Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Application of a forward bias to a p–n ...
Start Learning for Free
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction [2005]
- a)widens the depletion zone
- b)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zone
- c)increases the number of donors on the nside
- d)increases the electric field in the depletionzone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens th...
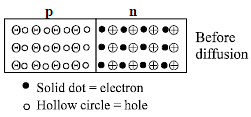
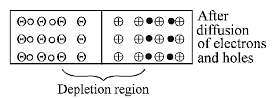

Number of donor s is more because
electrons from –ve terminal of the cell
pushes (enters) the n side and decreases
the number of uncompensated pentavalent
ion due to which potential barrier is
reduced. The neutralised pentavalent atom
are again in position to donate electrons.
electrons from –ve terminal of the cell
pushes (enters) the n side and decreases
the number of uncompensated pentavalent
ion due to which potential barrier is
reduced. The neutralised pentavalent atom
are again in position to donate electrons.
Most Upvoted Answer
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens th...
In the context of electronics, applying a forward bias refers to the process of connecting the positive terminal of a voltage source to the P-type region of a diode, while the negative terminal is connected to the N-type region. This causes the diode to conduct current and allows for various applications. Here are a few examples:
1. Rectification: One of the main applications of forward biasing a diode is in rectification, where an alternating current (AC) signal is converted into a direct current (DC) signal. By applying a forward bias to a diode, it allows the positive half-cycles of the AC signal to flow through the diode, while blocking the negative half-cycles. This results in a pulsating DC signal.
2. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Forward biasing an LED allows it to emit light. When a forward voltage is applied to the LED, electrons and holes recombine in the P-N junction, causing the release of energy in the form of light. The color of the emitted light depends on the materials used in the diode.
3. Photodiodes: Forward biasing a photodiode allows it to work as a light detector. When light falls on the P-N junction of the photodiode, it generates electron-hole pairs. The forward bias helps in faster collection of these electron-hole pairs, resulting in a current flow that is proportional to the intensity of the incident light.
4. Solar cells: Solar cells are essentially large-area photodiodes. By forward biasing a solar cell, it allows for the collection of the electron-hole pairs generated by incident light, resulting in a flow of current. This current can be used to power various electronic devices or stored in batteries for later use.
5. Amplification: In certain applications, a forward bias is applied to a diode to achieve amplification. This is done by operating the diode in its forward bias region, where it exhibits non-linear characteristics. By utilizing these non-linear characteristics, the diode can be used as a nonlinear amplifier in specific circuits.
Overall, the application of a forward bias to a diode allows for a wide range of electronic applications, including rectification, light emission, light detection, energy conversion, and amplification.
1. Rectification: One of the main applications of forward biasing a diode is in rectification, where an alternating current (AC) signal is converted into a direct current (DC) signal. By applying a forward bias to a diode, it allows the positive half-cycles of the AC signal to flow through the diode, while blocking the negative half-cycles. This results in a pulsating DC signal.
2. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Forward biasing an LED allows it to emit light. When a forward voltage is applied to the LED, electrons and holes recombine in the P-N junction, causing the release of energy in the form of light. The color of the emitted light depends on the materials used in the diode.
3. Photodiodes: Forward biasing a photodiode allows it to work as a light detector. When light falls on the P-N junction of the photodiode, it generates electron-hole pairs. The forward bias helps in faster collection of these electron-hole pairs, resulting in a current flow that is proportional to the intensity of the incident light.
4. Solar cells: Solar cells are essentially large-area photodiodes. By forward biasing a solar cell, it allows for the collection of the electron-hole pairs generated by incident light, resulting in a flow of current. This current can be used to power various electronic devices or stored in batteries for later use.
5. Amplification: In certain applications, a forward bias is applied to a diode to achieve amplification. This is done by operating the diode in its forward bias region, where it exhibits non-linear characteristics. By utilizing these non-linear characteristics, the diode can be used as a nonlinear amplifier in specific circuits.
Overall, the application of a forward bias to a diode allows for a wide range of electronic applications, including rectification, light emission, light detection, energy conversion, and amplification.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Application of a forward bias to a p–n junction[2005]a)widens the depletion zoneb)increases the potential difference acrossthe depletion zonec)increases the number of donors on the nsided)increases the electric field in the depletionzoneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















