Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Two reactions with different activation energ...
Start Learning for Free
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?
- a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be faster
- b)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster
- c)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature also
- d)Temperature range is also required
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at...
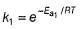

If temperature is increased to T`,
If 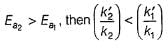
Thus, reaction with smaller activation energy will be faster on increasing temperature.
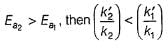
Thus, reaction with smaller activation energy will be faster on increasing temperature.
Most Upvoted Answer
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at...
The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster because the rate of reaction is inversely proportional to the activation energy of that reaction
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at...
Explanation:
When two reactions have the same rate at room temperature, it means that they have the same value for the rate constant (k) at that temperature. The rate constant is related to the activation energy (Ea) through the Arrhenius equation:
k = A * e^(-Ea/RT)
where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate:
Increasing the temperature of a reaction increases the rate of the reaction. This is because an increase in temperature leads to an increase in the kinetic energy of the reactant molecules, which in turn increases the rate of successful collisions between the reactant molecules.
Effect of Activation Energy:
The activation energy (Ea) is the energy barrier that reactant molecules must overcome in order to undergo the chemical reaction. Reactions with higher activation energies have a larger energy barrier to overcome, and therefore have a slower rate at a given temperature compared to reactions with lower activation energies.
Effect of Temperature on Activation Energy:
Increasing the temperature also affects the activation energy of a reaction. As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the reactant molecules increases, which means that a larger fraction of the molecules have the required energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. This effectively lowers the effective activation energy of the reaction at higher temperatures.
Comparison of Reactions at Higher Temperature:
When the temperature is increased, the effect on the rate of the reaction depends on the activation energy of the reaction.
- The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster at the higher temperature because it already has a lower energy barrier to overcome. The increase in temperature further lowers the effective activation energy, making it easier for the reactant molecules to overcome the barrier and undergo the reaction. Therefore, the reaction with the smaller activation energy will have a faster rate at the higher temperature.
- The reaction with the greater activation energy will be slower at the higher temperature because it has a higher energy barrier to overcome. Although the increase in temperature lowers the effective activation energy, it is still relatively higher compared to the reaction with the smaller activation energy. Therefore, the reaction with the greater activation energy will have a slower rate at the higher temperature.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct statement is option B: "The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster." This is because the reaction with the smaller activation energy already has a lower energy barrier to overcome and the increase in temperature further lowers the effective activation energy, resulting in a faster rate at the higher temperature.
When two reactions have the same rate at room temperature, it means that they have the same value for the rate constant (k) at that temperature. The rate constant is related to the activation energy (Ea) through the Arrhenius equation:
k = A * e^(-Ea/RT)
where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate:
Increasing the temperature of a reaction increases the rate of the reaction. This is because an increase in temperature leads to an increase in the kinetic energy of the reactant molecules, which in turn increases the rate of successful collisions between the reactant molecules.
Effect of Activation Energy:
The activation energy (Ea) is the energy barrier that reactant molecules must overcome in order to undergo the chemical reaction. Reactions with higher activation energies have a larger energy barrier to overcome, and therefore have a slower rate at a given temperature compared to reactions with lower activation energies.
Effect of Temperature on Activation Energy:
Increasing the temperature also affects the activation energy of a reaction. As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the reactant molecules increases, which means that a larger fraction of the molecules have the required energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. This effectively lowers the effective activation energy of the reaction at higher temperatures.
Comparison of Reactions at Higher Temperature:
When the temperature is increased, the effect on the rate of the reaction depends on the activation energy of the reaction.
- The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster at the higher temperature because it already has a lower energy barrier to overcome. The increase in temperature further lowers the effective activation energy, making it easier for the reactant molecules to overcome the barrier and undergo the reaction. Therefore, the reaction with the smaller activation energy will have a faster rate at the higher temperature.
- The reaction with the greater activation energy will be slower at the higher temperature because it has a higher energy barrier to overcome. Although the increase in temperature lowers the effective activation energy, it is still relatively higher compared to the reaction with the smaller activation energy. Therefore, the reaction with the greater activation energy will have a slower rate at the higher temperature.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct statement is option B: "The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster." This is because the reaction with the smaller activation energy already has a lower energy barrier to overcome and the increase in temperature further lowers the effective activation energy, resulting in a faster rate at the higher temperature.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be fasterb)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be fasterc)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature alsod)Temperature range is also requiredCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















