IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant ...
Start Learning for Free
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example of
- a)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and b
- b)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and b
- c)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to E
- d)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistatic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed...
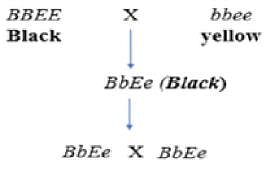
Recessive epistasis (or supplementary genes interaction) is the condition when homozygous recessive of one gene mask the effect of other gene in the dominant or recessive condition. Presence of B allele is dominant against E or e, results in black and E produces brown in the absence of B allele, whereas recessive homozygous ‘ee’ is epistatic to B or b and thus, gives yellow. The cross can be explained as follows


Most Upvoted Answer
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed...
Explanation:
- The black Labrador in this cross is homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE), which means it carries two dominant alleles for black coat color (B) and two dominant alleles for the expression of the pigment (E).
- The yellow Labrador is homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee), which means it carries two recessive alleles for brown coat color (bb) and two recessive alleles for the lack of pigment expression (ee).
- When these two Labrador parents are crossed, all the F1 progeny will be black because the dominant alleles (B and E) from the black Labrador will mask the expression of the recessive alleles (b and e) from the yellow Labrador.
- The F1 progeny will be heterozygous for both coat color (Bb) and pigment expression (Ee).
- When the F1 progeny are intercrossed, the possible genotypes and corresponding phenotypes of the F2 progeny can be determined using Punnett squares.
- The possible genotypes and phenotypes are as follows:
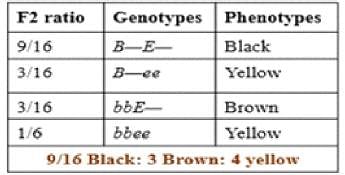
- 9 Black (BBEE or BBEe or BbEE or BbEe): These individuals have the dominant alleles for both black coat color and pigment expression.
- 3 Brown (Bbee or bbee): These individuals have the recessive alleles for brown coat color and lack of pigment expression. The brown coat color is expressed when both dominant alleles for black coat color are absent (bb) and both recessive alleles for lack of pigment expression are present (ee).
- 4 Yellow (bbeE or bbee): These individuals have the recessive alleles for lack of pigment expression and one dominant allele for black coat color. The yellow coat color is expressed when both dominant alleles for black coat color are absent (bb) and at least one dominant allele for pigment expression is absent (Ee or ee).
- The ratio of 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow in the F2 progeny indicates that the black coat color is dominant over brown and yellow coat colors. Additionally, the presence of both dominant alleles for pigment expression (E) is necessary for the expression of black coat color, while the presence of at least one dominant allele for pigment expression (E or e) is necessary for the expression of yellow coat color.
- This is an example of recessive epistasis where the e allele is epistatic to B and b, meaning that the presence of the recessive e allele masks the expression of both the dominant B and b alleles, resulting in the lack of pigment expression and the expression of yellow coat color.
- The black Labrador in this cross is homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE), which means it carries two dominant alleles for black coat color (B) and two dominant alleles for the expression of the pigment (E).
- The yellow Labrador is homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee), which means it carries two recessive alleles for brown coat color (bb) and two recessive alleles for the lack of pigment expression (ee).
- When these two Labrador parents are crossed, all the F1 progeny will be black because the dominant alleles (B and E) from the black Labrador will mask the expression of the recessive alleles (b and e) from the yellow Labrador.
- The F1 progeny will be heterozygous for both coat color (Bb) and pigment expression (Ee).
- When the F1 progeny are intercrossed, the possible genotypes and corresponding phenotypes of the F2 progeny can be determined using Punnett squares.
- The possible genotypes and phenotypes are as follows:
- 9 Black (BBEE or BBEe or BbEE or BbEe): These individuals have the dominant alleles for both black coat color and pigment expression.
- 3 Brown (Bbee or bbee): These individuals have the recessive alleles for brown coat color and lack of pigment expression. The brown coat color is expressed when both dominant alleles for black coat color are absent (bb) and both recessive alleles for lack of pigment expression are present (ee).
- 4 Yellow (bbeE or bbee): These individuals have the recessive alleles for lack of pigment expression and one dominant allele for black coat color. The yellow coat color is expressed when both dominant alleles for black coat color are absent (bb) and at least one dominant allele for pigment expression is absent (Ee or ee).
- The ratio of 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow in the F2 progeny indicates that the black coat color is dominant over brown and yellow coat colors. Additionally, the presence of both dominant alleles for pigment expression (E) is necessary for the expression of black coat color, while the presence of at least one dominant allele for pigment expression (E or e) is necessary for the expression of yellow coat color.
- This is an example of recessive epistasis where the e allele is epistatic to B and b, meaning that the presence of the recessive e allele masks the expression of both the dominant B and b alleles, resulting in the lack of pigment expression and the expression of yellow coat color.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example ofa)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to B and bb)Dominant epistasis where E allele is epistatic to B and bc)Recessive epistasis where e allele is epistatic to Ed)Complementary epistasis where b allele is epistaticCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















