IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzyl...
Start Learning for Free
In 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as a
- a)triplet
- b)quartet
- c)septet
- d)doublet
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tr...
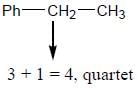
Most Upvoted Answer
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tr...
The 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene:
- Ethylbenzene is a compound with the formula C8H10. It consists of a benzene ring with an ethyl group attached to it.
- In the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton refers to the hydrogen atom directly attached to the carbon atom adjacent to the benzene ring.
- The benzylic proton appears as a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene.
Explanation:
The appearance of the benzylic proton as a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene can be explained by the concept of spin-spin coupling.
- Spin-spin coupling occurs when the magnetic field generated by one proton affects the resonance frequency of another nearby proton.
- In the case of the benzylic proton, it is coupled to the three neighboring protons on the benzene ring.
- The three neighboring protons on the benzene ring are equivalent, and they have a spin state that can be either aligned with or against the external magnetic field.
- When the benzylic proton is aligned with the magnetic field, it experiences a slightly higher resonance frequency due to the magnetic field generated by the neighboring protons.
- Conversely, when the benzylic proton is aligned against the magnetic field, it experiences a slightly lower resonance frequency due to the magnetic field generated by the neighboring protons.
- As a result, the benzylic proton splits into a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum.
- The quartet pattern arises from the splitting of the benzylic proton signal into four peaks, with relative intensities of 1:3:3:1, due to the three equivalent neighboring protons.
Conclusion:
In the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appears as a quartet due to spin-spin coupling with the three equivalent neighboring protons on the benzene ring. This quartet pattern arises from the splitting of the benzylic proton signal into four peaks, with relative intensities of 1:3:3:1.
- Ethylbenzene is a compound with the formula C8H10. It consists of a benzene ring with an ethyl group attached to it.
- In the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton refers to the hydrogen atom directly attached to the carbon atom adjacent to the benzene ring.
- The benzylic proton appears as a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene.
Explanation:
The appearance of the benzylic proton as a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene can be explained by the concept of spin-spin coupling.
- Spin-spin coupling occurs when the magnetic field generated by one proton affects the resonance frequency of another nearby proton.
- In the case of the benzylic proton, it is coupled to the three neighboring protons on the benzene ring.
- The three neighboring protons on the benzene ring are equivalent, and they have a spin state that can be either aligned with or against the external magnetic field.
- When the benzylic proton is aligned with the magnetic field, it experiences a slightly higher resonance frequency due to the magnetic field generated by the neighboring protons.
- Conversely, when the benzylic proton is aligned against the magnetic field, it experiences a slightly lower resonance frequency due to the magnetic field generated by the neighboring protons.
- As a result, the benzylic proton splits into a quartet in the 1H NMR spectrum.
- The quartet pattern arises from the splitting of the benzylic proton signal into four peaks, with relative intensities of 1:3:3:1, due to the three equivalent neighboring protons.
Conclusion:
In the 1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appears as a quartet due to spin-spin coupling with the three equivalent neighboring protons on the benzene ring. This quartet pattern arises from the splitting of the benzylic proton signal into four peaks, with relative intensities of 1:3:3:1.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In1H NMR spectrum of ethylbenzene, the benzylic proton appear as aa)tripletb)quartetc)septetd)doubletCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















