JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillati...
Start Learning for Free
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40 seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2 = 0.693).
- a)231 s
- b)208 s
- c)161 s
- d)142 s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small sp...
The damped oscillation the equation of displacement is given by,

Substitute the values for air
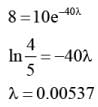
Substitute the values for carbon dioxide
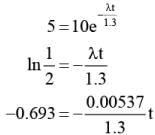

Substitute the values for air
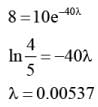
Substitute the values for carbon dioxide
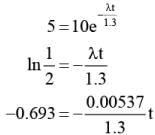
t = 167.7 sec
Thus, the closest time is 167 s .
Thus, the closest time is 167 s .
Most Upvoted Answer
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small sp...
Given: Amplitude of a simple pendulum oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40 seconds. Ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3. We need to find the time in which the amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in carbon dioxide.
Formula used: The amplitude of a simple pendulum decreases exponentially with time and is given as A(t) = A0e^(-bt), where A0 is the initial amplitude, b is a constant and t is time.
Approach:
1. First, we need to find the value of b using the given data. From Stokes law, the force of friction on the bob is given as F = 6πηrv, where η is the coefficient of viscosity, r is the radius of the bob and v is the velocity of the bob. As the bob moves through air, the force of friction is proportional to the velocity of the bob. Thus, we can write F = -bv, where b = 6πηr.
2. Using the above formula for b, we can find the value of b for air using the given ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide (1.3). Let the coefficient of viscosity of carbon dioxide be ηco2. Then, we have ηair/ηco2 = 1.3. Solving for ηco2, we get ηco2 = ηair/1.3.
3. Now, we can use the formula for A(t) to find the time in which the amplitude of the pendulum reduces from 10 cm to 5 cm in carbon dioxide. Let the time required be tco2. Then, we have A(tco2) = 5 cm and A0 = 10 cm. Using the formula A(t) = A0e^(-bt), we can write:
5 = 10e^(-btco2)
Solving for tco2, we get:
tco2 = -ln(0.5)/bco2
where bco2 = 6πηco2r.
4. Substituting the values of ηco2 and r, we get:
bco2 = 6π(ηair/1.3)(0.01 m) = 0.046 m^-1
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get:
tco2 = -ln(0.5)/0.046 = 161 s
Therefore, the time in which the amplitude of the pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in carbon dioxide is close to 161 seconds.
Answer: Option C (161 s)
Formula used: The amplitude of a simple pendulum decreases exponentially with time and is given as A(t) = A0e^(-bt), where A0 is the initial amplitude, b is a constant and t is time.
Approach:
1. First, we need to find the value of b using the given data. From Stokes law, the force of friction on the bob is given as F = 6πηrv, where η is the coefficient of viscosity, r is the radius of the bob and v is the velocity of the bob. As the bob moves through air, the force of friction is proportional to the velocity of the bob. Thus, we can write F = -bv, where b = 6πηr.
2. Using the above formula for b, we can find the value of b for air using the given ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide (1.3). Let the coefficient of viscosity of carbon dioxide be ηco2. Then, we have ηair/ηco2 = 1.3. Solving for ηco2, we get ηco2 = ηair/1.3.
3. Now, we can use the formula for A(t) to find the time in which the amplitude of the pendulum reduces from 10 cm to 5 cm in carbon dioxide. Let the time required be tco2. Then, we have A(tco2) = 5 cm and A0 = 10 cm. Using the formula A(t) = A0e^(-bt), we can write:
5 = 10e^(-btco2)
Solving for tco2, we get:
tco2 = -ln(0.5)/bco2
where bco2 = 6πηco2r.
4. Substituting the values of ηco2 and r, we get:
bco2 = 6π(ηair/1.3)(0.01 m) = 0.046 m^-1
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get:
tco2 = -ln(0.5)/0.046 = 161 s
Therefore, the time in which the amplitude of the pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in carbon dioxide is close to 161 seconds.
Answer: Option C (161 s)
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small spherical bob, decreases from 10 cm to 8 cm in 40seconds. Assuming that Stokes law is valid, and ratio of the coefficient of viscosity of air to that of carbon dioxide is 1.3, the time in which amplitude of this pendulum will reduce from 10 cm to 5 cm in, carbon dioxide will be close to (ln 5 = 1.601, ln 2= 0.693).a)231 sb)208 sc)161 sd)142 sCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























