JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie w...
Start Learning for Free
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :
- a)2λ A ,λ A
- b)λA,2λA
- c)λA,λA/2
- d)λA/2,λA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, unde...
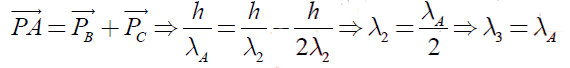
Most Upvoted Answer
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, unde...
Cay time, undergoes radioactive decay and transforms into a nucleus B. This process is random and cannot be predicted with certainty. The rate of radioactive decay is often described by a decay constant, which is a measure of how quickly the decay occurs. The decay constant is specific to each type of nucleus and is determined experimentally.
During radioactive decay, a nucleus A can emit various particles such as alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (electrons or positrons), or gamma rays (high-energy photons). The specific particles emitted depend on the type of nucleus and the particular decay mode.
The decay process follows an exponential decay law, which states that the number of remaining nuclei A at any given time t is given by the equation:
N(t) = N0 * e^(-λt)
where N0 is the initial number of nuclei A, λ is the decay constant, and e is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828.
The half-life of a nucleus is the time it takes for half of the initial number of nuclei to decay. It can be calculated using the decay constant:
t1/2 = ln(2) / λ
where ln(2) is the natural logarithm of 2, approximately equal to 0.693.
Radioactive decay is a spontaneous process that occurs in unstable nuclei in order to reach a more stable state. It is an important concept in various fields such as nuclear physics, medicine (e.g., radiation therapy), and archaeology (e.g., radiocarbon dating).
During radioactive decay, a nucleus A can emit various particles such as alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (electrons or positrons), or gamma rays (high-energy photons). The specific particles emitted depend on the type of nucleus and the particular decay mode.
The decay process follows an exponential decay law, which states that the number of remaining nuclei A at any given time t is given by the equation:
N(t) = N0 * e^(-λt)
where N0 is the initial number of nuclei A, λ is the decay constant, and e is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828.
The half-life of a nucleus is the time it takes for half of the initial number of nuclei to decay. It can be calculated using the decay constant:
t1/2 = ln(2) / λ
where ln(2) is the natural logarithm of 2, approximately equal to 0.693.
Radioactive decay is a spontaneous process that occurs in unstable nuclei in order to reach a more stable state. It is an important concept in various fields such as nuclear physics, medicine (e.g., radiation therapy), and archaeology (e.g., radiocarbon dating).
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A nucleus A, with a finite de–broglie wavelength λA, undergoes spontaneous fission into two nuclei B and C of equal mass. B flies in the same direction as that of A, while C flies in the opposite direction with a velocity equal to half of that of B. The de–Broglie wavelengths λB and λC of B and C are respectively :a)2λ A,λ Ab)λA,2λAc)λA,λA/2d)λA/2,λACorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















