Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2...
Start Learning for Free
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss?
Most Upvoted Answer
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylen...
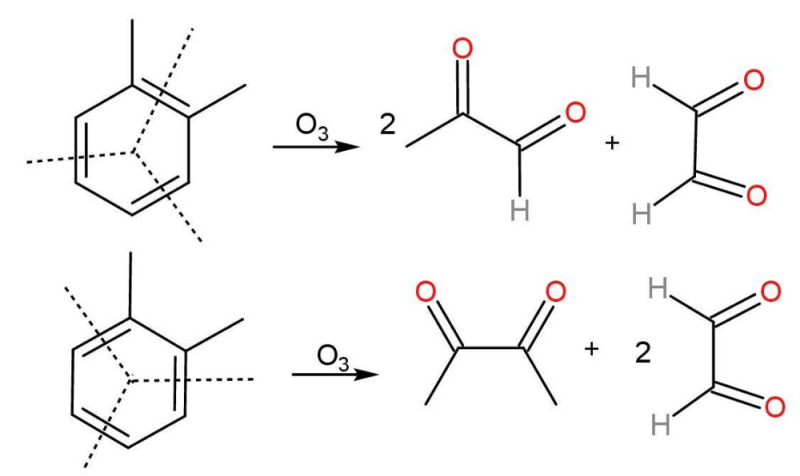
Community Answer
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylen...
Ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene) and its support for the Kekulé structure of benzene
Introduction:
Ozonolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the cleavage of carbon-carbon double bonds using ozone (O3). It is commonly used to determine the structure of organic compounds. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene), ozonolysis provides valuable insights into the arrangement of the carbon-carbon bonds in the benzene ring, supporting the Kekulé structure of benzene.
Ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene:
Ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene) involves the reaction of ozone with the double bonds present in the molecule. The ozonolysis reaction proceeds in two stages: oxidative cleavage and reductive workup.
Oxidative cleavage:
During oxidative cleavage, ozone adds to the double bond, resulting in the formation of an unstable primary ozonide. This ozonide can further rearrange to form more stable secondary ozonides. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, the oxidative cleavage leads to the formation of two secondary ozonides, as shown below:
- Secondary ozonide 1: Generated by cleavage between the carbon atoms attached to the methyl groups and the benzene ring.
- Secondary ozonide 2: Generated by cleavage between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring.
Reductive workup:
The second stage of ozonolysis involves reductive workup, which converts the secondary ozonides into specific products. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, the reductive workup yields the following products:
- Product 1: Generated from secondary ozonide 1. It consists of a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde, resulting from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the benzene ring and the methyl group.
- Product 2: Generated from secondary ozonide 2. It consists of two aldehydes, resulting from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring.
Support for the Kekulé structure:
The products obtained from the ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene provide support for the Kekulé structure of benzene, which is an important concept in organic chemistry. The Kekulé structure proposes that benzene consists of alternating single and double bonds between its carbon atoms.
Explanation:
The ozonolysis products of 1,2-dimethylbenzene are consistent with the Kekulé structure of benzene because they indicate the presence of alternating single and double bonds in the benzene ring. The formation of two aldehydes from the cleavage of a single carbon-carbon bond between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring supports the presence of a double bond between these carbon atoms.
Additionally, the formation of a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the benzene ring and the methyl
Introduction:
Ozonolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the cleavage of carbon-carbon double bonds using ozone (O3). It is commonly used to determine the structure of organic compounds. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene), ozonolysis provides valuable insights into the arrangement of the carbon-carbon bonds in the benzene ring, supporting the Kekulé structure of benzene.
Ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene:
Ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene) involves the reaction of ozone with the double bonds present in the molecule. The ozonolysis reaction proceeds in two stages: oxidative cleavage and reductive workup.
Oxidative cleavage:
During oxidative cleavage, ozone adds to the double bond, resulting in the formation of an unstable primary ozonide. This ozonide can further rearrange to form more stable secondary ozonides. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, the oxidative cleavage leads to the formation of two secondary ozonides, as shown below:
- Secondary ozonide 1: Generated by cleavage between the carbon atoms attached to the methyl groups and the benzene ring.
- Secondary ozonide 2: Generated by cleavage between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring.
Reductive workup:
The second stage of ozonolysis involves reductive workup, which converts the secondary ozonides into specific products. In the case of 1,2-dimethylbenzene, the reductive workup yields the following products:
- Product 1: Generated from secondary ozonide 1. It consists of a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde, resulting from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the benzene ring and the methyl group.
- Product 2: Generated from secondary ozonide 2. It consists of two aldehydes, resulting from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring.
Support for the Kekulé structure:
The products obtained from the ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene provide support for the Kekulé structure of benzene, which is an important concept in organic chemistry. The Kekulé structure proposes that benzene consists of alternating single and double bonds between its carbon atoms.
Explanation:
The ozonolysis products of 1,2-dimethylbenzene are consistent with the Kekulé structure of benzene because they indicate the presence of alternating single and double bonds in the benzene ring. The formation of two aldehydes from the cleavage of a single carbon-carbon bond between the two carbon atoms directly attached to the benzene ring supports the presence of a double bond between these carbon atoms.
Additionally, the formation of a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde from the cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond between the benzene ring and the methyl
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss?
Question Description
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss?.
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss?.
Solutions for Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss?, a detailed solution for Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? has been provided alongside types of Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene? Can anyone explain this plsss? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























