Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > For beams of uniform strength, if depth is co...
Start Learning for Free
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, then
- a)Width is directly proportional to bending moment
- b)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending moment
- c)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending moment
- d)Width is inversely proportional to bending moment
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is di...
Using Flexural Formula
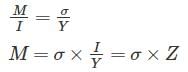
M ∝ Z
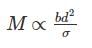
d is constant
M ∝ b (width)
Most Upvoted Answer
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is di...
Beams of Uniform Strength and Width
In beams of uniform strength, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. Let's understand why this is the case.
Understanding Beams of Uniform Strength
Beams are structural elements that support loads and resist bending. When a beam is subjected to a bending moment, it experiences internal stresses that cause it to deform. To ensure that the beam can withstand these stresses without failure, engineers design beams with sufficient strength.
In beams of uniform strength, the goal is to distribute the stress evenly throughout the beam. This means that the maximum stress in any part of the beam is the same, resulting in a uniform distribution of stress. To achieve this, the width of the beam is adjusted based on the bending moment.
Relationship between Width and Bending Moment
The bending moment in a beam is a measure of the internal forces that cause the beam to bend. It is calculated by multiplying the applied load by the distance from the load to a reference point.
The width of the beam determines the moment of inertia, which is a measure of the beam's resistance to bending. A larger width increases the moment of inertia, making the beam stiffer and more resistant to bending.
When the depth of the beam is constant, increasing the width also increases the moment of inertia. This means that a wider beam can withstand a higher bending moment without experiencing excessive deflection or failure.
Therefore, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. As the bending moment increases, the width of the beam must also increase to maintain uniform strength and prevent failure.
Conclusion
In beams of uniform strength, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. This relationship ensures that the beam has sufficient strength to withstand the internal stresses caused by bending. By increasing the width of the beam, the moment of inertia is increased, resulting in a stiffer and stronger beam.
In beams of uniform strength, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. Let's understand why this is the case.
Understanding Beams of Uniform Strength
Beams are structural elements that support loads and resist bending. When a beam is subjected to a bending moment, it experiences internal stresses that cause it to deform. To ensure that the beam can withstand these stresses without failure, engineers design beams with sufficient strength.
In beams of uniform strength, the goal is to distribute the stress evenly throughout the beam. This means that the maximum stress in any part of the beam is the same, resulting in a uniform distribution of stress. To achieve this, the width of the beam is adjusted based on the bending moment.
Relationship between Width and Bending Moment
The bending moment in a beam is a measure of the internal forces that cause the beam to bend. It is calculated by multiplying the applied load by the distance from the load to a reference point.
The width of the beam determines the moment of inertia, which is a measure of the beam's resistance to bending. A larger width increases the moment of inertia, making the beam stiffer and more resistant to bending.
When the depth of the beam is constant, increasing the width also increases the moment of inertia. This means that a wider beam can withstand a higher bending moment without experiencing excessive deflection or failure.
Therefore, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. As the bending moment increases, the width of the beam must also increase to maintain uniform strength and prevent failure.
Conclusion
In beams of uniform strength, the width of the beam is directly proportional to the bending moment. This relationship ensures that the beam has sufficient strength to withstand the internal stresses caused by bending. By increasing the width of the beam, the moment of inertia is increased, resulting in a stiffer and stronger beam.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant, thena)Width is directly proportional to bending momentb)Width is directly proportional to square root of bending momentc)Width is directly proportional to three times the square root of bending momentd)Width is inversely proportional to bending momentCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























