Defence Exam > Defence Questions > Which one of the following constitutional aut...
Start Learning for Free
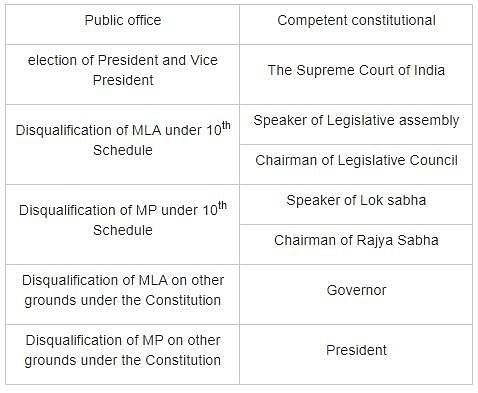
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?
- a)The Supreme Court of India
- b)The Election Commission of India
- c)The Parliamentary Committee
- d)The High Court of Delhi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and dec...
Most Upvoted Answer
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and dec...
Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country. It is responsible for interpreting the Constitution and ensuring its proper implementation. One of the important functions of the Supreme Court is to resolve doubts and disputes arising out of the election of the President and Vice President of India.
Constitutional Authority
The Supreme Court derives its authority to inquire and decide in case of doubts and disputes related to the election of the President and Vice President of India from the Constitution of India. Specifically, Article 71 of the Constitution deals with the election of the President, and Article 71(1) states that all doubts and disputes arising out of such an election shall be inquired into and decided by the Supreme Court.
Role of the Supreme Court
1. Inquiry: In case of doubts and disputes regarding the election of the President and Vice President, the Supreme Court conducts an inquiry to examine the validity of the election process. This includes examining the electoral process, scrutinizing the nomination papers, and investigating any allegations of malpractice or irregularities.
2. Decision-Making: Once the inquiry is complete, the Supreme Court makes a decision on the validity of the election. It can declare the election as valid or invalid based on the evidence presented and the constitutional provisions related to the election process.
3. Judicial Review: The Supreme Court also has the power of judicial review, which means it can review the actions of other authorities, including the Election Commission, in conducting the election. If the Supreme Court finds any irregularities or violations of the Constitution, it can take appropriate measures to rectify the situation.
4. Finality of Decision: The decision of the Supreme Court in matters related to the election of the President and Vice President is final and binding. There is no further appeal or review available after the Supreme Court's decision.
Therefore, the Supreme Court of India is the constitutional authority that has the power to inquire into and decide doubts and disputes arising out of the election of the President and Vice President of India. Its role is crucial in ensuring the fairness and integrity of the electoral process and upholding the principles of democracy.
The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country. It is responsible for interpreting the Constitution and ensuring its proper implementation. One of the important functions of the Supreme Court is to resolve doubts and disputes arising out of the election of the President and Vice President of India.
Constitutional Authority
The Supreme Court derives its authority to inquire and decide in case of doubts and disputes related to the election of the President and Vice President of India from the Constitution of India. Specifically, Article 71 of the Constitution deals with the election of the President, and Article 71(1) states that all doubts and disputes arising out of such an election shall be inquired into and decided by the Supreme Court.
Role of the Supreme Court
1. Inquiry: In case of doubts and disputes regarding the election of the President and Vice President, the Supreme Court conducts an inquiry to examine the validity of the election process. This includes examining the electoral process, scrutinizing the nomination papers, and investigating any allegations of malpractice or irregularities.
2. Decision-Making: Once the inquiry is complete, the Supreme Court makes a decision on the validity of the election. It can declare the election as valid or invalid based on the evidence presented and the constitutional provisions related to the election process.
3. Judicial Review: The Supreme Court also has the power of judicial review, which means it can review the actions of other authorities, including the Election Commission, in conducting the election. If the Supreme Court finds any irregularities or violations of the Constitution, it can take appropriate measures to rectify the situation.
4. Finality of Decision: The decision of the Supreme Court in matters related to the election of the President and Vice President is final and binding. There is no further appeal or review available after the Supreme Court's decision.
Therefore, the Supreme Court of India is the constitutional authority that has the power to inquire into and decide doubts and disputes arising out of the election of the President and Vice President of India. Its role is crucial in ensuring the fairness and integrity of the electoral process and upholding the principles of democracy.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2024 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2024 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Defence.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Defence Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which one of the following constitutional authorities inquires and decides in case of doubts and disputes arising out of election of the President and Vice President of India?a)The Supreme Court of Indiab)The Election Commission of Indiac)The Parliamentary Committeed)The High Court of DelhiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Defence tests.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















