IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Which of the following neurotransmitters is t...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan derived
- a)Dopamine
- b)GABA
- c)Norepinephrine
- d)Serotonin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopami...
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopami...
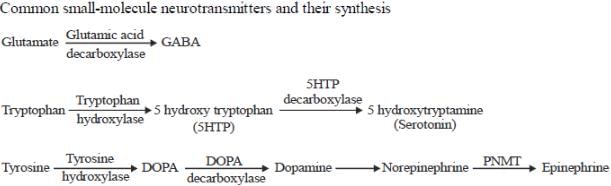
Tryptophan and Neurotransmitters:
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various neurotransmitters in the brain. It is obtained from the diet and serves as a precursor for the synthesis of several important neurotransmitters, including serotonin, melatonin, and niacin.
Neurotransmitters derived from Tryptophan:
Among the given options, the neurotransmitter derived from tryptophan is serotonin (option B).
Explanation:
1. Tryptophan Metabolism:
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet. It is primarily found in protein-rich foods such as meat, dairy products, eggs, and certain plant-based sources like seeds and nuts. Once ingested, tryptophan is metabolized through various pathways.
2. Tryptophan Hydroxylase:
Tryptophan hydroxylase is the enzyme responsible for the initial step in the synthesis of serotonin. It catalyzes the conversion of tryptophan into 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP). This reaction requires the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and oxygen.
3. Aromatic L-amino Acid Decarboxylase:
Following the conversion of tryptophan to 5-HTP, the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase converts 5-HTP into serotonin. This enzyme removes a carboxyl group from 5-HTP, resulting in the formation of serotonin.
4. Serotonin as a Neurotransmitter:
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and various other physiological processes. It is involved in the modulation of emotions, cognition, and behavior.
Conclusion:
In summary, tryptophan serves as a precursor for the synthesis of serotonin. The conversion of tryptophan to serotonin involves the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. Serotonin functions as a neurotransmitter and is involved in various physiological processes in the brain and body.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various neurotransmitters in the brain. It is obtained from the diet and serves as a precursor for the synthesis of several important neurotransmitters, including serotonin, melatonin, and niacin.
Neurotransmitters derived from Tryptophan:
Among the given options, the neurotransmitter derived from tryptophan is serotonin (option B).
Explanation:
1. Tryptophan Metabolism:
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet. It is primarily found in protein-rich foods such as meat, dairy products, eggs, and certain plant-based sources like seeds and nuts. Once ingested, tryptophan is metabolized through various pathways.
2. Tryptophan Hydroxylase:
Tryptophan hydroxylase is the enzyme responsible for the initial step in the synthesis of serotonin. It catalyzes the conversion of tryptophan into 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP). This reaction requires the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and oxygen.
3. Aromatic L-amino Acid Decarboxylase:
Following the conversion of tryptophan to 5-HTP, the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase converts 5-HTP into serotonin. This enzyme removes a carboxyl group from 5-HTP, resulting in the formation of serotonin.
4. Serotonin as a Neurotransmitter:
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and various other physiological processes. It is involved in the modulation of emotions, cognition, and behavior.
Conclusion:
In summary, tryptophan serves as a precursor for the synthesis of serotonin. The conversion of tryptophan to serotonin involves the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. Serotonin functions as a neurotransmitter and is involved in various physiological processes in the brain and body.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following neurotransmitters is tryptophan deriveda)Dopamineb)GABAc)Norepinephrined)SerotoninCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















