IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value ...
Start Learning for Free
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mM
s-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction will
be______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]
s-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction will
be______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the v...
Vmax of an enzyme reaction is double of the velocity when [S] = Km
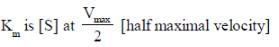
So velocity was 20 mMs-1 when [S] =Km
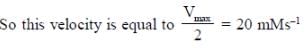
Therefore vmax for the given reaction is
20 x 2 = 40 mMs-1
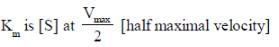
So velocity was 20 mMs-1 when [S] =Km
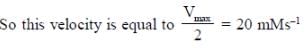
Therefore vmax for the given reaction is
20 x 2 = 40 mMs-1
Most Upvoted Answer
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the v...
Enzyme Kinetics
In enzyme kinetics, the study of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, two important parameters are the Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) and the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction. The Michaelis-Menten equation describes the relationship between the rate of a reaction and the substrate concentration.
Michaelis-Menten Equation:
The Michaelis-Menten equation is given by:
V = (Vmax * [S]) / (Km + [S])
where:
V = velocity of the reaction
[S] = substrate concentration
Vmax = maximum velocity of the reaction
Km = Michaelis-Menten constant
Km and Vmax:
Km represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity. It is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. A lower Km value indicates a higher affinity of the enzyme for the substrate.
Vmax represents the maximum velocity that can be achieved by the enzyme-catalyzed reaction. It indicates the rate of reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
Given Information:
Km = 0.6 mM
Velocity (V) = 20 mM/s (at the time point when [S] = Km)
Determining Vmax:
We can use the Michaelis-Menten equation to determine Vmax using the given information.
At the time point when [S] = Km, the velocity of the reaction (V) is equal to Vmax/2. Therefore, we can write:
Vmax/2 = (Vmax * Km) / (Km + Km)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
Vmax/2 = (Vmax * Km) / (2Km)
Cross-multiplying and simplifying further, we get:
2Vmax * Km = Vmax * Km
Cancelling out Vmax and Km, we get:
2 = 1
This equation is not possible mathematically, which means our assumption that Vmax/2 = Vmax * Km / (Km + Km) is incorrect.
Correcting the Assumption:
We need to correct our assumption by considering that the velocity at the time point when [S] = Km is not exactly equal to Vmax/2. Instead, it is closer to Vmax/2.
To find the value of Vmax, we need more information about the velocity at different substrate concentrations or the initial rate of the reaction.
Therefore, we cannot determine the exact value of Vmax based on the given information.
In enzyme kinetics, the study of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, two important parameters are the Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) and the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction. The Michaelis-Menten equation describes the relationship between the rate of a reaction and the substrate concentration.
Michaelis-Menten Equation:
The Michaelis-Menten equation is given by:
V = (Vmax * [S]) / (Km + [S])
where:
V = velocity of the reaction
[S] = substrate concentration
Vmax = maximum velocity of the reaction
Km = Michaelis-Menten constant
Km and Vmax:
Km represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity. It is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. A lower Km value indicates a higher affinity of the enzyme for the substrate.
Vmax represents the maximum velocity that can be achieved by the enzyme-catalyzed reaction. It indicates the rate of reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
Given Information:
Km = 0.6 mM
Velocity (V) = 20 mM/s (at the time point when [S] = Km)
Determining Vmax:
We can use the Michaelis-Menten equation to determine Vmax using the given information.
At the time point when [S] = Km, the velocity of the reaction (V) is equal to Vmax/2. Therefore, we can write:
Vmax/2 = (Vmax * Km) / (Km + Km)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
Vmax/2 = (Vmax * Km) / (2Km)
Cross-multiplying and simplifying further, we get:
2Vmax * Km = Vmax * Km
Cancelling out Vmax and Km, we get:
2 = 1
This equation is not possible mathematically, which means our assumption that Vmax/2 = Vmax * Km / (Km + Km) is incorrect.
Correcting the Assumption:
We need to correct our assumption by considering that the velocity at the time point when [S] = Km is not exactly equal to Vmax/2. Instead, it is closer to Vmax/2.
To find the value of Vmax, we need more information about the velocity at different substrate concentrations or the initial rate of the reaction.
Therefore, we cannot determine the exact value of Vmax based on the given information.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer?.
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In basic enzyme kinetics reaction, the value of Km is 0.6 mM and the velocity of a reaction was 20 mMs-1 at the time point when substrate concentration was equal to Km The value of Vmax for this reaction willbe______________(in mM s-l). [Answer in integer]Correct answer is '40'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















