Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > What is the difference between electric and m...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how doe...
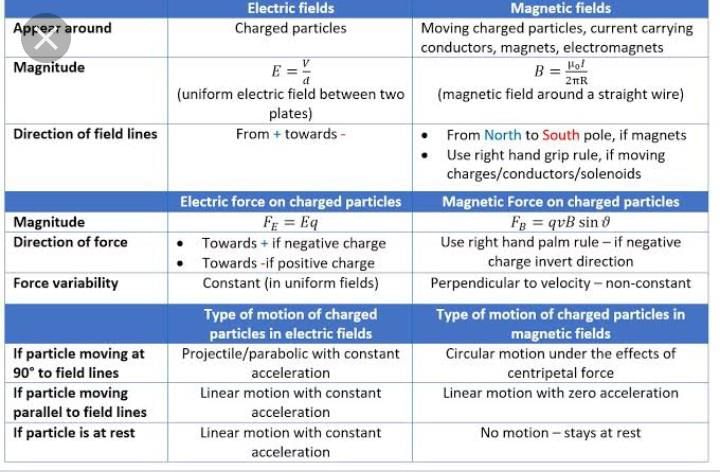
Community Answer
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how doe...
Difference between Electric and Magnetic Fields
Electric and magnetic fields are two fundamental components of electromagnetic waves. They are closely related but have distinct characteristics. Let's explore the differences between electric and magnetic fields and how they originate.
1. Nature of Fields:
- Electric Field: An electric field is produced by electric charges. It is a force field that surrounds charged particles and exerts a force on other charged particles present in its vicinity. The electric field is responsible for the attraction or repulsion between charged objects.
- Magnetic Field: A magnetic field is produced by moving electric charges or currents. It is a region in which magnetic forces are experienced by magnetic materials or moving charged particles. The magnetic field is responsible for the interaction between magnets and the deflection of charged particles in a magnetic field.
2. Orientation:
- Electric Field: Electric fields are produced by stationary charges and are radial in nature. They emanate outward from positive charges and inward toward negative charges. The electric field lines are always perpendicular to the surface of a charged object.
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic fields are produced by moving charges or currents and exhibit a circular or helical pattern around the current-carrying wire or a magnet. The magnetic field lines form closed loops and do not have a definite starting or ending point.
3. Induction:
- Electric Field: An electric field can induce an electric current in a conductor or a closed circuit. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction and is the basis for the functioning of generators and transformers.
- Magnetic Field: A magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor only if there is a change in the magnetic field strength. This is known as Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and is utilized in devices like electric generators and transformers.
4. Effects and Applications:
- Electric Field: Electric fields play a crucial role in electrical circuits, electrical appliances, and the functioning of electronic devices. They are responsible for the flow of electric current and the transmission of electrical energy.
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic fields have various applications, including the operation of electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. They are also involved in the Earth's magnetic field and play a vital role in compass navigation.
Origins of the Difference:
The difference between electric and magnetic fields arises from the fundamental properties of electric charges and their motion. Electric fields are produced by stationary charges and are associated with the attraction or repulsion between charged particles. On the other hand, magnetic fields are generated by moving charges or currents and are related to the interaction of magnetic materials or moving charged particles. The interplay between electric and magnetic fields gives rise to electromagnetic waves, which propagate through space and carry energy and information.
In conclusion, electric and magnetic fields are distinct in nature, orientation, induction effects, and applications. The differences originate from the properties of electric charges and their motion. Understanding these differences is essential in comprehending electromagnetic phenomena and their applications in various fields.
Electric and magnetic fields are two fundamental components of electromagnetic waves. They are closely related but have distinct characteristics. Let's explore the differences between electric and magnetic fields and how they originate.
1. Nature of Fields:
- Electric Field: An electric field is produced by electric charges. It is a force field that surrounds charged particles and exerts a force on other charged particles present in its vicinity. The electric field is responsible for the attraction or repulsion between charged objects.
- Magnetic Field: A magnetic field is produced by moving electric charges or currents. It is a region in which magnetic forces are experienced by magnetic materials or moving charged particles. The magnetic field is responsible for the interaction between magnets and the deflection of charged particles in a magnetic field.
2. Orientation:
- Electric Field: Electric fields are produced by stationary charges and are radial in nature. They emanate outward from positive charges and inward toward negative charges. The electric field lines are always perpendicular to the surface of a charged object.
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic fields are produced by moving charges or currents and exhibit a circular or helical pattern around the current-carrying wire or a magnet. The magnetic field lines form closed loops and do not have a definite starting or ending point.
3. Induction:
- Electric Field: An electric field can induce an electric current in a conductor or a closed circuit. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction and is the basis for the functioning of generators and transformers.
- Magnetic Field: A magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor only if there is a change in the magnetic field strength. This is known as Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and is utilized in devices like electric generators and transformers.
4. Effects and Applications:
- Electric Field: Electric fields play a crucial role in electrical circuits, electrical appliances, and the functioning of electronic devices. They are responsible for the flow of electric current and the transmission of electrical energy.
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic fields have various applications, including the operation of electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. They are also involved in the Earth's magnetic field and play a vital role in compass navigation.
Origins of the Difference:
The difference between electric and magnetic fields arises from the fundamental properties of electric charges and their motion. Electric fields are produced by stationary charges and are associated with the attraction or repulsion between charged particles. On the other hand, magnetic fields are generated by moving charges or currents and are related to the interaction of magnetic materials or moving charged particles. The interplay between electric and magnetic fields gives rise to electromagnetic waves, which propagate through space and carry energy and information.
In conclusion, electric and magnetic fields are distinct in nature, orientation, induction effects, and applications. The differences originate from the properties of electric charges and their motion. Understanding these differences is essential in comprehending electromagnetic phenomena and their applications in various fields.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate?
Question Description
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate?.
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate?.
Solutions for What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between electric and magnetic field and how does this difference originate? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















