JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water th...
Start Learning for Free
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]
- a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.
- b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding
- c)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bonding
- d)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols b...
Compounds involved in chelation become non-polar.
Consequently such compounds are soluble in nonpolar solvents like ether, benzene etc. and are only sparingly soluble in water whereas meta and para isomers are more soluble in water & less soluble in non-polar solvents.
Consequently such compounds are soluble in nonpolar solvents like ether, benzene etc. and are only sparingly soluble in water whereas meta and para isomers are more soluble in water & less soluble in non-polar solvents.
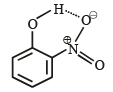
intra-molecular H-bonding
Most Upvoted Answer
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols b...
Explanation:
Ortho-nitrophenol (o-nitrophenol) is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenols due to the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and is also attracted to another electronegative atom within the same molecule. In the case of o-nitrophenol, the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) forms a hydrogen bond with the oxygen atom of the nitro group (-NO2) within the same molecule.
Effect on Solubility:
The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in o-nitrophenol affects its solubility in water. When a compound is soluble in water, it means that it is able to form favorable interactions with water molecules through hydrogen bonding. However, in the case of o-nitrophenol, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding restricts the availability of the hydroxyl group for interaction with water molecules. This decreases the solubility of o-nitrophenol in water.
Comparison with p- and m-Nitrophenols:
On the other hand, p- and m-nitrophenols do not exhibit intramolecular hydrogen bonding because the hydroxyl group is not in close proximity to the nitro group. As a result, the hydroxyl group in p- and m-nitrophenols is more readily available for interaction with water molecules, leading to higher solubility in water compared to o-nitrophenol.
Other Factors:
The other options given in the question are not the correct explanations for the difference in solubility between o-nitrophenol and p- and m-nitrophenols. The volatility of a compound does not directly affect its solubility in water. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding and melting point differences also do not explain the observed difference in solubility.
Conclusion:
In summary, o-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenols due to the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding, which restricts the availability of the hydroxyl group for interaction with water molecules.
Ortho-nitrophenol (o-nitrophenol) is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenols due to the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and is also attracted to another electronegative atom within the same molecule. In the case of o-nitrophenol, the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) forms a hydrogen bond with the oxygen atom of the nitro group (-NO2) within the same molecule.
Effect on Solubility:
The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in o-nitrophenol affects its solubility in water. When a compound is soluble in water, it means that it is able to form favorable interactions with water molecules through hydrogen bonding. However, in the case of o-nitrophenol, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding restricts the availability of the hydroxyl group for interaction with water molecules. This decreases the solubility of o-nitrophenol in water.
Comparison with p- and m-Nitrophenols:
On the other hand, p- and m-nitrophenols do not exhibit intramolecular hydrogen bonding because the hydroxyl group is not in close proximity to the nitro group. As a result, the hydroxyl group in p- and m-nitrophenols is more readily available for interaction with water molecules, leading to higher solubility in water compared to o-nitrophenol.
Other Factors:
The other options given in the question are not the correct explanations for the difference in solubility between o-nitrophenol and p- and m-nitrophenols. The volatility of a compound does not directly affect its solubility in water. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding and melting point differences also do not explain the observed difference in solubility.
Conclusion:
In summary, o-nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and m-nitrophenols due to the presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding, which restricts the availability of the hydroxyl group for interaction with water molecules.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ortho-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than p- and mNitrophenols because : [2012]a)o-Nitrophenol is more volatile steam than those of mand p-isomers.b)o-Nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bondingc)o-Nitrophenol shows intermolecular H-bondingd)Melting point of o-Nitrophenol is lower than those of m- and p-isomers.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















