Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)am...
Start Learning for Free
A blue colouration is not obtained when:
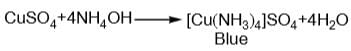
- a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate
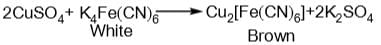
- b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6]
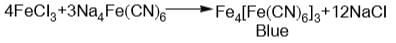
- c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide
- d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolve...

Most Upvoted Answer
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolve...
Explanation:
When copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a blue coloration is not obtained. This can be explained by the following points:
1. Formation of Precipitate:
When copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a double displacement reaction occurs. The potassium ions (K+) from K4[Fe(CN)6] react with the sulphate ions (SO4^2-) from copper sulphate (CuSO4) to form potassium sulphate (K2SO4). Similarly, the copper ions (Cu^2+) from copper sulphate react with the ferrocyanide ions (Fe(CN)6^-4) from K4[Fe(CN)6] to form a complex compound called copper ferrocyanide (Cu2[Fe(CN)6]), which is insoluble in water.
2. Insolubility of Copper Ferrocyanide:
Copper ferrocyanide is a blue precipitate that is formed during the reaction. Since it is insoluble in water, it does not dissolve and remains as a solid in the solution. This is why a blue coloration is not obtained.
3. Absence of Cu^2+ Ions:
The blue color in copper sulphate solution is due to the presence of Cu^2+ ions. However, during the reaction with K4[Fe(CN)6], the Cu^2+ ions are consumed in the formation of copper ferrocyanide. As a result, there are no free Cu^2+ ions available to impart the blue color to the solution.
4. Formation of White Precipitate:
Instead of the blue color, a white precipitate of copper ferrocyanide is formed. This white precipitate may give the impression of a colorless solution, but it is actually the result of the reaction between copper sulphate and K4[Fe(CN)6].
Therefore, when copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a blue coloration is not obtained due to the formation of insoluble copper ferrocyanide.
When copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a blue coloration is not obtained. This can be explained by the following points:
1. Formation of Precipitate:
When copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a double displacement reaction occurs. The potassium ions (K+) from K4[Fe(CN)6] react with the sulphate ions (SO4^2-) from copper sulphate (CuSO4) to form potassium sulphate (K2SO4). Similarly, the copper ions (Cu^2+) from copper sulphate react with the ferrocyanide ions (Fe(CN)6^-4) from K4[Fe(CN)6] to form a complex compound called copper ferrocyanide (Cu2[Fe(CN)6]), which is insoluble in water.
2. Insolubility of Copper Ferrocyanide:
Copper ferrocyanide is a blue precipitate that is formed during the reaction. Since it is insoluble in water, it does not dissolve and remains as a solid in the solution. This is why a blue coloration is not obtained.
3. Absence of Cu^2+ Ions:
The blue color in copper sulphate solution is due to the presence of Cu^2+ ions. However, during the reaction with K4[Fe(CN)6], the Cu^2+ ions are consumed in the formation of copper ferrocyanide. As a result, there are no free Cu^2+ ions available to impart the blue color to the solution.
4. Formation of White Precipitate:
Instead of the blue color, a white precipitate of copper ferrocyanide is formed. This white precipitate may give the impression of a colorless solution, but it is actually the result of the reaction between copper sulphate and K4[Fe(CN)6].
Therefore, when copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6], a blue coloration is not obtained due to the formation of insoluble copper ferrocyanide.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A blue colouration is not obtained when: a)ammonium hydroxide dissolves in copper sulphate b)copper sulphate solution reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] c)ferric chloride reacts with sodium ferrocyanide d)anhydrous white CuSO4 is dissolved in waterCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















