Upvoted Answer
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl...
Explanation:
Schotten-Baumann reaction:
The Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction of phenols with benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxide. This reaction is commonly used to acylate phenols to form esters.
Reaction:
Phenol + Benzoyl chloride + Sodium hydroxide → Phenyl benzoate + Sodium chloride + Water
Mechanism:
1. The reaction begins with the nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion from sodium hydroxide on the benzoyl chloride, forming a reactive acyl-oxygen intermediate.
2. The phenol then attacks the acyl-oxygen intermediate, resulting in the formation of the ester product.
3. The final products are phenyl benzoate, sodium chloride, and water.
Significance:
The Schotten-Baumann reaction is a useful method for synthesizing esters from phenols. Ester formation is important in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various compounds.
Applications:
- The Schotten-Baumann reaction is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of drug molecules.
- It is also utilized in the production of fragrances, flavors, and other fine chemicals.
Conclusion:
The Schotten-Baumann reaction involving phenols, benzoyl chloride, and sodium hydroxide is a significant method for the formation of esters. This reaction finds wide applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the pharmaceutical and fragrance industries.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Schotten-Baumann reaction is a reaction ofphenols with [1994]a)Benzoyl chloride and sodium hydroxideb)Acetyl chloride and sodium hydroxidec)Salicylic acid and conc. H2SO4d)Acetyl chloride and conc H2SO4Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















