Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > What is conservative and non conservative for...
Start Learning for Free
What is conservative and non conservative forces?
Verified Answer
What is conservative and non conservative forces?
Conservative forces:
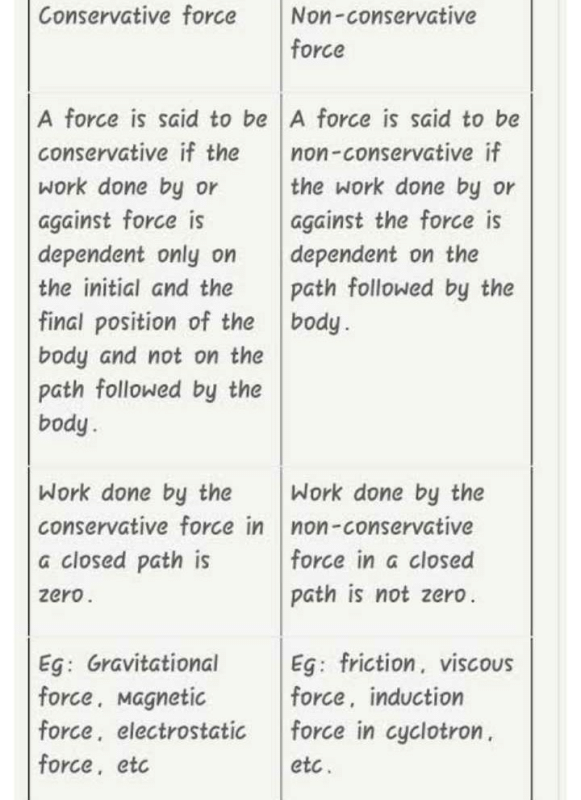
- The force is called conservative if work done by the force is the dependent only initial and final position of the body not depend on path followed by the body.
- The work done by the conservative force in the close path is zero.
Non-conservative forces:
- The force is called non-conservative force if work is done by the force is dependent on the path followed by the body.
- The work done by the non-conservative force in a closed path is not zero.
- The work done by the non-conservative force in a closed path is not zero.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is conservative and non conservative forces?
Community Answer
What is conservative and non conservative forces?
Conservative and Non-conservative Forces
Conservative Forces:
-------------------
A conservative force is a type of force that does not dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another. Instead, conservative forces store and release energy within a system without any net loss or gain. The work done by a conservative force is path-independent, meaning it only depends on the initial and final positions of an object and not on the path taken.
Key Points:
-----------
- Conservative forces are derived from a potential energy function that depends only on the position of an object.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravity, electrostatic forces, and spring forces.
- The total mechanical energy of an object subjected to conservative forces is conserved, meaning it remains constant over time.
- Conservative forces can be represented by a potential energy function, and the negative gradient of this function gives the force.
Non-conservative Forces:
-----------------------
Non-conservative forces, on the other hand, are forces that do not have a corresponding potential energy function. These forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another, resulting in a net loss or gain of energy within a system. The work done by non-conservative forces is path-dependent, meaning it depends on the specific path taken by an object.
Key Points:
-----------
- Non-conservative forces are usually associated with dissipative processes, such as friction, air resistance, and viscous drag.
- These forces convert mechanical energy into other forms, such as heat or sound, leading to a decrease in the total mechanical energy of the system.
- The work done by non-conservative forces depends on the specific path taken by an object because energy is dissipated or gained along the way.
Comparison:
-----------
1. Path Independence:
- Conservative forces are path-independent, meaning the work done by these forces depends only on the initial and final positions of an object.
- Non-conservative forces are path-dependent, meaning the work done depends on the specific path taken by an object.
2. Potential Energy:
- Conservative forces have a corresponding potential energy function that depends only on the position of an object.
- Non-conservative forces do not have a potential energy function associated with them.
3. Energy Conservation:
- Conservative forces conserve the total mechanical energy of a system, as energy is stored and released without any net loss or gain.
- Non-conservative forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy into other forms, resulting in a net decrease in the total mechanical energy of the system.
In summary, conservative forces store and release energy without any net loss or gain, while non-conservative forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another, resulting in a net loss or gain. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various areas of physics, such as mechanics, electromagnetism, and thermodynamics.
Conservative Forces:
-------------------
A conservative force is a type of force that does not dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another. Instead, conservative forces store and release energy within a system without any net loss or gain. The work done by a conservative force is path-independent, meaning it only depends on the initial and final positions of an object and not on the path taken.
Key Points:
-----------
- Conservative forces are derived from a potential energy function that depends only on the position of an object.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravity, electrostatic forces, and spring forces.
- The total mechanical energy of an object subjected to conservative forces is conserved, meaning it remains constant over time.
- Conservative forces can be represented by a potential energy function, and the negative gradient of this function gives the force.
Non-conservative Forces:
-----------------------
Non-conservative forces, on the other hand, are forces that do not have a corresponding potential energy function. These forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another, resulting in a net loss or gain of energy within a system. The work done by non-conservative forces is path-dependent, meaning it depends on the specific path taken by an object.
Key Points:
-----------
- Non-conservative forces are usually associated with dissipative processes, such as friction, air resistance, and viscous drag.
- These forces convert mechanical energy into other forms, such as heat or sound, leading to a decrease in the total mechanical energy of the system.
- The work done by non-conservative forces depends on the specific path taken by an object because energy is dissipated or gained along the way.
Comparison:
-----------
1. Path Independence:
- Conservative forces are path-independent, meaning the work done by these forces depends only on the initial and final positions of an object.
- Non-conservative forces are path-dependent, meaning the work done depends on the specific path taken by an object.
2. Potential Energy:
- Conservative forces have a corresponding potential energy function that depends only on the position of an object.
- Non-conservative forces do not have a potential energy function associated with them.
3. Energy Conservation:
- Conservative forces conserve the total mechanical energy of a system, as energy is stored and released without any net loss or gain.
- Non-conservative forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy into other forms, resulting in a net decrease in the total mechanical energy of the system.
In summary, conservative forces store and release energy without any net loss or gain, while non-conservative forces dissipate or convert mechanical energy from one form to another, resulting in a net loss or gain. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various areas of physics, such as mechanics, electromagnetism, and thermodynamics.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
What is conservative and non conservative forces?
Question Description
What is conservative and non conservative forces? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about What is conservative and non conservative forces? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is conservative and non conservative forces?.
What is conservative and non conservative forces? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about What is conservative and non conservative forces? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is conservative and non conservative forces?.
Solutions for What is conservative and non conservative forces? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is conservative and non conservative forces? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is conservative and non conservative forces?, a detailed solution for What is conservative and non conservative forces? has been provided alongside types of What is conservative and non conservative forces? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is conservative and non conservative forces? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























