Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?
Start Learning for Free
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?
Most Upvoted Answer
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?
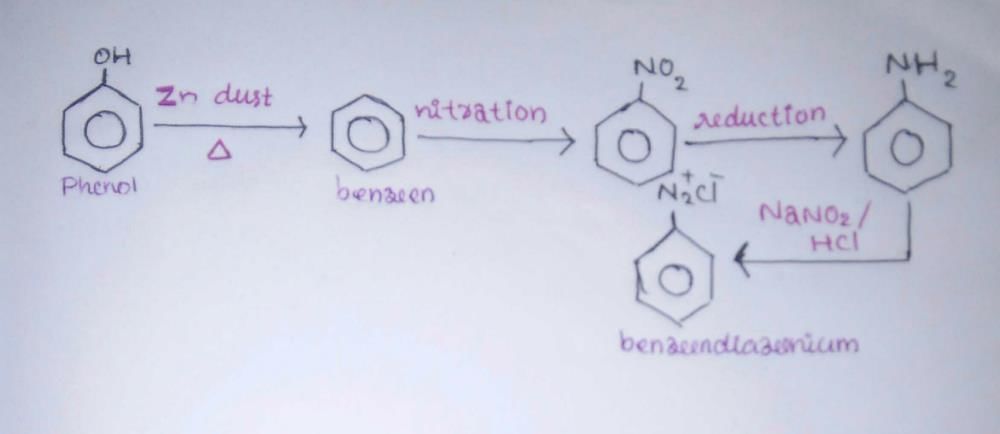
Community Answer
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?
Conversion of Phenol to Benzene Diazonium
Phenol can be converted into benzene diazonium through a series of reactions. The conversion involves the formation of a diazonium salt, which is a key intermediate in various organic reactions. Here is a detailed explanation of the process:
1. Diazotization Reaction:
The first step in the conversion is the diazotization reaction, which involves the formation of a diazonium salt. This reaction is carried out by treating phenol with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) at low temperature (0-5°C). The reaction proceeds as follows:
Phenol + NaNO2 + HCl → Diazonium Salt + Water
2. Formation of Diazonium Salt:
The diazonium salt is formed by the replacement of the hydroxyl group (-OH) of phenol with a diazonium group (-N2+). This reaction occurs through the electrophilic substitution of the phenolic ring. The diazonium salt is highly reactive and can be used in various organic transformations.
3. Isolation and Purification:
After the diazotization reaction, the diazonium salt needs to be isolated and purified. This can be done by precipitating the diazonium salt as its insoluble component, which is often a tetrafluoroborate or chloride salt. The precipitate can be filtered and washed to obtain a pure diazonium salt.
4. Conversion to Benzene Diazonium:
The final step in the process is the conversion of the diazonium salt to benzene diazonium. This can be achieved by treating the diazonium salt with a strong reducing agent such as hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) or sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). The reaction proceeds as follows:
Diazonium Salt + Reducing Agent → Benzene Diazonium + By-products
Important Points:
- The diazotization reaction should be carried out at low temperature (0-5°C) to prevent unwanted side reactions.
- The purity of the diazonium salt is crucial for the success of subsequent reactions.
- The conversion of the diazonium salt to benzene diazonium should be done carefully, as it involves the use of strong reducing agents.
- Benzene diazonium is highly reactive and can be used in various organic reactions, such as Sandmeyer reaction, coupling reactions, and azo dye synthesis.
By following these steps, phenol can be successfully converted into benzene diazonium, which is an important intermediate in organic chemistry.
Phenol can be converted into benzene diazonium through a series of reactions. The conversion involves the formation of a diazonium salt, which is a key intermediate in various organic reactions. Here is a detailed explanation of the process:
1. Diazotization Reaction:
The first step in the conversion is the diazotization reaction, which involves the formation of a diazonium salt. This reaction is carried out by treating phenol with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) at low temperature (0-5°C). The reaction proceeds as follows:
Phenol + NaNO2 + HCl → Diazonium Salt + Water
2. Formation of Diazonium Salt:
The diazonium salt is formed by the replacement of the hydroxyl group (-OH) of phenol with a diazonium group (-N2+). This reaction occurs through the electrophilic substitution of the phenolic ring. The diazonium salt is highly reactive and can be used in various organic transformations.
3. Isolation and Purification:
After the diazotization reaction, the diazonium salt needs to be isolated and purified. This can be done by precipitating the diazonium salt as its insoluble component, which is often a tetrafluoroborate or chloride salt. The precipitate can be filtered and washed to obtain a pure diazonium salt.
4. Conversion to Benzene Diazonium:
The final step in the process is the conversion of the diazonium salt to benzene diazonium. This can be achieved by treating the diazonium salt with a strong reducing agent such as hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) or sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). The reaction proceeds as follows:
Diazonium Salt + Reducing Agent → Benzene Diazonium + By-products
Important Points:
- The diazotization reaction should be carried out at low temperature (0-5°C) to prevent unwanted side reactions.
- The purity of the diazonium salt is crucial for the success of subsequent reactions.
- The conversion of the diazonium salt to benzene diazonium should be done carefully, as it involves the use of strong reducing agents.
- Benzene diazonium is highly reactive and can be used in various organic reactions, such as Sandmeyer reaction, coupling reactions, and azo dye synthesis.
By following these steps, phenol can be successfully converted into benzene diazonium, which is an important intermediate in organic chemistry.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?
Question Description
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?.
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?.
Solutions for How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium?, a detailed solution for How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? has been provided alongside types of How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice How to convert phenol to benzeen diazonium? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















