Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7g...
Start Learning for Free
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total ...
From Dalton’s law, find pressure of mixture of nitrogen and oxygen
p = p1+ p2
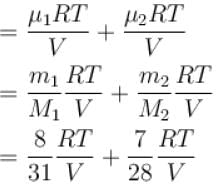
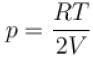 ...(i)
...(i)
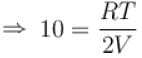
when oxygen is absorbed, then for nitrogen let pressure be p
and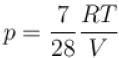 ...(ii)
...(ii)
From (1) and (2) p = 5 atm.
The correct answer is: 5
p = p1+ p2
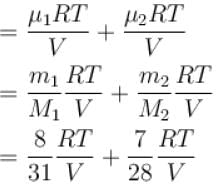
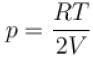 ...(i)
...(i)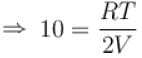
when oxygen is absorbed, then for nitrogen let pressure be p
and
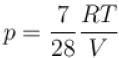 ...(ii)
...(ii)From (1) and (2) p = 5 atm.
The correct answer is: 5
Most Upvoted Answer
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total ...
Given information:
- The vessel contains 8 gm of oxygen and 7 gm of nitrogen.
- The total pressure is 10 atm.
- Oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent.
To find:
The pressure of the remaining gas after the oxygen is absorbed.
Explanation:
1. Calculation of moles:
- To calculate the pressure of the remaining gas, we need to first calculate the number of moles of oxygen and nitrogen present in the vessel.
- The molar mass of oxygen (O2) is 32 g/mol, and the molar mass of nitrogen (N2) is 28 g/mol.
- Using the formula:
Number of moles = Mass of substance / Molar mass
Number of moles of oxygen = 8 gm / 32 g/mol = 0.25 mol
Number of moles of nitrogen = 7 gm / 28 g/mol = 0.25 mol
2. Calculation of partial pressures:
- The partial pressure exerted by a gas is proportional to the number of moles of that gas.
- Since both oxygen and nitrogen have the same number of moles, their partial pressures will be the same.
- Let the partial pressure of oxygen and nitrogen be P.
Partial pressure of oxygen (P) = Partial pressure of nitrogen (P) = P
- According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of each gas.
Total pressure = Partial pressure of oxygen + Partial pressure of nitrogen
10 atm = P + P
10 atm = 2P
Therefore, P = 10 atm / 2 = 5 atm
3. Absorption of oxygen:
- The question states that oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent.
- When oxygen is absorbed, the number of moles of oxygen becomes zero.
- Since the partial pressure of oxygen was the same as the partial pressure of nitrogen, the partial pressure of the remaining gas (nitrogen) will still be P.
4. Calculation of remaining pressure:
- The total pressure of the remaining gas (nitrogen) will be the sum of the partial pressures of nitrogen.
Remaining pressure = Partial pressure of nitrogen = P = 5 atm
Therefore, the pressure of the remaining gas after the oxygen is absorbed will be 5 atm.
- The vessel contains 8 gm of oxygen and 7 gm of nitrogen.
- The total pressure is 10 atm.
- Oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent.
To find:
The pressure of the remaining gas after the oxygen is absorbed.
Explanation:
1. Calculation of moles:
- To calculate the pressure of the remaining gas, we need to first calculate the number of moles of oxygen and nitrogen present in the vessel.
- The molar mass of oxygen (O2) is 32 g/mol, and the molar mass of nitrogen (N2) is 28 g/mol.
- Using the formula:
Number of moles = Mass of substance / Molar mass
Number of moles of oxygen = 8 gm / 32 g/mol = 0.25 mol
Number of moles of nitrogen = 7 gm / 28 g/mol = 0.25 mol
2. Calculation of partial pressures:
- The partial pressure exerted by a gas is proportional to the number of moles of that gas.
- Since both oxygen and nitrogen have the same number of moles, their partial pressures will be the same.
- Let the partial pressure of oxygen and nitrogen be P.
Partial pressure of oxygen (P) = Partial pressure of nitrogen (P) = P
- According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of each gas.
Total pressure = Partial pressure of oxygen + Partial pressure of nitrogen
10 atm = P + P
10 atm = 2P
Therefore, P = 10 atm / 2 = 5 atm
3. Absorption of oxygen:
- The question states that oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent.
- When oxygen is absorbed, the number of moles of oxygen becomes zero.
- Since the partial pressure of oxygen was the same as the partial pressure of nitrogen, the partial pressure of the remaining gas (nitrogen) will still be P.
4. Calculation of remaining pressure:
- The total pressure of the remaining gas (nitrogen) will be the sum of the partial pressures of nitrogen.
Remaining pressure = Partial pressure of nitrogen = P = 5 atm
Therefore, the pressure of the remaining gas after the oxygen is absorbed will be 5 atm.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas (in atm) will be?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















