IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium ...
Start Learning for Free
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 min...
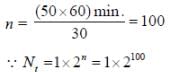
Most Upvoted Answer
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 min...
Calculation:
To determine the number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours, we need to calculate the number of divisions the bacterium undergoes in that time period.
Conversion:
First, we need to convert the given time period from hours to minutes, as the bacteria divide every 30 minutes.
50 hours x 60 minutes/hour = 3000 minutes
Number of Divisions:
Since the bacterium divides every 30 minutes, we can calculate the number of divisions by dividing the total time period in minutes by 30.
3000 minutes / 30 minutes/division = 100 divisions
Growth Factor:
Each division results in the formation of two daughter cells, which means the number of bacteria doubles after each division. Therefore, the growth factor is 2.
Total Number of Bacteria:
To calculate the total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours, we need to raise the growth factor to the power of the number of divisions.
Total number of bacteria = (growth factor)^(number of divisions) = 2^100
Calculating the Answer:
Now, let's calculate 2^100 using the concept of exponentiation.
2^100 = (2^10)^10 = 1024^10 = (1000 + 24)^10
Using the binomial expansion formula, we can expand (1000 + 24)^10 and ignore the terms after the first term, as they would be negligible compared to 1000^10.
(1000 + 24)^10 ≈ 1000^10 + 10*(1000^9)*(24) + higher-order terms
The higher-order terms can be ignored, as they are relatively small in comparison.
Therefore, the total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours is approximately 1000^10, which is equal to 1 followed by 30 zeros.
Final Answer:
The total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours is 1 x 10^30 or simply 1 followed by 30 zeros.
To determine the number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours, we need to calculate the number of divisions the bacterium undergoes in that time period.
Conversion:
First, we need to convert the given time period from hours to minutes, as the bacteria divide every 30 minutes.
50 hours x 60 minutes/hour = 3000 minutes
Number of Divisions:
Since the bacterium divides every 30 minutes, we can calculate the number of divisions by dividing the total time period in minutes by 30.
3000 minutes / 30 minutes/division = 100 divisions
Growth Factor:
Each division results in the formation of two daughter cells, which means the number of bacteria doubles after each division. Therefore, the growth factor is 2.
Total Number of Bacteria:
To calculate the total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours, we need to raise the growth factor to the power of the number of divisions.
Total number of bacteria = (growth factor)^(number of divisions) = 2^100
Calculating the Answer:
Now, let's calculate 2^100 using the concept of exponentiation.
2^100 = (2^10)^10 = 1024^10 = (1000 + 24)^10
Using the binomial expansion formula, we can expand (1000 + 24)^10 and ignore the terms after the first term, as they would be negligible compared to 1000^10.
(1000 + 24)^10 ≈ 1000^10 + 10*(1000^9)*(24) + higher-order terms
The higher-order terms can be ignored, as they are relatively small in comparison.
Therefore, the total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours is approximately 1000^10, which is equal to 1 followed by 30 zeros.
Final Answer:
The total number of bacteria at the end of 50 hours is 1 x 10^30 or simply 1 followed by 30 zeros.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?.
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A rich medium is inoculated with a bacterium that divides every 30 minutes. The number of bacteria at end of 50 hours is _______ x 2100.Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















