JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental fr...
Start Learning for Free
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :
- a)f/2
- b)3f/4
- c)2f
- d)f
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pip...
Most Upvoted Answer
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pip...
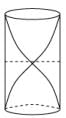
The given scenario involves a pipe that is open at both ends and has a fundamental frequency f in air. When the pipe is dipped vertically in water, half of it is submerged in water. We need to determine the fundamental frequency of the air column in this new configuration.
When a pipe is open at both ends, it can support standing waves with nodes at both ends and an antinode in the middle. The fundamental frequency corresponds to the first harmonic, which has one complete wavelength fitting within the length of the pipe.
When the pipe is in air, the length of the pipe corresponds to the wavelength of the fundamental frequency. Therefore, the wavelength of the fundamental frequency in air is equal to 2 times the length of the pipe.
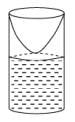
When the pipe is half dipped in water, the effective length of the air column is reduced by half. This is because the water acts as a closed end for the air column, creating an additional node at the water surface. As a result, the length of the air column is effectively halved.
Now let's analyze the effect of this change on the fundamental frequency:
- The wavelength of the fundamental frequency in air is halved because the length of the air column is halved.
- The speed of sound in air remains the same.
- Using the equation v = fλ, where v is the speed of sound and λ is the wavelength, we can see that as the wavelength decreases, the frequency must increase to maintain a constant speed of sound.
Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the air column when the pipe is dipped vertically in water and half of it is submerged is twice the original frequency f. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D'.
When a pipe is open at both ends, it can support standing waves with nodes at both ends and an antinode in the middle. The fundamental frequency corresponds to the first harmonic, which has one complete wavelength fitting within the length of the pipe.
When the pipe is in air, the length of the pipe corresponds to the wavelength of the fundamental frequency. Therefore, the wavelength of the fundamental frequency in air is equal to 2 times the length of the pipe.
When the pipe is half dipped in water, the effective length of the air column is reduced by half. This is because the water acts as a closed end for the air column, creating an additional node at the water surface. As a result, the length of the air column is effectively halved.
Now let's analyze the effect of this change on the fundamental frequency:
- The wavelength of the fundamental frequency in air is halved because the length of the air column is halved.
- The speed of sound in air remains the same.
- Using the equation v = fλ, where v is the speed of sound and λ is the wavelength, we can see that as the wavelength decreases, the frequency must increase to maintain a constant speed of sound.
Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the air column when the pipe is dipped vertically in water and half of it is submerged is twice the original frequency f. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental frequency f in air. The pipe is dipped vertically in water so that half of it is in water. The fundamental frequency of the air column is now :a)f/2b)3f/4c)2fd)fCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























