IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Consider a cross between heterozygous individ...
Start Learning for Free
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]
Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The a...
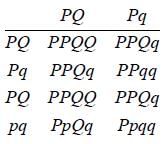
∴ 2 genotypes out of 8 would show a recessive character.
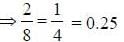
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The a...
Introduction:
In this problem, we are given two individuals, PpQq and PPQq, who are heterozygous for two different genes P and Q. We are asked to determine the fraction of their progeny that will show at least one homozygous recessive character. We are also given that the alleles assort independently.
Independent Assortment:
Independent assortment refers to the random distribution of alleles during gamete formation. It occurs when genes are located on different chromosomes or when they are far apart on the same chromosome. In our problem, since the genes P and Q are located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome, we can assume that they assort independently.
Genotypes of the parents:
The genotype of the first parent is PpQq, which means it has one dominant allele (P) and one recessive allele (p) for gene P, and one dominant allele (Q) and one recessive allele (q) for gene Q. The genotype of the second parent is PPQq, which means it has two dominant alleles (P) and one recessive allele (q) for gene Q.
Calculating the possible genotypes of the progeny:
To determine the possible genotypes of the progeny, we need to consider the different combinations of alleles that can be inherited from the parents. Since the alleles assort independently, we can consider each gene separately.
For gene P:
- The first parent can pass on either the dominant allele (P) or the recessive allele (p).
- The second parent can only pass on the dominant allele (P).
For gene Q:
- The first parent can pass on either the dominant allele (Q) or the recessive allele (q).
- The second parent can pass on either the dominant allele (Q) or the recessive allele (q).
Determining the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive character:
To determine the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive character, we need to consider the different possible genotypes of the progeny.
Possible genotypes for gene P:
- PP (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the dominant allele (P) and the second parent also passes on the dominant allele (P).
- Pp (50% chance): This genotype can occur if either parent passes on the dominant allele (P) and the other parent passes on the recessive allele (p).
- pp (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the recessive allele (p) and the second parent also passes on the recessive allele (p).
Possible genotypes for gene Q:
- QQ (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the dominant allele (Q) and the second parent also passes on the dominant allele (Q).
- Qq (50% chance): This genotype can occur if either parent passes on the dominant allele (Q) and the other parent passes on the recessive allele (q).
- qq (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the recessive allele (q) and the second parent also passes on the recessive allele (q).
To calculate the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive
In this problem, we are given two individuals, PpQq and PPQq, who are heterozygous for two different genes P and Q. We are asked to determine the fraction of their progeny that will show at least one homozygous recessive character. We are also given that the alleles assort independently.
Independent Assortment:
Independent assortment refers to the random distribution of alleles during gamete formation. It occurs when genes are located on different chromosomes or when they are far apart on the same chromosome. In our problem, since the genes P and Q are located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome, we can assume that they assort independently.
Genotypes of the parents:
The genotype of the first parent is PpQq, which means it has one dominant allele (P) and one recessive allele (p) for gene P, and one dominant allele (Q) and one recessive allele (q) for gene Q. The genotype of the second parent is PPQq, which means it has two dominant alleles (P) and one recessive allele (q) for gene Q.
Calculating the possible genotypes of the progeny:
To determine the possible genotypes of the progeny, we need to consider the different combinations of alleles that can be inherited from the parents. Since the alleles assort independently, we can consider each gene separately.
For gene P:
- The first parent can pass on either the dominant allele (P) or the recessive allele (p).
- The second parent can only pass on the dominant allele (P).
For gene Q:
- The first parent can pass on either the dominant allele (Q) or the recessive allele (q).
- The second parent can pass on either the dominant allele (Q) or the recessive allele (q).
Determining the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive character:
To determine the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive character, we need to consider the different possible genotypes of the progeny.
Possible genotypes for gene P:
- PP (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the dominant allele (P) and the second parent also passes on the dominant allele (P).
- Pp (50% chance): This genotype can occur if either parent passes on the dominant allele (P) and the other parent passes on the recessive allele (p).
- pp (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the recessive allele (p) and the second parent also passes on the recessive allele (p).
Possible genotypes for gene Q:
- QQ (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the dominant allele (Q) and the second parent also passes on the dominant allele (Q).
- Qq (50% chance): This genotype can occur if either parent passes on the dominant allele (Q) and the other parent passes on the recessive allele (q).
- qq (25% chance): This genotype can only occur if the first parent passes on the recessive allele (q) and the second parent also passes on the recessive allele (q).
To calculate the fraction of progeny with at least one homozygous recessive

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider a cross between heterozygous individuals PpQq and PPQq. The alleles assort independently. What fraction of the progeny will show atleast one homozygous recessive characters? [Answer upto two decimal points]Correct answer is '0.25'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















