Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcohol...
Start Learning for Free
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]
- a)Any primary amine and chloroform
- b)Chloroform and silver powder
- c)A primary amine and an alkyl halide
- d)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any pr...
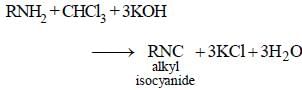
Any primary amine means both aliphatic as well as aromatic but onoalkylamines means only 1° aliphatic amines. Therefore, option (a) is correct while (d) is wrong.
Most Upvoted Answer
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any pr...
Carbylamine Reaction:
The carbylamine reaction is a chemical test used to distinguish primary amines from secondary and tertiary amines. It involves the reaction of a primary amine with chloroform (trichloromethane) and hot alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) to form an isocyanide compound or carbylamine.
Reaction:
The reaction can be represented as follows:
Primary amine + Chloroform + Hot alcoholic KOH → Carbylamine (Isocyanide) + Potassium chloride + Water
Explanation:
The correct answer for the given question is option 'A' - Any primary amine and chloroform. Here's the explanation for why option 'A' is the correct answer:
1. Hot Alcoholic KOH:
Hot alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used as the reagent in the carbylamine reaction. The hot alcoholic KOH serves as a strong base and helps in the formation of the carbylamine.
2. Chloroform:
Chloroform (trichloromethane) is the reactant that undergoes substitution with the primary amine in the carbylamine reaction. It reacts with the primary amine in the presence of hot alcoholic KOH to form the carbylamine product.
3. Any Primary Amine:
The carbylamine reaction can be performed with any primary amine. Primary amines have a functional group consisting of an amino group (-NH2) attached to a primary carbon. Some examples of primary amines include methylamine (CH3NH2), ethylamine (C2H5NH2), and propylamine (C3H7NH2).
4. Formation of Carbylamine:
During the carbylamine reaction, the primary amine reacts with chloroform in the presence of hot alcoholic KOH. This results in the substitution of one chlorine atom in chloroform with the amino group of the primary amine, forming an isocyanide compound or carbylamine. The carbylamine is characterized by its foul odor.
5. Other Options:
Options 'B', 'C', and 'D' are incorrect because they involve different reactants or conditions that do not lead to the carbylamine reaction. Option 'B' suggests using silver powder, which is not involved in the carbylamine reaction. Option 'C' suggests using an alkyl halide along with a primary amine, which does not result in the carbylamine product. Option 'D' suggests using a monoalkylamine instead of a primary amine, which also does not lead to the carbylamine product.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the carbylamine reaction can be performed using hot alcoholic KOH and chloroform with any primary amine. This reaction leads to the formation of a carbylamine or isocyanide compound, which is characterized by its foul odor. The other options given in the question do not result in the carbylamine product.
The carbylamine reaction is a chemical test used to distinguish primary amines from secondary and tertiary amines. It involves the reaction of a primary amine with chloroform (trichloromethane) and hot alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) to form an isocyanide compound or carbylamine.
Reaction:
The reaction can be represented as follows:
Primary amine + Chloroform + Hot alcoholic KOH → Carbylamine (Isocyanide) + Potassium chloride + Water
Explanation:
The correct answer for the given question is option 'A' - Any primary amine and chloroform. Here's the explanation for why option 'A' is the correct answer:
1. Hot Alcoholic KOH:
Hot alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used as the reagent in the carbylamine reaction. The hot alcoholic KOH serves as a strong base and helps in the formation of the carbylamine.
2. Chloroform:
Chloroform (trichloromethane) is the reactant that undergoes substitution with the primary amine in the carbylamine reaction. It reacts with the primary amine in the presence of hot alcoholic KOH to form the carbylamine product.
3. Any Primary Amine:
The carbylamine reaction can be performed with any primary amine. Primary amines have a functional group consisting of an amino group (-NH2) attached to a primary carbon. Some examples of primary amines include methylamine (CH3NH2), ethylamine (C2H5NH2), and propylamine (C3H7NH2).
4. Formation of Carbylamine:
During the carbylamine reaction, the primary amine reacts with chloroform in the presence of hot alcoholic KOH. This results in the substitution of one chlorine atom in chloroform with the amino group of the primary amine, forming an isocyanide compound or carbylamine. The carbylamine is characterized by its foul odor.
5. Other Options:
Options 'B', 'C', and 'D' are incorrect because they involve different reactants or conditions that do not lead to the carbylamine reaction. Option 'B' suggests using silver powder, which is not involved in the carbylamine reaction. Option 'C' suggests using an alkyl halide along with a primary amine, which does not result in the carbylamine product. Option 'D' suggests using a monoalkylamine instead of a primary amine, which also does not lead to the carbylamine product.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the carbylamine reaction can be performed using hot alcoholic KOH and chloroform with any primary amine. This reaction leads to the formation of a carbylamine or isocyanide compound, which is characterized by its foul odor. The other options given in the question do not result in the carbylamine product.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and [1992]a)Any primary amine and chloroformb)Chloroform and silver powderc)A primary amine and an alkyl halided)A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















