JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The reactivity of compound Z with different h...
Start Learning for Free
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)
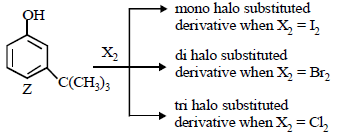
The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained by
- a)The steric effect of the halogen
- b)The steric effect of the tert-butyl group
- c)The electronic effect of the phenolic group
- d)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl group
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate...
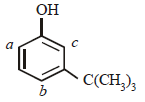
—OH group is strongly activating and o, p-directing due to +M effect. Thus positions a, b and c are the sites for attack by an electrophile. However, sites b and c are not preferred by bulky electrophile due to steric crowding. Thus more bulky electrophile (like I2) can attack only site a, which is least sterically hindered, a bit smaller electrophile (Br2) can attack at sites a and also b (relatively less sterically hindered site) and the smallest electrophile (Cl2) can attack all the three sites, viz., a, b and c (most sterically hindered site).

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below: (JEE Adv. 2014)The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained bya)The steric effect of the halogenb)The steric effect of the tert-butyl groupc)The electronic effect of the phenolic groupd)The electronic effect of the tert-butyl groupCorrect answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























