Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Derive the mutual inductance of two long sole...
Start Learning for Free
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?
Most Upvoted Answer
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?
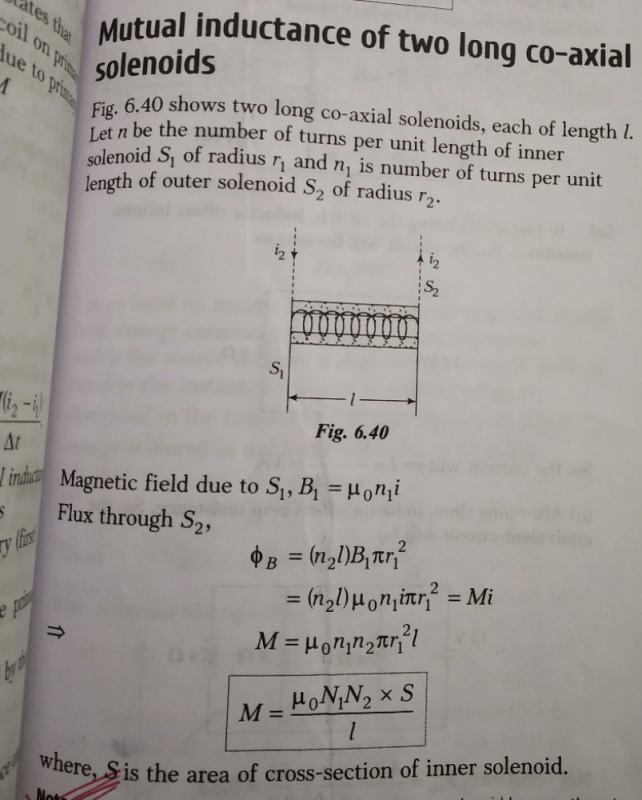
Community Answer
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?
**Derivation of Mutual Inductance of Two Long Solenoids**
To derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoids, we can consider the magnetic field produced by one solenoid and calculate the magnetic flux through the other solenoid. By using Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, we can then relate the induced emf to the rate of change of magnetic flux. This will allow us to determine the mutual inductance between the two solenoids.
**Magnetic Field Produced by One Solenoid**
The magnetic field produced by a long solenoid is given by the formula:
B = μ₀nI
Where B is the magnetic field, μ₀ is the permeability of free space, n is the number of turns per unit length, and I is the current flowing through the solenoid.
**Magnetic Flux through the Second Solenoid**
Consider two long solenoids, labeled as Solenoid 1 and Solenoid 2, placed parallel to each other. We want to calculate the magnetic flux through Solenoid 2 due to the magnetic field produced by Solenoid 1.
The magnetic flux (Φ₂) through Solenoid 2 can be calculated by integrating the magnetic field (B₁) produced by Solenoid 1 over the cross-sectional area (A₂) of Solenoid 2:
Φ₂ = ∫∫ B₁ · dA₂
**Induced EMF and Mutual Inductance**
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the induced electromotive force (emf) in a circuit is equal to the negative rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
Therefore, the induced emf (ε₂) in Solenoid 2 due to the changing magnetic flux through it can be given by:
ε₂ = -dΦ₂/dt
To relate the induced emf to the rate of change of magnetic flux, we introduce the concept of mutual inductance (M) between the two solenoids. Mutual inductance is a measure of how much of the magnetic field produced by one solenoid threads through the other.
The mutual inductance (M) between Solenoid 1 and Solenoid 2 is given by:
M = Φ₂/I₁
Where I₁ is the current flowing through Solenoid 1.
Therefore, the induced emf in Solenoid 2 due to the changing current in Solenoid 1 can be expressed as:
ε₂ = -M(dI₁/dt)
Hence, by calculating the magnetic flux through Solenoid 2 and using Faraday's law, we can determine the mutual inductance between the two long solenoids.
To derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoids, we can consider the magnetic field produced by one solenoid and calculate the magnetic flux through the other solenoid. By using Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, we can then relate the induced emf to the rate of change of magnetic flux. This will allow us to determine the mutual inductance between the two solenoids.
**Magnetic Field Produced by One Solenoid**
The magnetic field produced by a long solenoid is given by the formula:
B = μ₀nI
Where B is the magnetic field, μ₀ is the permeability of free space, n is the number of turns per unit length, and I is the current flowing through the solenoid.
**Magnetic Flux through the Second Solenoid**
Consider two long solenoids, labeled as Solenoid 1 and Solenoid 2, placed parallel to each other. We want to calculate the magnetic flux through Solenoid 2 due to the magnetic field produced by Solenoid 1.
The magnetic flux (Φ₂) through Solenoid 2 can be calculated by integrating the magnetic field (B₁) produced by Solenoid 1 over the cross-sectional area (A₂) of Solenoid 2:
Φ₂ = ∫∫ B₁ · dA₂
**Induced EMF and Mutual Inductance**
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the induced electromotive force (emf) in a circuit is equal to the negative rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
Therefore, the induced emf (ε₂) in Solenoid 2 due to the changing magnetic flux through it can be given by:
ε₂ = -dΦ₂/dt
To relate the induced emf to the rate of change of magnetic flux, we introduce the concept of mutual inductance (M) between the two solenoids. Mutual inductance is a measure of how much of the magnetic field produced by one solenoid threads through the other.
The mutual inductance (M) between Solenoid 1 and Solenoid 2 is given by:
M = Φ₂/I₁
Where I₁ is the current flowing through Solenoid 1.
Therefore, the induced emf in Solenoid 2 due to the changing current in Solenoid 1 can be expressed as:
ε₂ = -M(dI₁/dt)
Hence, by calculating the magnetic flux through Solenoid 2 and using Faraday's law, we can determine the mutual inductance between the two long solenoids.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?
Question Description
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?.
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?.
Solutions for Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid?, a detailed solution for Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? has been provided alongside types of Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Derive the mutual inductance of two long solenoid? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















