Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > The activation energy for a simple chemical r...
Start Learning for Free
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]
- a)Is always double of Ea
- b)Is negative of Ea
- c)Is always less than Ea
- d)Can be less than or more than Ea
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea ...
The activation energy of reverse reaction will depend upon whether the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
As ΔH = Ea (forward reaction) – Ea(backward reaction)
For exothermic reaction
As ΔH = Ea (forward reaction) – Ea(backward reaction)
For exothermic reaction
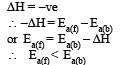
for endothermic reaction
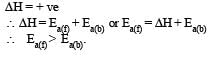
Most Upvoted Answer
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea ...
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A is the minimum amount of energy required for the reactant molecules to undergo a chemical reaction and form products. It is the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to occur.
The activation energy is determined by the specific reaction and the nature of the reactants involved. It depends on factors such as the bond strengths, molecular collisions, and the stability of the transition state.
In order for a reaction to occur, the reactant molecules must collide with enough energy and in the correct orientation to overcome the activation energy barrier. If the colliding molecules do not have enough energy, they will simply bounce off each other without undergoing a reaction.
Catalysts can lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower energy barrier. This allows the reaction to occur more readily and at a faster rate.
The activation energy is an important factor in determining the rate of a chemical reaction. Reactions with higher activation energies generally occur at slower rates, whereas reactions with lower activation energies occur more quickly.
The concept of activation energy is used to explain why certain reactions occur spontaneously while others require external energy input to proceed. It is also used to understand and optimize reaction conditions in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and industrial processes.
The activation energy is determined by the specific reaction and the nature of the reactants involved. It depends on factors such as the bond strengths, molecular collisions, and the stability of the transition state.
In order for a reaction to occur, the reactant molecules must collide with enough energy and in the correct orientation to overcome the activation energy barrier. If the colliding molecules do not have enough energy, they will simply bounce off each other without undergoing a reaction.
Catalysts can lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower energy barrier. This allows the reaction to occur more readily and at a faster rate.
The activation energy is an important factor in determining the rate of a chemical reaction. Reactions with higher activation energies generally occur at slower rates, whereas reactions with lower activation energies occur more quickly.
The concept of activation energy is used to explain why certain reactions occur spontaneously while others require external energy input to proceed. It is also used to understand and optimize reaction conditions in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and industrial processes.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A → B is Ea in forward direction. The activation energy for reverse reaction [2003]a)Is always double of Eab)Is negative of Eac)Is always less than Ead)Can be less than or more than EaCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















